Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Dufresnes PLOSONE2018 12-1.png|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Broad-scale genetic diversity of Cannabis for forensic applications|Broad-scale genetic diversity of Cannabis for forensic applications]]"''' | ||
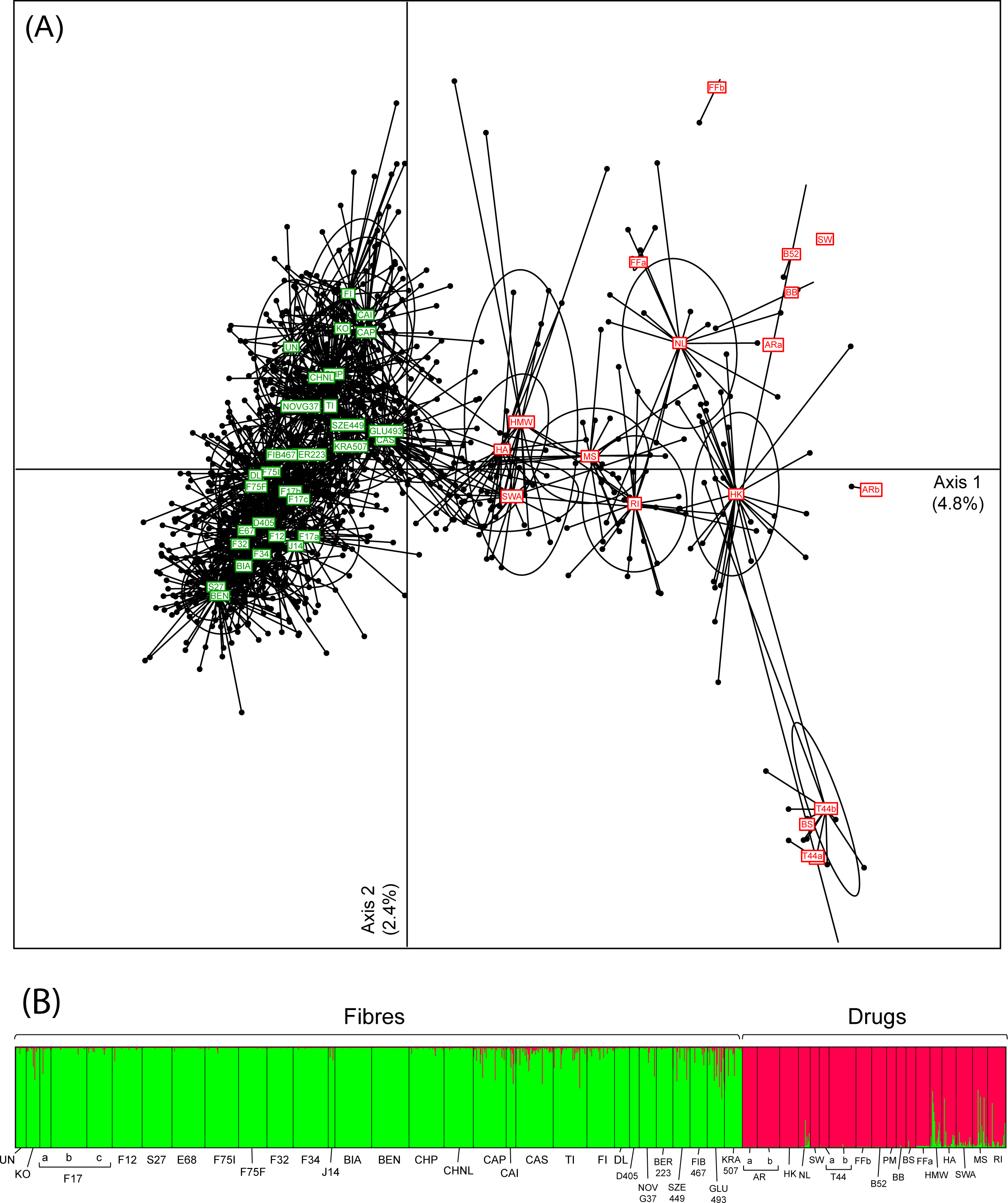
''Cannabis'' (hemp and marijuana) is an iconic yet controversial crop. On the one hand, it represents a growing market for pharmaceutical and agricultural sectors. On the other hand, plants synthesizing the psychoactive THC produce the most widespread illicit drug in the world. Yet, the difficulty to reliably distinguish between ''Cannabis'' varieties based on morphological or biochemical criteria impedes the development of promising industrial programs and hinders the fight against narcotrafficking. Genetics offers an appropriate alternative to characterize drug vs. non-drug ''Cannabis''. However, forensic applications require rapid and affordable genotyping of informative and reliable molecular markers for which a broad-scale reference database, representing both intra- and inter-variety variation, is available. Here we provide such a resource for ''Cannabis'', by genotyping 13 microsatellite loci (STRs) in 1,324 samples selected specifically for fiber (24 hemp varieties) and drug (15 marijuana varieties) production. We showed that these loci are sufficient to capture most of the genome-wide diversity patterns recently revealed by [[DNA sequencing#High-throughput methods|next-generation sequencing]] (NGS) data. ('''[[Journal:Broad-scale genetic diversity of Cannabis for forensic applications|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Arkheia: Data management and communication for open computational neuroscience|Arkheia: Data management and communication for open computational neuroscience]] | |||
: ▪ [[Journal:Developing a bioinformatics program and supporting infrastructure in a biomedical library|Developing a bioinformatics program and supporting infrastructure in a biomedical library]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Developing a bioinformatics program and supporting infrastructure in a biomedical library|Developing a bioinformatics program and supporting infrastructure in a biomedical library]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Big data and public health systems: Issues and opportunities|Big data and public health systems: Issues and opportunities]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Big data and public health systems: Issues and opportunities|Big data and public health systems: Issues and opportunities]] | ||
Revision as of 15:06, 29 May 2018
"Broad-scale genetic diversity of Cannabis for forensic applications"
Cannabis (hemp and marijuana) is an iconic yet controversial crop. On the one hand, it represents a growing market for pharmaceutical and agricultural sectors. On the other hand, plants synthesizing the psychoactive THC produce the most widespread illicit drug in the world. Yet, the difficulty to reliably distinguish between Cannabis varieties based on morphological or biochemical criteria impedes the development of promising industrial programs and hinders the fight against narcotrafficking. Genetics offers an appropriate alternative to characterize drug vs. non-drug Cannabis. However, forensic applications require rapid and affordable genotyping of informative and reliable molecular markers for which a broad-scale reference database, representing both intra- and inter-variety variation, is available. Here we provide such a resource for Cannabis, by genotyping 13 microsatellite loci (STRs) in 1,324 samples selected specifically for fiber (24 hemp varieties) and drug (15 marijuana varieties) production. We showed that these loci are sufficient to capture most of the genome-wide diversity patterns recently revealed by next-generation sequencing (NGS) data. (Full article...)
Recently featured: