Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1_Bellary_PerspectivesClinRes2014_5-4.jpg|220px]]</div> | ||
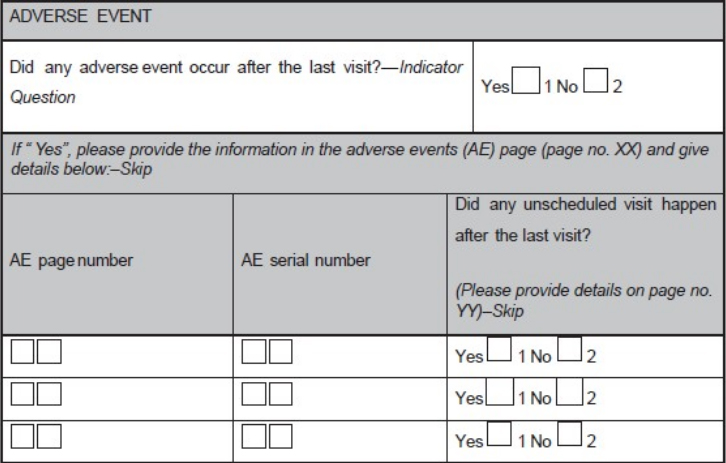
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Basics of case report form designing in clinical research|Basics of case report form designing in clinical research]]"''' | ||
Case report form (CRF) is a specialized document in clinical research. It should be study protocol driven, robust in content and have material to collect the study specific data. Though paper CRFs are still used largely, use of electronic CRFs (eCRFs) are gaining popularity due to the advantages they offer such as improved data quality, online discrepancy management and faster database lock etc. Main objectives behind CRF development are preserving and maintaining quality and integrity of data. CRF design should be standardized to address the needs of all users such as investigator, site coordinator, study monitor, data entry personnel, medical coder and statistician. Data should be organized in a format that facilitates and simplifies data analysis. Collection of large amount of data will result in wasted resources in collecting and processing it and in many circumstances, will not be utilized for analysis. Apart from that, standard guidelines should be followed while designing the CRF. CRF completion manual should be provided to the site personnel to promote accurate data entry by them. ('''[[Journal:Why health services research needs geoinformatics: Rationale and case example|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': [[Journal:Return on investment in electronic health records in primary care practices: A mixed-methods study|Return on investment in electronic health records in primary care practices: A mixed-methods study]], [[Journal:Use of handheld computers in clinical practice: A systematic review|Use of handheld computers in clinical practice: A systematic review | ''Recently featured'': [[Journal:Why health services research needs geoinformatics: Rationale and case example|Why health services research needs geoinformatics: Rationale and case example]], [[Journal:Return on investment in electronic health records in primary care practices: A mixed-methods study|Return on investment in electronic health records in primary care practices: A mixed-methods study]], [[Journal:Use of handheld computers in clinical practice: A systematic review|Use of handheld computers in clinical practice: A systematic review]] | ||
Revision as of 17:48, 25 August 2015
"Basics of case report form designing in clinical research"
Case report form (CRF) is a specialized document in clinical research. It should be study protocol driven, robust in content and have material to collect the study specific data. Though paper CRFs are still used largely, use of electronic CRFs (eCRFs) are gaining popularity due to the advantages they offer such as improved data quality, online discrepancy management and faster database lock etc. Main objectives behind CRF development are preserving and maintaining quality and integrity of data. CRF design should be standardized to address the needs of all users such as investigator, site coordinator, study monitor, data entry personnel, medical coder and statistician. Data should be organized in a format that facilitates and simplifies data analysis. Collection of large amount of data will result in wasted resources in collecting and processing it and in many circumstances, will not be utilized for analysis. Apart from that, standard guidelines should be followed while designing the CRF. CRF completion manual should be provided to the site personnel to promote accurate data entry by them. (Full article...)
Recently featured: Why health services research needs geoinformatics: Rationale and case example, Return on investment in electronic health records in primary care practices: A mixed-methods study, Use of handheld computers in clinical practice: A systematic review