Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Munkhdalai JCheminformatics2015 7-1.jpg|220px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Incorporating domain knowledge in chemical and biomedical named entity recognition with word representations|Incorporating domain knowledge in chemical and biomedical named entity recognition with word representations]]"''' | ||
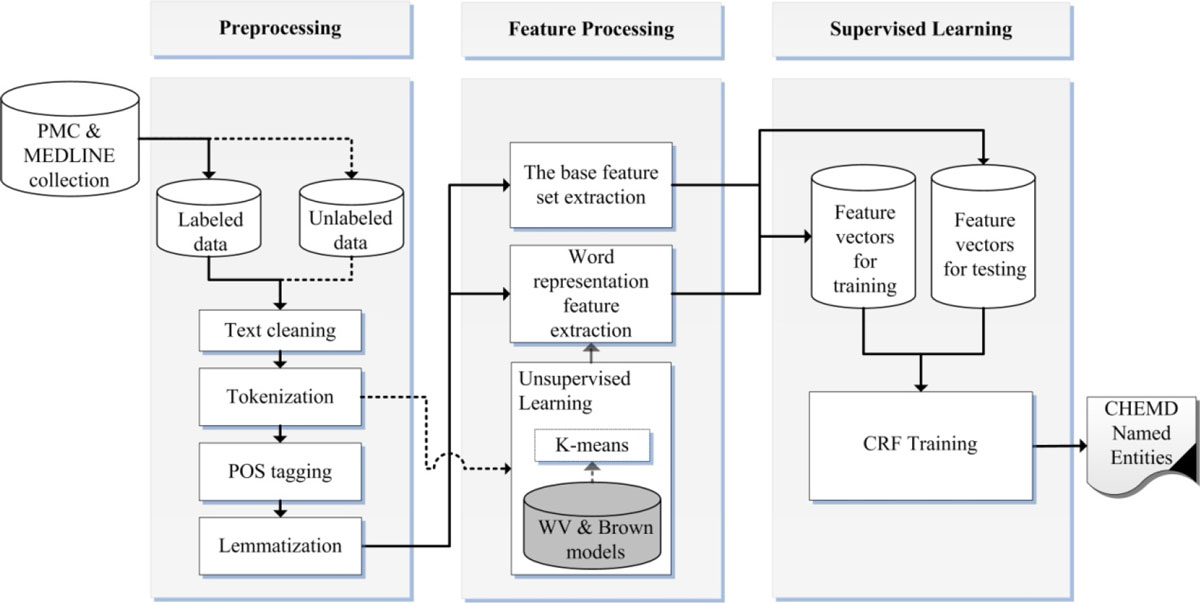
Chemical and biomedical Named Entity Recognition (NER) is an essential prerequisite task before effective text mining can begin for biochemical-text data. Exploiting unlabeled text data to leverage system performance has been an active and challenging research topic in text mining due to the recent growth in the amount of biomedical literature. | |||
We present a semi-supervised learning method that efficiently exploits unlabeled data in order to incorporate domain knowledge into a named entity recognition model and to leverage system performance. The proposed method includes Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks for text preprocessing, learning word representation features from a large amount of text data for feature extraction, and conditional random fields for token classification. Other than the free text in the domain, the proposed method does not rely on any lexicon nor any dictionary in order to keep the system applicable to other NER tasks in bio-text data. ('''[[Journal:Incorporating domain knowledge in chemical and biomedical named entity recognition with word representations|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': [[Journal:4273π: Bioinformatics education on low cost ARM hardware|4273π: Bioinformatics education on low cost ARM hardware]], [[Journal:University-level practical activities in bioinformatics benefit voluntary groups of pupils in the last 2 years of school|University-level practical activities in bioinformatics benefit voluntary groups of pupils in the last 2 years of school | ''Recently featured'': [[Journal:Requirements for data integration platforms in biomedical research networks: A reference model|Requirements for data integration platforms in biomedical research networks: A reference model]], [[Journal:4273π: Bioinformatics education on low cost ARM hardware|4273π: Bioinformatics education on low cost ARM hardware]], [[Journal:University-level practical activities in bioinformatics benefit voluntary groups of pupils in the last 2 years of school|University-level practical activities in bioinformatics benefit voluntary groups of pupils in the last 2 years of school]] | ||
Revision as of 15:55, 23 December 2015
Chemical and biomedical Named Entity Recognition (NER) is an essential prerequisite task before effective text mining can begin for biochemical-text data. Exploiting unlabeled text data to leverage system performance has been an active and challenging research topic in text mining due to the recent growth in the amount of biomedical literature.
We present a semi-supervised learning method that efficiently exploits unlabeled data in order to incorporate domain knowledge into a named entity recognition model and to leverage system performance. The proposed method includes Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks for text preprocessing, learning word representation features from a large amount of text data for feature extraction, and conditional random fields for token classification. Other than the free text in the domain, the proposed method does not rely on any lexicon nor any dictionary in order to keep the system applicable to other NER tasks in bio-text data. (Full article...)
Recently featured: Requirements for data integration platforms in biomedical research networks: A reference model, 4273π: Bioinformatics education on low cost ARM hardware, University-level practical activities in bioinformatics benefit voluntary groups of pupils in the last 2 years of school