Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) m (Internal link) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Облачные_вычисления.jpg|280px]]</div> | ||
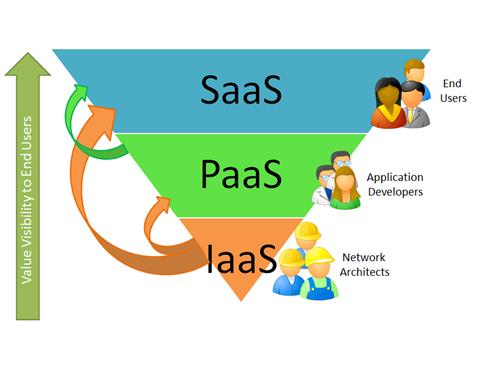
'''[[ | '''[[Software as a service]]''' ('''SaaS''') — sometimes referred to as "on-demand software" — is a software delivery model in which software and its associated data are hosted centrally (on the [[Cloud computing|cloud]], for example) and are typically accessed by users using a thin client, normally using a web browser over the Internet. The customer subscribes to this "service" rather than requiring a software license, and the software doesn't require an implementation on customer premises. | ||
A SaaS solution is typically a "multi-tenant solution," meaning more than one entity is sharing the server and database resource(s) hosted by the vendor, though in the process potentially limiting customer customization. With this model, a single version of the application with a single configuration (hardware, network, operating system, etc.) is used for all customers. To support scalability, the application is installed on multiple machines. In some cases, a second version of the application may be set up to offer a select group of customers a separate instance of the software environment, better enabling customers to customize their configuration. (This could be accomplished with platform as a service (PaaS), for example. This is contrasted with traditional software, where multiple physical copies of the software — each potentially of a different version, with a potentially different configuration, and often customized — are installed across various customer sites. ('''[[Software as a service |Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': [[Content delivery network]], [[Federally qualified health center | ''Recently featured'': [[Health informatics]], [[Content delivery network]], [[Federally qualified health center]] | ||
Revision as of 16:05, 13 April 2015
Software as a service (SaaS) — sometimes referred to as "on-demand software" — is a software delivery model in which software and its associated data are hosted centrally (on the cloud, for example) and are typically accessed by users using a thin client, normally using a web browser over the Internet. The customer subscribes to this "service" rather than requiring a software license, and the software doesn't require an implementation on customer premises.
A SaaS solution is typically a "multi-tenant solution," meaning more than one entity is sharing the server and database resource(s) hosted by the vendor, though in the process potentially limiting customer customization. With this model, a single version of the application with a single configuration (hardware, network, operating system, etc.) is used for all customers. To support scalability, the application is installed on multiple machines. In some cases, a second version of the application may be set up to offer a select group of customers a separate instance of the software environment, better enabling customers to customize their configuration. (This could be accomplished with platform as a service (PaaS), for example. This is contrasted with traditional software, where multiple physical copies of the software — each potentially of a different version, with a potentially different configuration, and often customized — are installed across various customer sites. (Full article...)
Recently featured: Health informatics, Content delivery network, Federally qualified health center