Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
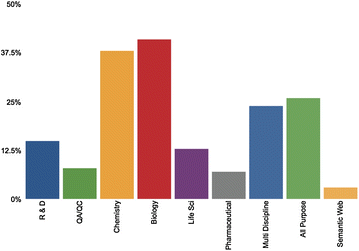
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Kanza JofCheminformatics2017 9.gif|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Electronic lab notebooks: Can they replace paper?|Electronic lab notebooks: Can they replace paper?]]"''' | ||
Despite the increasingly digital nature of society, there are some areas of research that remain firmly rooted in the past; in this case the [[laboratory notebook]], the last remaining paper component of an experiment. Countless [[electronic laboratory notebook]]s (ELNs) have been created in an attempt to digitize record keeping processes in the lab, but none of them have become a "key player" in the ELN market, due to the many adoption barriers that have been identified in previous research and further explored in the user studies presented here. The main issues identified are the cost of the current available ELNs, their ease of use (or lack of it), and their accessibility issues across different devices and operating systems. Evidence suggests that whilst scientists willingly make use of generic notebooking software, spreadsheets, and other general office and scientific tools to aid their work, current ELNs are lacking in the required functionality to meet the needs of researchers. In this paper we present our extensive research and user study results, proposing an ELN built upon a pre-existing cloud notebook platform that makes use of accessible popular scientific software and semantic web technologies to help overcome the identified barriers to adoption. ('''[[Journal:Electronic lab notebooks: Can they replace paper?|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Earth science data analytics: Definitions, techniques and skills|Earth science data analytics: Definitions, techniques and skills]] | |||
: ▪ [[Journal:Bioinformatics: Indispensable, yet hidden in plain sight|Bioinformatics: Indispensable, yet hidden in plain sight]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Bioinformatics: Indispensable, yet hidden in plain sight|Bioinformatics: Indispensable, yet hidden in plain sight]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Global data quality assessment and the situated nature of “best” research practices in biology|Global data quality assessment and the situated nature of “best” research practices in biology]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Global data quality assessment and the situated nature of “best” research practices in biology|Global data quality assessment and the situated nature of “best” research practices in biology]] | ||
Revision as of 18:59, 11 September 2017
"Electronic lab notebooks: Can they replace paper?"
Despite the increasingly digital nature of society, there are some areas of research that remain firmly rooted in the past; in this case the laboratory notebook, the last remaining paper component of an experiment. Countless electronic laboratory notebooks (ELNs) have been created in an attempt to digitize record keeping processes in the lab, but none of them have become a "key player" in the ELN market, due to the many adoption barriers that have been identified in previous research and further explored in the user studies presented here. The main issues identified are the cost of the current available ELNs, their ease of use (or lack of it), and their accessibility issues across different devices and operating systems. Evidence suggests that whilst scientists willingly make use of generic notebooking software, spreadsheets, and other general office and scientific tools to aid their work, current ELNs are lacking in the required functionality to meet the needs of researchers. In this paper we present our extensive research and user study results, proposing an ELN built upon a pre-existing cloud notebook platform that makes use of accessible popular scientific software and semantic web technologies to help overcome the identified barriers to adoption. (Full article...)
Recently featured: