Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Hussain AppliedCompInfo2016.jpg|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Multilevel classification of security concerns in cloud computing|Multilevel classification of security concerns in cloud computing]]"''' | ||
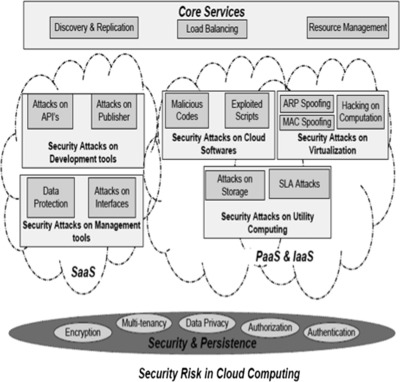
Threats jeopardize some basic security requirements in a cloud. These threats generally constitute privacy breach, data leakage and unauthorized data access at different cloud layers. This paper presents a novel multilevel classification model of different security attacks across different cloud services at each layer. It also identifies attack types and risk levels associated with different cloud services at these layers. The risks are ranked as low, medium and high. The intensity of these risk levels depends upon the position of cloud layers. The attacks get more severe for lower layers where infrastructure and platform are involved. The intensity of these risk levels is also associated with security requirements of data encryption, multi-tenancy, data privacy, authentication and authorization for different cloud services. The multilevel classification model leads to the provision of dynamic security contract for each cloud layer that dynamically decides about security requirements for cloud consumer and provider. ('''[[Journal:Multilevel classification of security concerns in cloud computing|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
The | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Assessment of and response to data needs of clinical and translational science researchers and beyond|Assessment of and response to data needs of clinical and translational science researchers and beyond]] | |||
: ▪ [[Journal:SUSHI: An exquisite recipe for fully documented, reproducible and reusable NGS data analysis|SUSHI: An exquisite recipe for fully documented, reproducible and reusable NGS data analysis]] | : ▪ [[Journal:SUSHI: An exquisite recipe for fully documented, reproducible and reusable NGS data analysis|SUSHI: An exquisite recipe for fully documented, reproducible and reusable NGS data analysis]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Open source data logger for low-cost environmental monitoring|Open source data logger for low-cost environmental monitoring]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Open source data logger for low-cost environmental monitoring|Open source data logger for low-cost environmental monitoring]] | ||
Revision as of 17:07, 19 September 2016
"Multilevel classification of security concerns in cloud computing"
Threats jeopardize some basic security requirements in a cloud. These threats generally constitute privacy breach, data leakage and unauthorized data access at different cloud layers. This paper presents a novel multilevel classification model of different security attacks across different cloud services at each layer. It also identifies attack types and risk levels associated with different cloud services at these layers. The risks are ranked as low, medium and high. The intensity of these risk levels depends upon the position of cloud layers. The attacks get more severe for lower layers where infrastructure and platform are involved. The intensity of these risk levels is also associated with security requirements of data encryption, multi-tenancy, data privacy, authentication and authorization for different cloud services. The multilevel classification model leads to the provision of dynamic security contract for each cloud layer that dynamically decides about security requirements for cloud consumer and provider. (Full article...)
Recently featured: