Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig0.5 Alperin JofCheminformatics2016 8.gif|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Terminology spectrum analysis of natural-language chemical documents: Term-like phrases retrieval routine|Terminology spectrum analysis of natural-language chemical documents: Term-like phrases retrieval routine]]"''' | ||
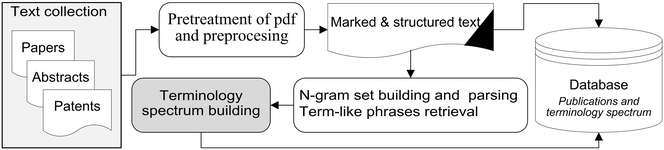
This study seeks to develop, test and assess a methodology for automatic extraction of a complete set of ‘term-like phrases’ and to create a terminology spectrum from a collection of natural language PDF documents in the field of chemistry. The definition of ‘term-like phrases’ is one or more consecutive words and/or alphanumeric string combinations with unchanged spelling which convey specific scientific meanings. A terminology spectrum for a natural language document is an indexed list of tagged entities including: recognized general scientific concepts, terms linked to existing thesauri, names of chemical substances/reactions and term-like phrases. The retrieval routine is based on n-gram textual analysis with a sequential execution of various ‘accept and reject’ rules with taking into account the morphological and structural [[information]]. | |||
The | The assessment of the retrieval process, expressed quantitatively with a precision (P), recall (R) and F1-measure, which are calculated manually from a limited set of documents (the full set of text abstracts belonging to five EuropaCat events were processed) by professional chemical scientists, has proved the effectiveness of the developed approach. ('''[[Journal:Terminology spectrum analysis of natural-language chemical documents: Term-like phrases retrieval routine|Full article...]]''')<br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:A legal framework to support development and assessment of digital health services|A legal framework to support development and assessment of digital health services]] | |||
: ▪ [[Journal:The GAAIN Entity Mapper: An active-learning system for medical data mapping|The GAAIN Entity Mapper: An active-learning system for medical data mapping]] | : ▪ [[Journal:The GAAIN Entity Mapper: An active-learning system for medical data mapping|The GAAIN Entity Mapper: An active-learning system for medical data mapping]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Visualizing the quality of partially accruing data for use in decision making|Visualizing the quality of partially accruing data for use in decision making]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Visualizing the quality of partially accruing data for use in decision making|Visualizing the quality of partially accruing data for use in decision making]] | ||
Revision as of 15:05, 8 August 2016
This study seeks to develop, test and assess a methodology for automatic extraction of a complete set of ‘term-like phrases’ and to create a terminology spectrum from a collection of natural language PDF documents in the field of chemistry. The definition of ‘term-like phrases’ is one or more consecutive words and/or alphanumeric string combinations with unchanged spelling which convey specific scientific meanings. A terminology spectrum for a natural language document is an indexed list of tagged entities including: recognized general scientific concepts, terms linked to existing thesauri, names of chemical substances/reactions and term-like phrases. The retrieval routine is based on n-gram textual analysis with a sequential execution of various ‘accept and reject’ rules with taking into account the morphological and structural information.
The assessment of the retrieval process, expressed quantitatively with a precision (P), recall (R) and F1-measure, which are calculated manually from a limited set of documents (the full set of text abstracts belonging to five EuropaCat events were processed) by professional chemical scientists, has proved the effectiveness of the developed approach. (Full article...)
Recently featured: