Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Boland PLOSCompBio2017 13-1.png|240px]]</div> | |||
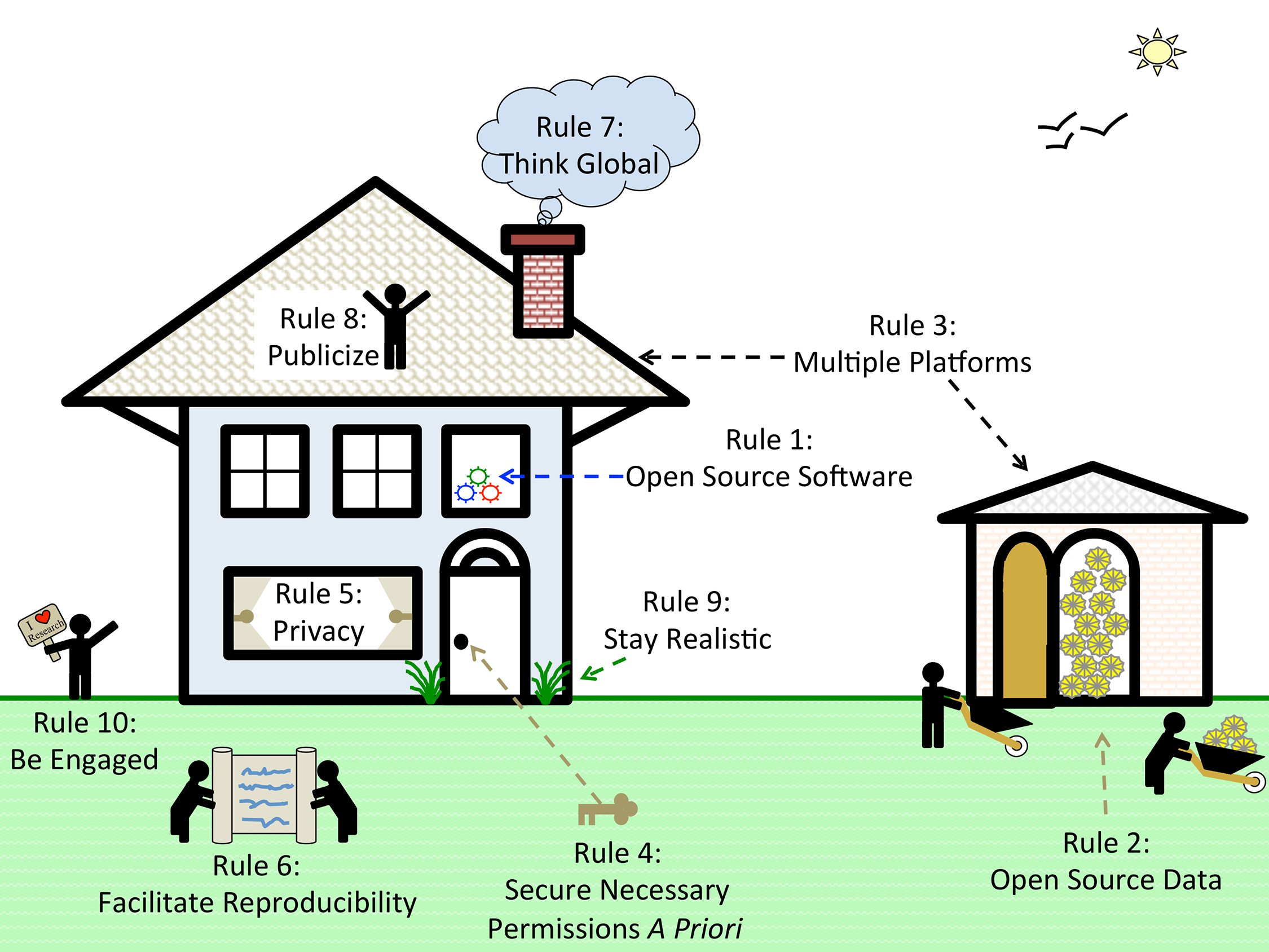
'''"[[Journal:Ten simple rules to enable multi-site collaborations through data sharing|Ten simple rules to enable multi-site collaborations through data sharing]]"''' | |||
Open access, open data, and software are critical for advancing science and enabling collaboration across multiple institutions and throughout the world. Despite near universal recognition of its importance, major barriers still exist to sharing raw data, software, and research products throughout the scientific community. Many of these barriers vary by specialty, increasing the difficulties for interdisciplinary and/or translational researchers to engage in collaborative research. Multi-site collaborations are vital for increasing both the impact and the generalizability of research results. However, they often present unique data sharing challenges. We discuss enabling multi-site collaborations through enhanced data sharing in this set of ''Ten Simple Rules''. ('''[[Journal:Ten simple rules to enable multi-site collaborations through data sharing|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Ten simple rules for developing usable software in computational biology|Ten simple rules for developing usable software in computational biology]] | |||
: ▪ [[Journal:The effect of the General Data Protection Regulation on medical research|The effect of the General Data Protection Regulation on medical research]] | : ▪ [[Journal:The effect of the General Data Protection Regulation on medical research|The effect of the General Data Protection Regulation on medical research]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Methods for specifying scientific data standards and modeling relationships with applications to neuroscience|Methods for specifying scientific data standards and modeling relationships with applications to neuroscience]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Methods for specifying scientific data standards and modeling relationships with applications to neuroscience|Methods for specifying scientific data standards and modeling relationships with applications to neuroscience]] | ||
Revision as of 16:14, 8 May 2017
"Ten simple rules to enable multi-site collaborations through data sharing"
Open access, open data, and software are critical for advancing science and enabling collaboration across multiple institutions and throughout the world. Despite near universal recognition of its importance, major barriers still exist to sharing raw data, software, and research products throughout the scientific community. Many of these barriers vary by specialty, increasing the difficulties for interdisciplinary and/or translational researchers to engage in collaborative research. Multi-site collaborations are vital for increasing both the impact and the generalizability of research results. However, they often present unique data sharing challenges. We discuss enabling multi-site collaborations through enhanced data sharing in this set of Ten Simple Rules. (Full article...)
Recently featured: