Featured article of the week: May 09–15:"Development of a core competency framework for clinical informatics"
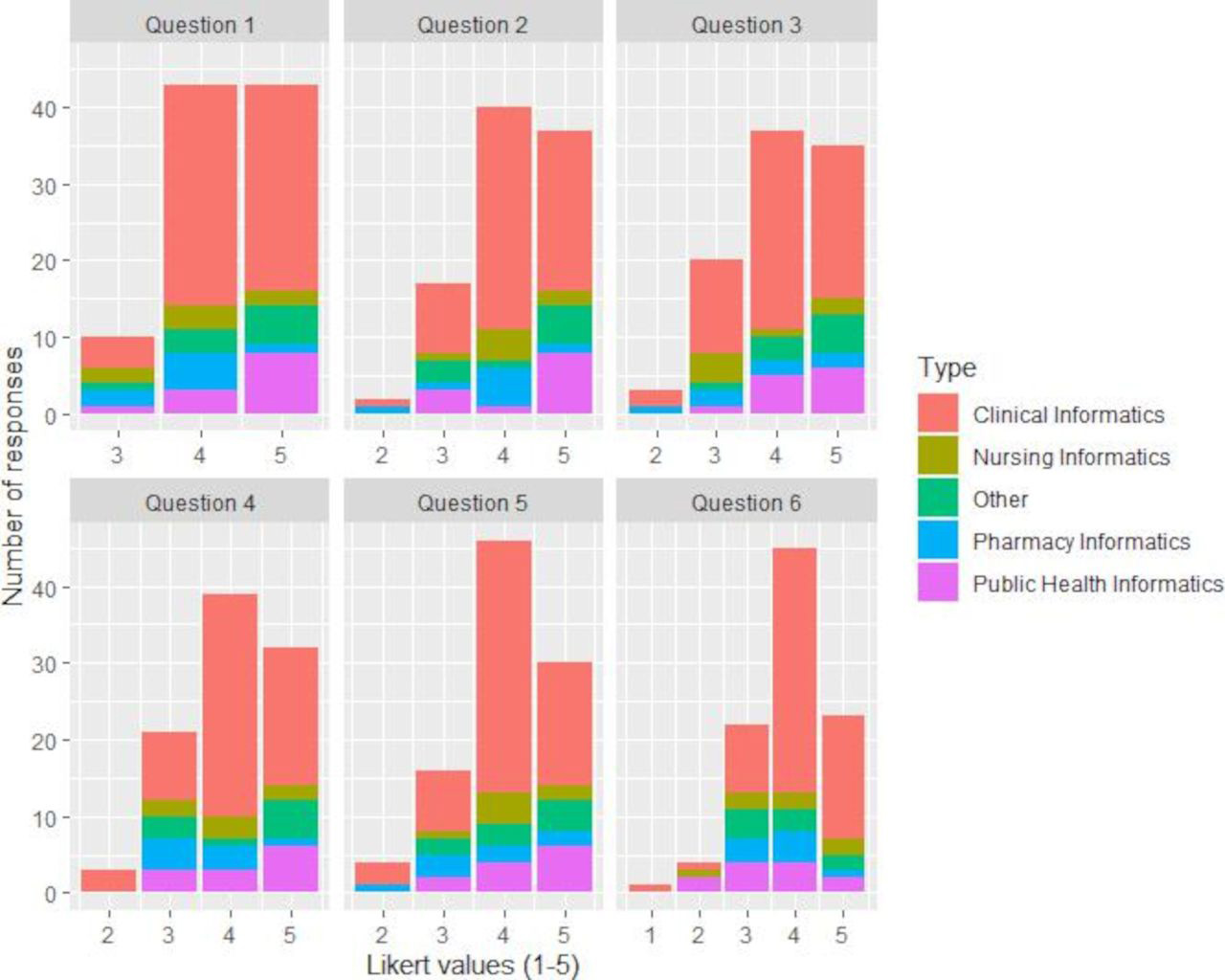
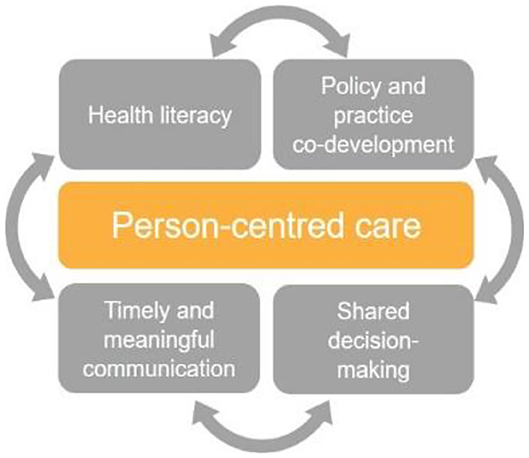
Up to this point, there has not been a national core competency framework for clinical informatics in the U.K. Here we report on the final two iterations of work carried out towards the formation of a national core competency framework. This follows an initial systematic literature review of existing skills and competencies and a job listing analysis. An iterative approach was applied to framework development. Using a mixed-methods design, we carried out semi-structured interviews with participants involved in informatics (n = 15). The framework was updated based on the interview findings and was subsequently distributed as part of a bespoke online digital survey for wider participation (n = 87). The final version of the framework is based on the findings of the survey.(Full article...)
Featured article of the week: May 02–08:
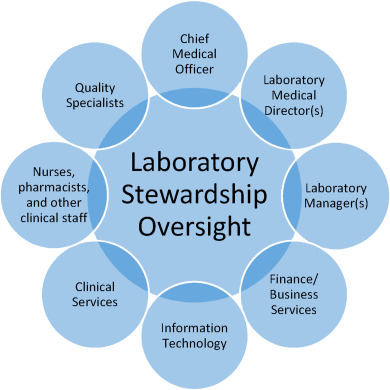
"Strategies for laboratory professionals to drive laboratory stewardship"
Appropriate laboratory testing is critical in today's healthcare environment that aims to improve patient care while reducing cost. In recent years, laboratory stewardship has emerged as a strategy for assuring quality in laboratory medicine with the goal of providing the right test for the right patient at the right time. Implementing a laboratory stewardship program now presents a valuable opportunity for laboratory professionals to exercise leadership within health systems and to drive change toward realizing aims in healthcare. The proposed framework for program implementation includes five key elements: 1) a clear vision and organizational alignment; 2) appropriate skills for program execution and management; 3) resources to support the program; 4) incentives to motivate participation; and, 5) a plan of action that articulates program objectives and metrics. This framework builds upon principles of change management, with emphasis on engagement with clinical and administrative stakeholders and the use of clinical data as the basis for change. These strategies enable laboratory professionals to cultivate organizational support for improving laboratory use and take a leading role in providing high-quality patient care. (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: April 25–May 01:
"Cybersecurity impacts for artificial intelligence use within Industry 4.0"
In today’s modern digital manufacturing landscape, new and emerging technologies can shape how an organization can compete, while others will view those technologies as a necessity to survive, as manufacturing has been identified as a critical infrastructure. Universities struggle to hire university professors that are adequately trained or willing to enter academia due to competitive salary offers in the industry. Meanwhile, the demand for people knowledgeable in fields such as artificial intelligence, data science, and cybersecurity continuously rises, with no foreseeable drop in demand in the next several years. This results in organizations deploying technologies with a staff that inadequately understands what new cybersecurity risks they are introducing into the company. This work examines how organizations can potentially mitigate some of the risk associated with integrating these new technologies and developing their workforce to be better prepared for looming changes in technological skill need. (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: April 18–24:
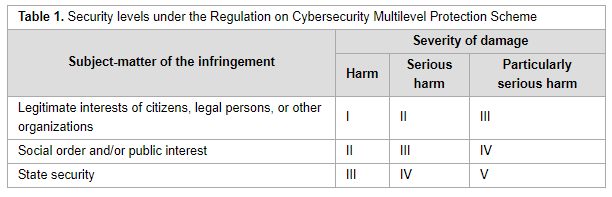
"Cross-border data transfer regulation in China"
With the growing participation of emerging countries in global data governance, the traditional legislative paradigm dominated by the European Union and the United States is constantly being analyzed and reshaped. It is of particular importance for China to establish the regulatory framework of cross-border data transfer, for not only does it involve the rights of Chinese citizens and entities, but also the concepts of cyber-sovereignty and national security, as well as the framing of global cyberspace rules. China continues to leverage data sovereignty to persuade lawmakers to support the development of critical technology in digital domains and infrastructure construction. This paper aims to systematically and chronologically describe Chinese regulations for cross-border data exchange. Enacted and draft provisions—as well as binding and non-binding regulatory rules—are studied, and various positive dynamic developments in the framing of China’s cross-border data regulation are shown ... (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: April 11–17:
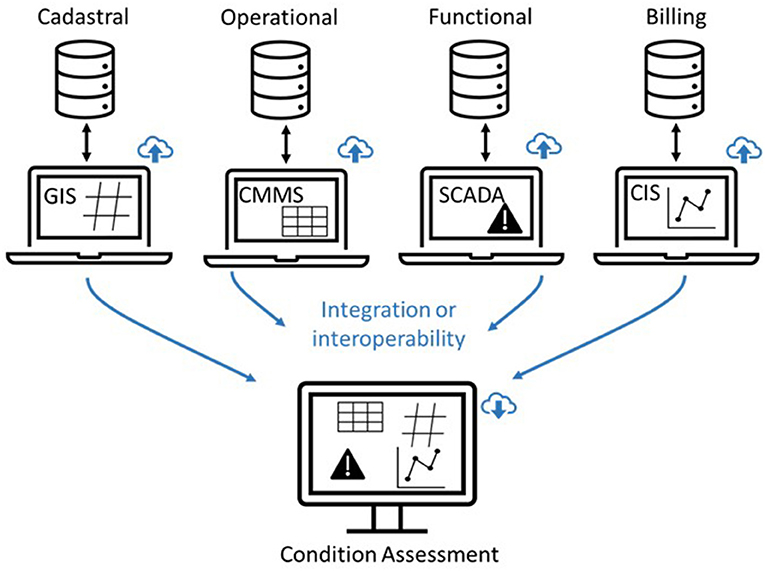
"Data and information systems management for urban water infrastructure condition assessment"
Most of the urban water infrastructure around the world was built several decades ago and nowadays they are deteriorated. As such, the assets that constitute these infrastructures need to be updated or replaced. Since most of the assets are buried, water utilities face the challenge of deciding where, when, and how to update or replace those assets. Condition assessment is a vital component of any planned update and replacement activities and is mostly based on the data collected from the managed networks. This collected data needs to be organized and managed in order to be transformed into useful information. Nonetheless, the large amount of assets and data involved makes data and information management a challenging task for water utilities, especially those with as lower digital maturity level. This paper highlights the importance of data and information systems' management for urban water infrastructure condition assessment based on the authors' experiences. (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: April 04–10:
"Diagnostic informatics: The role of digital health in diagnostic stewardship and the achievement of excellence, safety, and value"
Diagnostic investigations (i.e., pathology laboratory analysis and medical imaging) aim to increase the certainty of the presence of or absence of disease by supporting the process of differential diagnosis, support clinical management, and monitor a patient's trajectory (e.g., disease progression or response to treatment). Digital health—defined as the collection, storage, retrieval, transmission, and utilization of data, information, and knowledge to support healthcare—has become an essential component of the diagnostic investigational process, helping to facilitate the accuracy and timeliness of information transfer and enhance the effectiveness of decision-making processes. Digital health is also important to diagnostic stewardship, which involves coordinated guidance and interventions to ensure the appropriate utilization of diagnostic tests for therapeutic decision-making. (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: March 28–April 03:
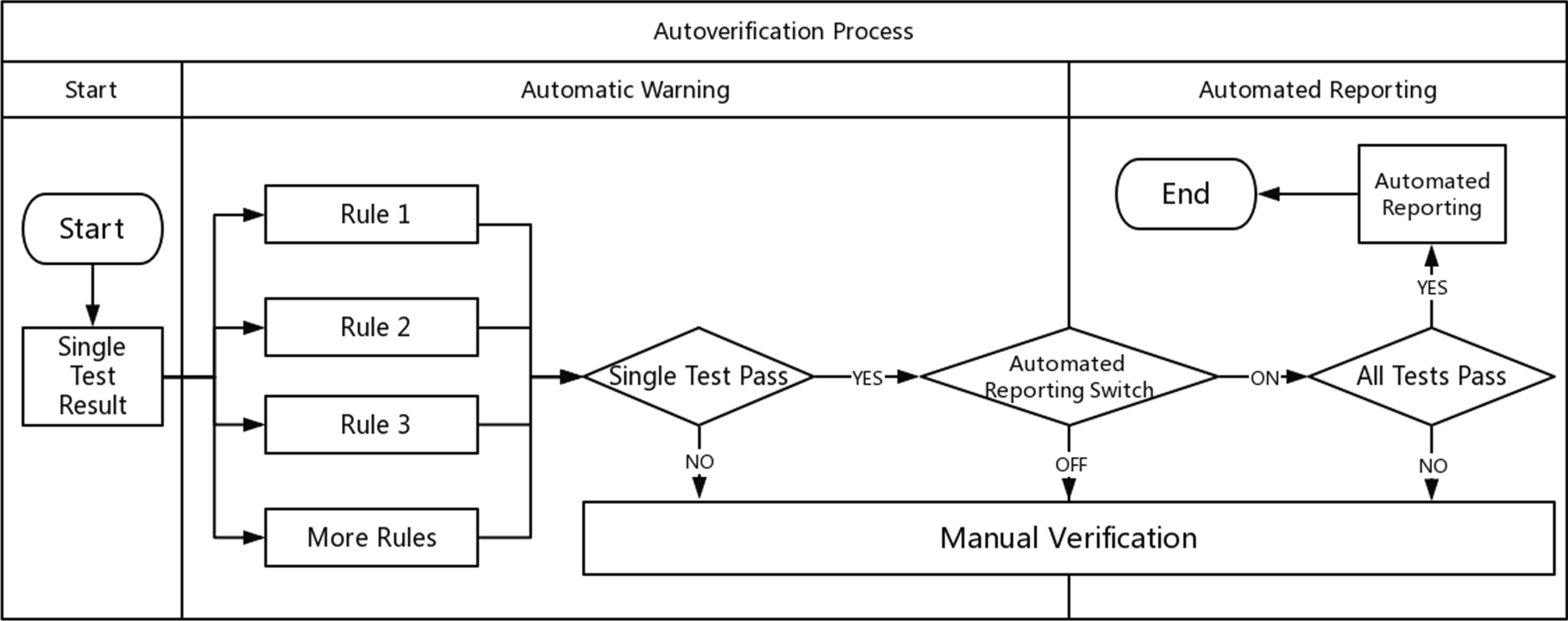
"Development and implementation of an LIS-based validation system for autoverification toward zero defects in the automated reporting of laboratory test results"
For laboratory informatics applications, validation of the autoverification function is one of the critical steps to confirm its effectiveness before use. It is crucial to verify whether the programmed algorithm follows the expected logic and produces the expected results. This process has always relied on the assessment of human–machine consistency and is mostly a manually recorded and time-consuming activity with inherent subjectivity and arbitrariness that cannot guarantee a comprehensive, timely, and continuous effectiveness evaluation of the autoverification function. To overcome these inherent limitations, we independently developed and implemented a laboratory information system (LIS)-based validation system for autoverification. We developed a correctness verification and integrity validation method (hereinafter referred to as the "new method") in the form of a human–machine dialog ... (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: March 21–27:
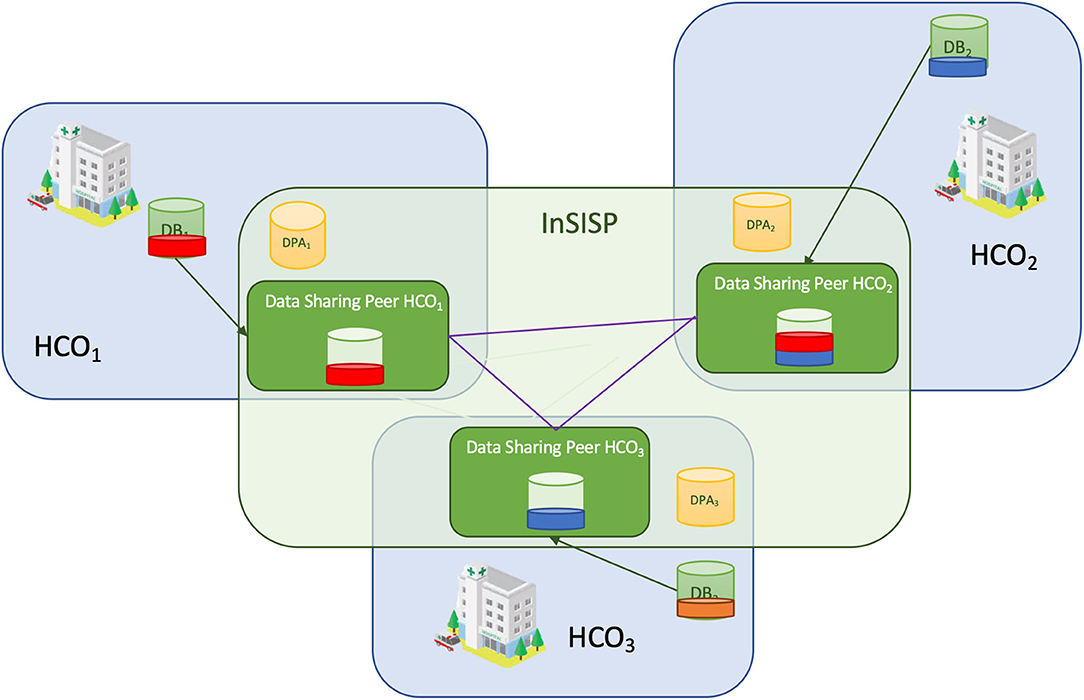
"Emerging and established trends to support secure health information exchange"
This work aims to provide information, guidelines, established practices and standards, and an extensive evaluation on new and promising technologies for the implementation of a secure information sharing platform for health-related data. We focus strictly on the technical aspects and specifically on the sharing of health information, studying innovative techniques for secure information sharing within the healthcare domain, and we describe our solution and evaluate the use of blockchain methodologically for integrating within our implementation. To do so, we analyze health information sharing within the concept of the PANACEA project, which facilitates the design, implementation, and deployment of a relevant platform. The research presented in this paper provides evidence and argumentation toward advanced and novel implementation strategies for a state-of-the-art information sharing environment; a description of high-level requirements for the national and cross-border transfer of data between different healthcare organizations ... (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: March 14–20:
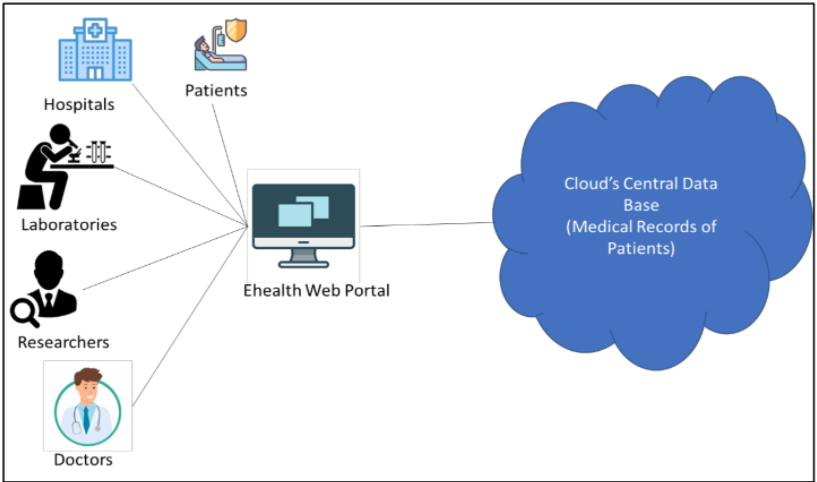
"Security and privacy in cloud-based eHealth systems"
Cloud-based healthcare computing has changed the face of healthcare in many ways. The main advantages of cloud computing in healthcare are scalability of the required service and the provision to upscale or downsize the data storge, particularly in conjunction with approaches to artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. This paper examines various research studies to explore the utilization of intelligent techniques in health systems and mainly focuses on the security and privacy issues in the current technologies. Despite the various benefits related to cloud computing applications for healthcare, there are different types of management, technology handling, security measures, and legal issues to be considered and addressed. The key focus of this paper is to address the increased demand for cloud computing and its definition, technologies widely used in healthcare, their problems and possibilities, and the way protection mechanisms are organized and prepared when the company chooses to implement the latest evolving service model. (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: March 7–13:
"Using interactive digital notebooks for bioscience and informatics education"
Interactive digital notebooks provide an opportunity for researchers and educators to carry out data analysis and report results in a single digital format. Further to just being digital, the format allows for rich content to be created in order to interact with the code and data contained in such a notebook to form an educational narrative. This primer introduces some of the fundamental aspects involved in using Jupyter Notebook in an educational setting for teaching in the bioinformatics and health informatics disciplines. We also provide two case studies that detail 1. how we used Jupyter Notebooks to teach non-coders programming skills on a blended master’s degree module for a health informatics program, and 2. a fully online distance learning unit on programming for a postgraduate certificate (PG Cert) in clinical bioinformatics, with a more technical audience. (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: February 28–March 6:
"The Application of Informatics to Scientific Work: Laboratory Informatics for Newbies"
The purpose of this piece is to introduce people who are not intimately familiar with laboratory work to the basics of laboratory operations and the role that informatics can play in assisting scientists, engineers, and technicians in their efforts. The concepts are important because they provide a functional foundation for understanding lab work and how that work is done in the early part of the twenty-first century (things will change, just wait for it). This material is intended for anyone who is interested in seeing how modern informatics tools can help those doing scientific work. It will provide an orientation to scientific and laboratory work, as well as the systems that have been developed to make that work more productive. (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: February 21–27:
"Blockchain-based healthcare workflow for IoT-connected laboratories in federated hospital clouds"
In a pandemic-related situation such as that caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, the need for telemedicine and other distanced services becomes dramatically fundamental to reducing the movement of patients, and by extension reducing the risk of infection in healthcare settings. One potential avenue for achieving this is through leveraging cloud computing and internet of things (IoT) technologies. This paper proposes an IoT-connected laboratory service where clinical exams are performed on patients directly in a hospital by technicians through the use of IoT medical diagnostic devices, with results automatically being sent via the hospital's cloud to doctors of federated hospitals for validation and/or consultation. In particular, we discuss a distributed scenario where nurses, technicians, and medical doctors belonging to different hospitals cooperate through their federated hospital clouds ... (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: February 14–20:
"Informatics-driven quality improvement in the modern histology lab"
Laboratory information systems (LISs) and data visualization techniques have untapped potential in anatomic pathology laboratories. The pre-built functionalities of an LIS do not address all the needs of a modern histology laboratory. For instance, “go live” is not the end of LIS customization, only the beginning. After closely evaluating various histology lab workflows, we implemented several custom data analytics dashboards and additional LIS functionalities to monitor and address weaknesses. Herein, we present our experience with LIS and data-tracking solutions that improved trainee education, slide logistics, staffing and instrumentation lobbying, and task tracking. The latter was addressed through the creation of a novel “status board” akin to those seen in inpatient wards. These use-cases can benefit other histology laboratories. (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: February 07–13:
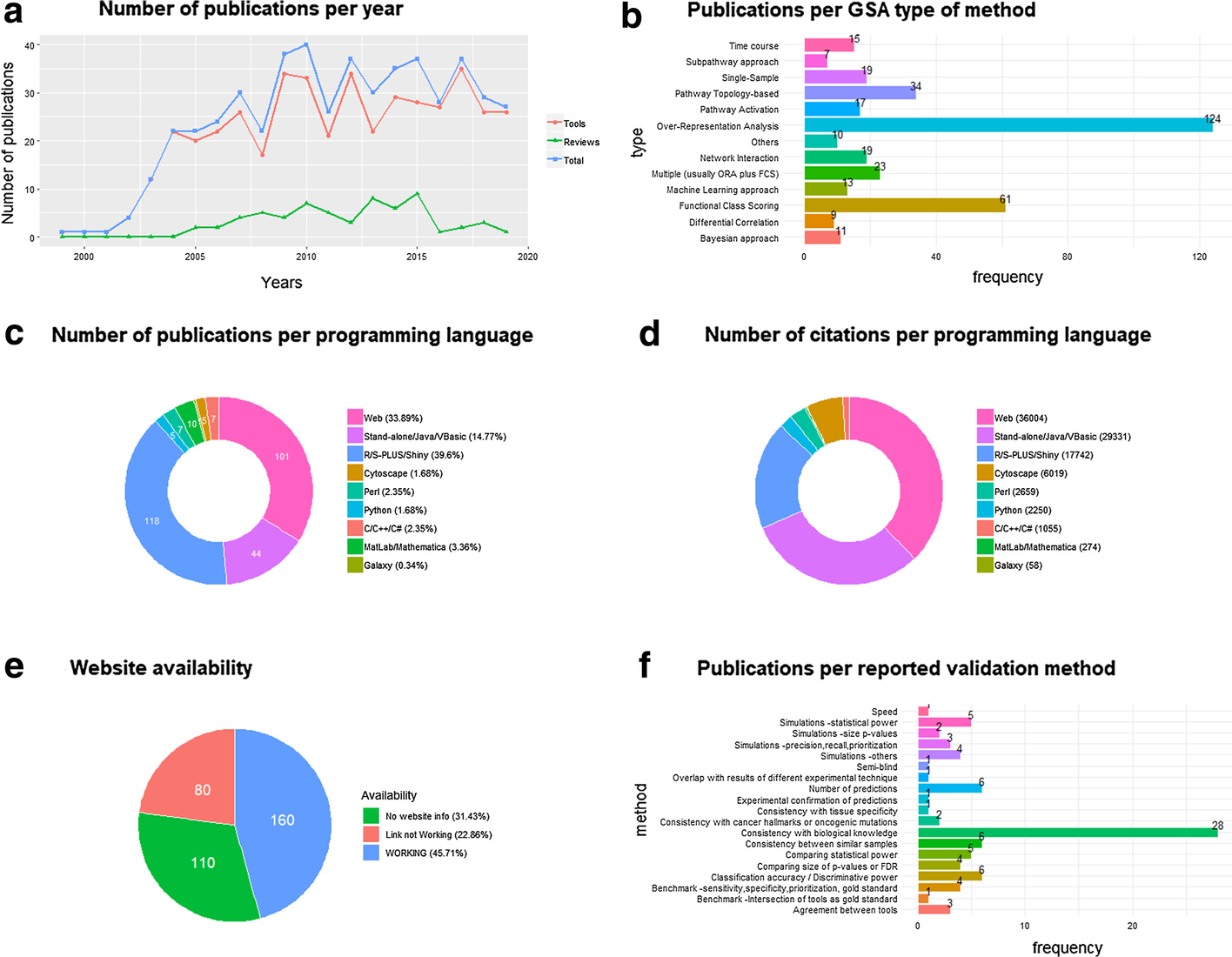
"Popularity and performance of bioinformatics software: The case of gene set analysis"
Gene set analysis (GSA) is arguably the method of choice for the functional interpretation of omics results. This work explores the popularity and the performance of all the GSA methodologies and software published during the 20 years since its inception. "Popularity" is estimated according to each paper's citation counts, while "performance" is based on a comprehensive evaluation of the validation strategies used by papers in the field, as well as the consolidated results from the existing benchmark studies. Regarding popularity, data is collected into an online open database ("GSARefDB") which allows browsing bibliographic and method-descriptive information from 503 GSA paper references; regarding performance, we introduce a repository of Jupyter Notebook workflows and Shiny apps for automated benchmarking of GSA methods (“GSA-BenchmarKING”). After comparing popularity versus performance, results show discrepancies between the most popular and the best performing GSA methods. (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: January 31–February 06:
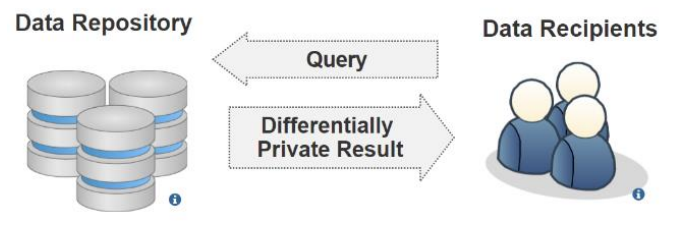
"Privacy-preserving healthcare informatics: A review"
The electronic health record (EHR) is the key to an efficient healthcare service delivery system. The publication of healthcare data is highly beneficial to healthcare industries and government institutions to support a variety of medical and census research. However, healthcare data contains sensitive information of patients, and the publication of such data could lead to unintended privacy disclosures. In this paper, we present a comprehensive survey of the state-of-the-art privacy-enhancing methods that ensure a secure healthcare data sharing environment. We focus on the recently proposed schemes based on data anonymization and differential privacy approaches in the protection of healthcare data privacy. We highlight the strengths and limitations of the two approaches and discuss some promising future research directions in this area. (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: January 24–30:
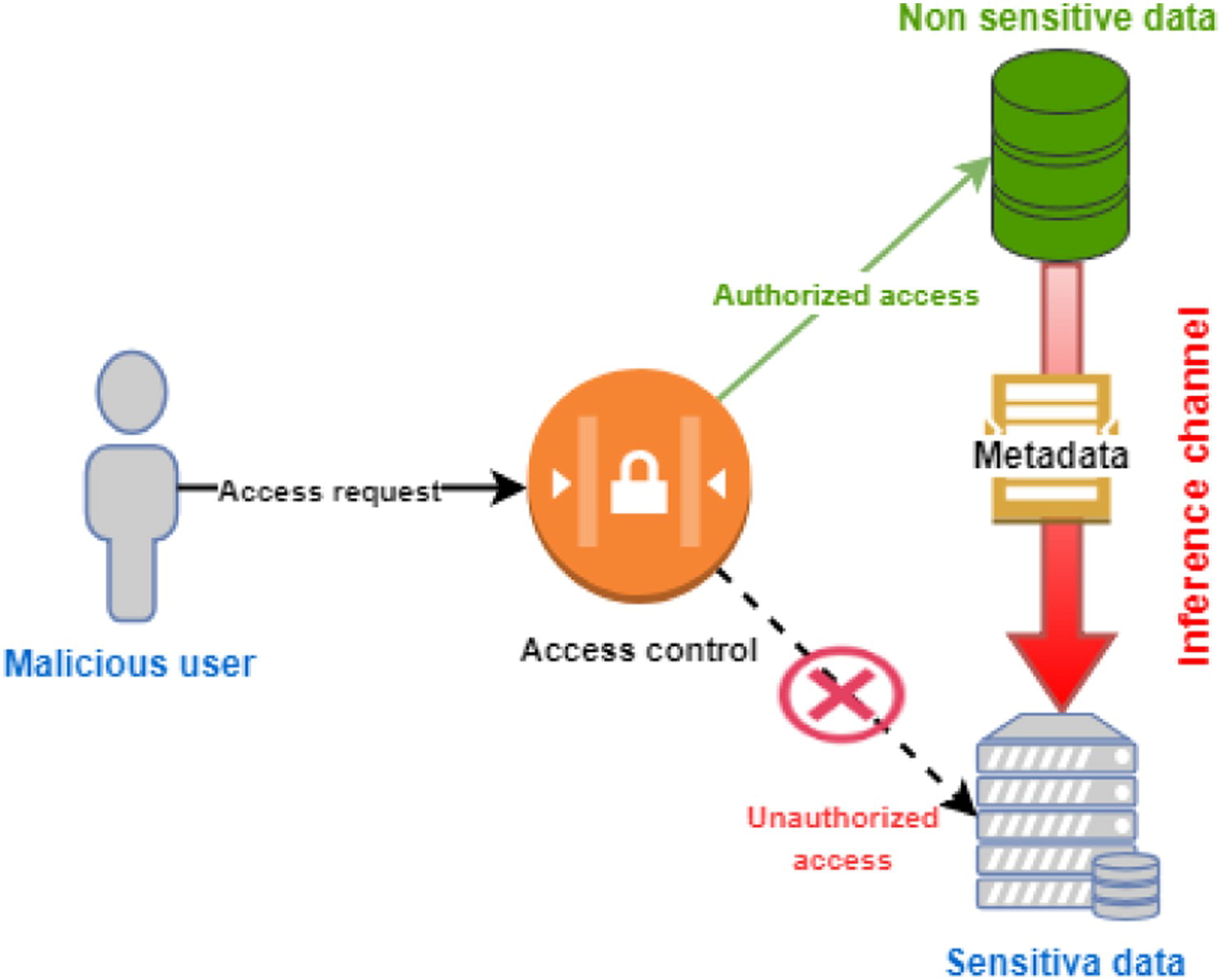
"Secure data outsourcing in presence of the inference problem: Issues and directions"
With the emergence of the cloud computing paradigms, secure data outsourcing—moving some or most data to a third-party provider of secure data management services—has become one of the crucial challenges of modern computing. Data owners place their data among cloud service providers (CSPs) in order to increase flexibility, optimize storage, enhance data manipulation, and decrease processing time. Nevertheless, from a security point of view, access control proves to be a major concern in this situation seeing that the security policy of the data owner must be preserved when data is moved to the cloud. The lack of a comprehensive and systematic review on this topic in the available literature motivated us to review this research problem. Here, we discuss current and emerging research on privacy and confidentiality concerns in cloud-based data outsourcing and pinpoint potential issues that are still unresolved. (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: January 17–23:
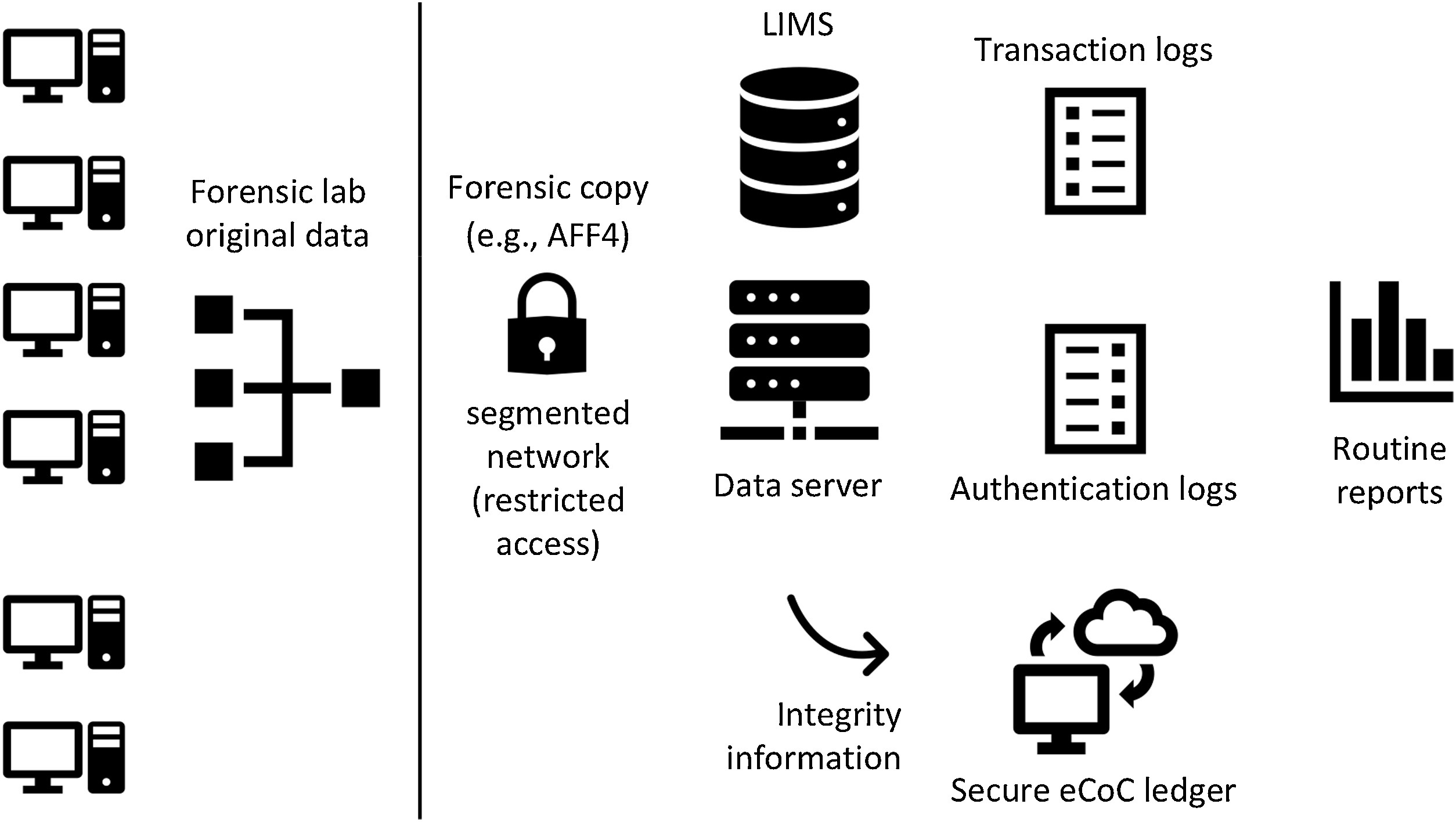
"Digital transformation risk management in forensic science laboratories"
Technological advances are changing how forensic laboratories operate in all forensic disciplines, not only digital. Computers support workflow management and enable evidence analysis (physical and digital), while new technology enables previously unavailable forensic capabilities. Used properly, the integration of digital systems supports greater efficiency and reproducibility, and drives digital transformation of forensic laboratories. However, without the necessary preparations, these digital transformations can undermine the core principles and processes of forensic laboratories. Forensic preparedness concentrating on digital data reduces the cost and operational disruption of responding to various kinds of problems, including misplaced exhibits, allegations of employee misconduct, disclosure requirements, and information security breaches ... (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: January 10–16:
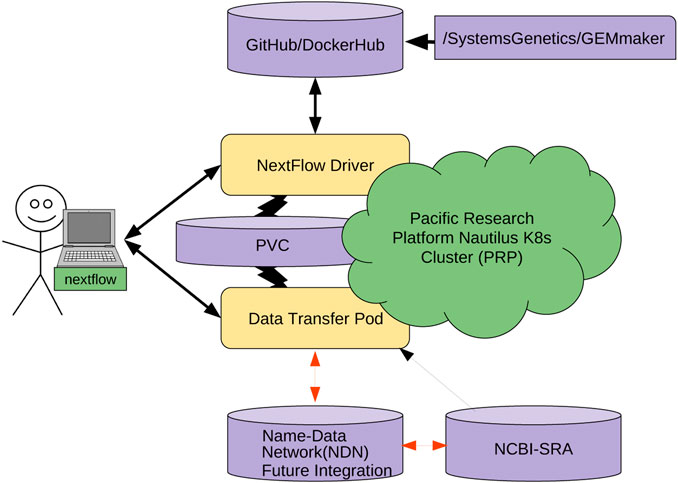
"Named data networking for genomics data management and integrated workflows"
Advanced imaging and DNA sequencing technologies now enable the diverse biology community to routinely generate and analyze terabytes of high-resolution biological data. The community is rapidly heading toward the petascale in single-investigator laboratory settings. As evidence, the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Sequence Read Archive (SRA) central DNA sequence repository alone contains over 45 petabytes of biological data. Given the geometric growth of this and other genomics repositories, an exabyte of mineable biological data is imminent. The challenges of effectively utilizing these datasets are enormous, as they are not only large in size but also stored in various geographically distributed repositories such as those hosted by the NCBI, as well as in the DNA Data Bank of Japan (DDBJ), European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), and NASA’s GeneLab. (Full article...)
|
Featured article of the week: January 3–9:
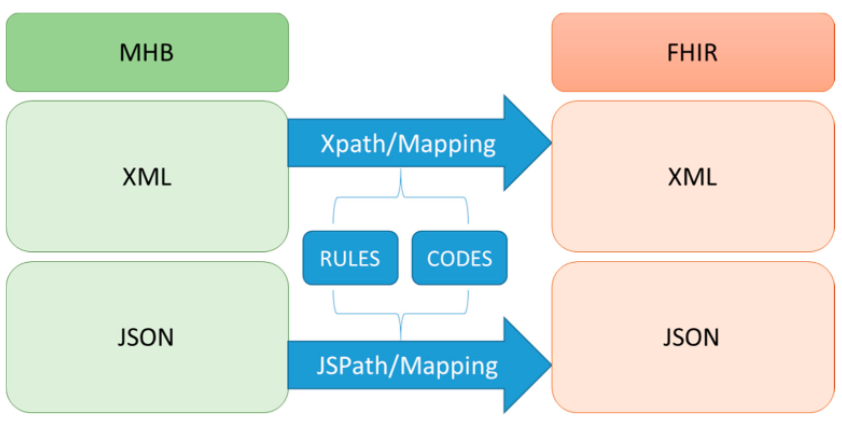
"Implement an international interoperable PHR by FHIR: A Taiwan innovative application"
Personal health records (PHRs) have many benefits for things such as health surveillance, epidemiological surveillance, self-control, links to various services, public health and health management, and international surveillance. The implementation of an international standard for interoperability is essential to accessing PHRs. In Taiwan, the nationwide exchange platform for electronic medical records (EMRs) has been in use for many years. The Health Level Seven International (HL7) Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) was used as the standard for those EMRs. However, the complication of implementing CDA became a barrier for many hospitals to realizing standard EMRs. In this study, we implemented a Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR)-based PHR transformation process, including a user interface module to review the contents of PHRs. (Full article...)
|
|