Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig2 Buabbas JMIRMedInfo2016 4-2.png|240px]]</div> | ||
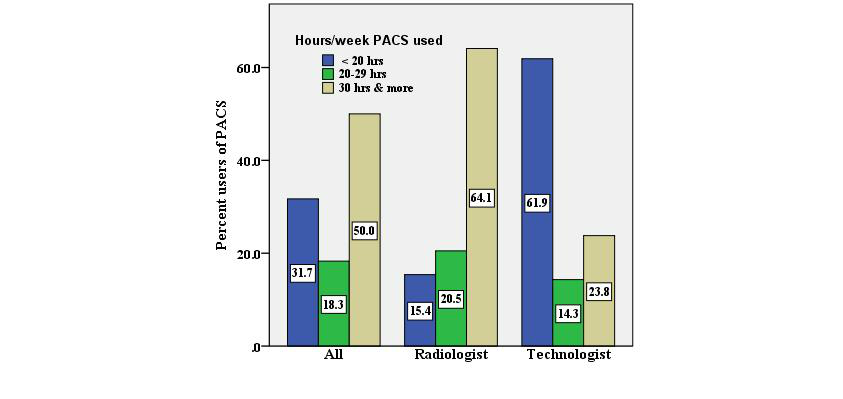
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Users’ perspectives on a picture archiving and communication system (PACS): An in-depth study in a teaching hospital in Kuwait|Users’ perspectives on a picture archiving and communication system (PACS): An in-depth study in a teaching hospital in Kuwait]]"''' | ||
The [[picture archiving and communication system]] (PACS) is a well-known [[imaging informatics]] application in health care organizations, specifically designed for the radiology department. Health care providers have exhibited willingness toward evaluating PACS in hospitals to ascertain the critical success and failure of the technology, considering that evaluation is a basic requirement. | |||
This study aimed to evaluate the success of a PACS in a regional teaching hospital of Kuwait, from users’ perspectives, using information systems success criteria. | |||
An in-depth study was conducted by using quantitative and qualitative methods. This mixed-method study was based on: (1) questionnaires, distributed to all radiologists and technologists and (2) interviews, conducted with PACS administrators. ('''[[Journal:Users’ perspectives on a picture archiving and communication system (PACS): An in-depth study in a teaching hospital in Kuwait|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Effective information extraction framework for heterogeneous clinical reports using online machine learning and controlled vocabularies|Effective information extraction framework for heterogeneous clinical reports using online machine learning and controlled vocabularies]] | |||
: ▪ [[Journal:Selecting a laboratory information management system for biorepositories in low- and middle-income countries: The H3Africa experience and lessons learned|Selecting a laboratory information management system for biorepositories in low- and middle-income countries: The H3Africa experience and lessons learned]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Selecting a laboratory information management system for biorepositories in low- and middle-income countries: The H3Africa experience and lessons learned|Selecting a laboratory information management system for biorepositories in low- and middle-income countries: The H3Africa experience and lessons learned]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Baobab Laboratory Information Management System: Development of an open-source laboratory information management system for biobanking|Baobab Laboratory Information Management System: Development of an open-source laboratory information management system for biobanking]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Baobab Laboratory Information Management System: Development of an open-source laboratory information management system for biobanking|Baobab Laboratory Information Management System: Development of an open-source laboratory information management system for biobanking]] | ||
Revision as of 14:19, 26 July 2017
The picture archiving and communication system (PACS) is a well-known imaging informatics application in health care organizations, specifically designed for the radiology department. Health care providers have exhibited willingness toward evaluating PACS in hospitals to ascertain the critical success and failure of the technology, considering that evaluation is a basic requirement.
This study aimed to evaluate the success of a PACS in a regional teaching hospital of Kuwait, from users’ perspectives, using information systems success criteria.
An in-depth study was conducted by using quantitative and qualitative methods. This mixed-method study was based on: (1) questionnaires, distributed to all radiologists and technologists and (2) interviews, conducted with PACS administrators. (Full article...)
Recently featured:
- ▪ Effective information extraction framework for heterogeneous clinical reports using online machine learning and controlled vocabularies
- ▪ Selecting a laboratory information management system for biorepositories in low- and middle-income countries: The H3Africa experience and lessons learned
- ▪ Baobab Laboratory Information Management System: Development of an open-source laboratory information management system for biobanking