|
If you're looking for other "Article of the Week" archives: 2014 - 2015 - 2016 - 2017 |
Featured article of the week archive - 2017
Welcome to the LIMSwiki 2017 archive for the Featured Article of the Week.
Featured article of the week: February 06–12:
"The impact of electronic health record (EHR) interoperability on immunization information system (IIS) data quality"
Objectives: To evaluate the impact of electronic health record (EHR) interoperability on the quality of immunization data in the North Dakota Immunization Information System (NDIIS).
NDIIS "doses administered" data was evaluated for completeness of the patient and dose-level core data elements for records that belong to interoperable and non-interoperable providers. Data was compared at three months prior to EHR interoperability enhancement to data at three, six, nine and 12 months post-enhancement following the interoperability go live date. Doses administered per month and by age group, timeliness of vaccine entry and the number of duplicate clients added to the NDIIS was also compared, in addition to immunization rates for children 19–35 months of age and adolescents 11–18 years of age. (Full article...)
Featured article of the week: January 30–February 05:
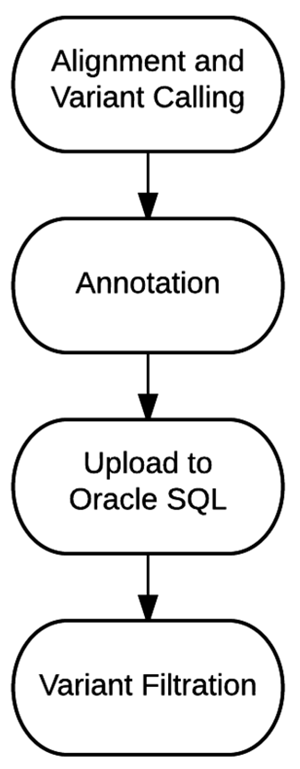
"Bioinformatics workflow for clinical whole genome sequencing at Partners HealthCare Personalized Medicine"
Effective implementation of precision medicine will be enhanced by a thorough understanding of each patient’s genetic composition to better treat his or her presenting symptoms or mitigate the onset of disease. This ideally includes the sequence information of a complete genome for each individual. At Partners HealthCare Personalized Medicine, we have developed a clinical process for whole genome sequencing (WGS) with application in both healthy individuals and those with disease. In this manuscript, we will describe our bioinformatics strategy to efficiently process and deliver genomic data to geneticists for clinical interpretation. We describe the handling of data from FASTQ to the final variant list for clinical review for the final report. We will also discuss our methodology for validating this workflow and the cost implications of running WGS. (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: January 23–29:
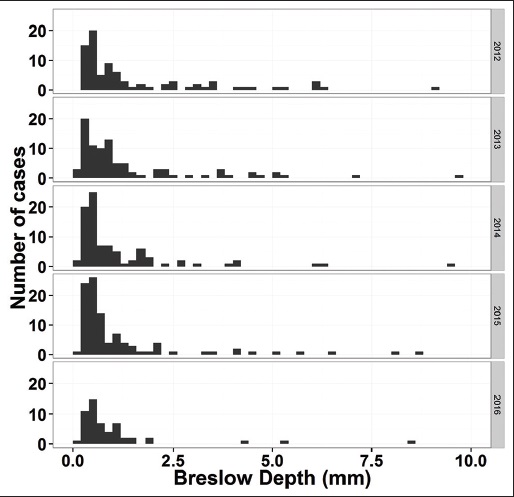
"Pathology report data extraction from relational database using R, with extraction from reports on melanoma of skin as an example"
The olog approach of Spivak and Kent is applied to the practical development of data transfer frameworks, yielding simple rules for construction and assessment of data transfer standards. The simplicity, extensibility and modularity of such descriptions allows discipline experts unfamiliar with complex ontological constructs or toolsets to synthesize multiple pre-existing standards, potentially including a variety of file formats, into a single overarching ontology. These ontologies nevertheless capture all scientifically-relevant prior knowledge, and when expressed in machine-readable form are sufficiently expressive to mediate translation between legacy and modern data formats. A format-independent programming interface informed by this ontology consists of six functions, of which only two handle data. Demonstration software implementing this interface is used to translate between two common diffraction image formats using such an ontology in place of an intermediate format. (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: January 16–22:
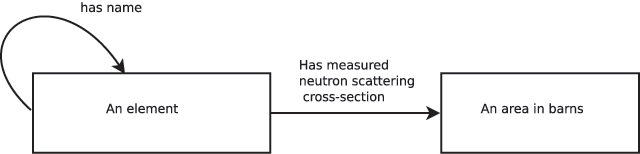
"A robust, format-agnostic scientific data transfer framework"
The olog approach of Spivak and Kent is applied to the practical development of data transfer frameworks, yielding simple rules for construction and assessment of data transfer standards. The simplicity, extensibility and modularity of such descriptions allows discipline experts unfamiliar with complex ontological constructs or toolsets to synthesize multiple pre-existing standards, potentially including a variety of file formats, into a single overarching ontology. These ontologies nevertheless capture all scientifically-relevant prior knowledge, and when expressed in machine-readable form are sufficiently expressive to mediate translation between legacy and modern data formats. A format-independent programming interface informed by this ontology consists of six functions, of which only two handle data. Demonstration software implementing this interface is used to translate between two common diffraction image formats using such an ontology in place of an intermediate format. (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: January 9–15:
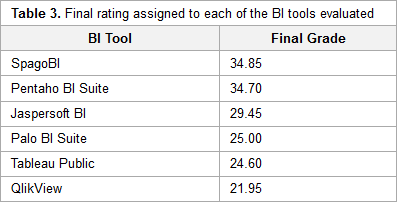
"A benchmarking analysis of open-source business intelligence tools in healthcare environments"
In recent years, a wide range of business intelligence (BI) technologies have been applied to different areas in order to support the decision-making process. BI enables the extraction of knowledge from the data stored. The healthcare industry is no exception, and so BI applications have been under investigation across multiple units of different institutions. Thus, in this article, we intend to analyze some open-source/free BI tools on the market and their applicability in the clinical sphere, taking into consideration the general characteristics of the clinical environment. For this purpose, six BI tools were selected, analyzed, and tested in a practical environment. Then, a comparison metric and a ranking were defined for the tested applications in order to choose the one that best applies to the extraction of useful knowledge and clinical data in a healthcare environment. Finally, a pervasive BI platform was developed using a real case in order to prove the tool's viability. (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: January 2–8:
|
|