Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Ashish FrontInNeuroinformatics2016 9.jpg|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:The GAAIN Entity Mapper: An active-learning system for medical data mapping|The GAAIN Entity Mapper: An active-learning system for medical data mapping]]"''' | ||
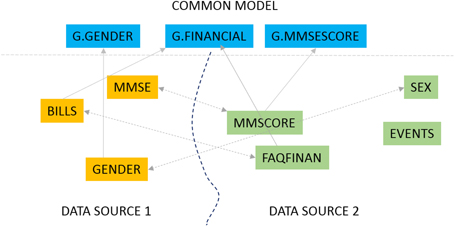
This work is focused on mapping biomedical datasets to a common representation, as an integral part of data harmonization for integrated biomedical data access and sharing. We present GEM, an intelligent software assistant for automated data mapping across different datasets or from a dataset to a common data model. The GEM system automates data mapping by providing precise suggestions for data element mappings. It leverages the detailed metadata about elements in associated dataset documentation such as data dictionaries that are typically available with biomedical datasets. It employs unsupervised text mining techniques to determine similarity between data elements and also employs machine-learning classifiers to identify element matches. It further provides an active-learning capability where the process of training the GEM system is optimized. Our experimental evaluations show that the GEM system provides highly accurate data mappings (over 90 percent accuracy) for real datasets of thousands of data elements each, in the Alzheimer's disease research domain. ('''[[Journal:The GAAIN Entity Mapper: An active-learning system for medical data mapping|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Visualizing the quality of partially accruing data for use in decision making|Visualizing the quality of partially accruing data for use in decision making]] | |||
: ▪ [[Journal:Digital pathology and anatomic pathology laboratory information system integration to support digital pathology sign-out]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Digital pathology and anatomic pathology laboratory information system integration to support digital pathology sign-out]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:A polyglot approach to bioinformatics data integration: A phylogenetic analysis of HIV-1|A polyglot approach to bioinformatics data integration: A phylogenetic analysis of HIV-1]] | : ▪ [[Journal:A polyglot approach to bioinformatics data integration: A phylogenetic analysis of HIV-1|A polyglot approach to bioinformatics data integration: A phylogenetic analysis of HIV-1]] | ||
Revision as of 17:41, 25 July 2016
"The GAAIN Entity Mapper: An active-learning system for medical data mapping"
This work is focused on mapping biomedical datasets to a common representation, as an integral part of data harmonization for integrated biomedical data access and sharing. We present GEM, an intelligent software assistant for automated data mapping across different datasets or from a dataset to a common data model. The GEM system automates data mapping by providing precise suggestions for data element mappings. It leverages the detailed metadata about elements in associated dataset documentation such as data dictionaries that are typically available with biomedical datasets. It employs unsupervised text mining techniques to determine similarity between data elements and also employs machine-learning classifiers to identify element matches. It further provides an active-learning capability where the process of training the GEM system is optimized. Our experimental evaluations show that the GEM system provides highly accurate data mappings (over 90 percent accuracy) for real datasets of thousands of data elements each, in the Alzheimer's disease research domain. (Full article...)
Recently featured:
- ▪ Visualizing the quality of partially accruing data for use in decision making
- ▪ Journal:Digital pathology and anatomic pathology laboratory information system integration to support digital pathology sign-out
- ▪ A polyglot approach to bioinformatics data integration: A phylogenetic analysis of HIV-1