Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Zakutayev SciData2018 5.jpg|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:An open experimental database for exploring inorganic materials|An open experimental database for exploring inorganic materials]]"''' | ||
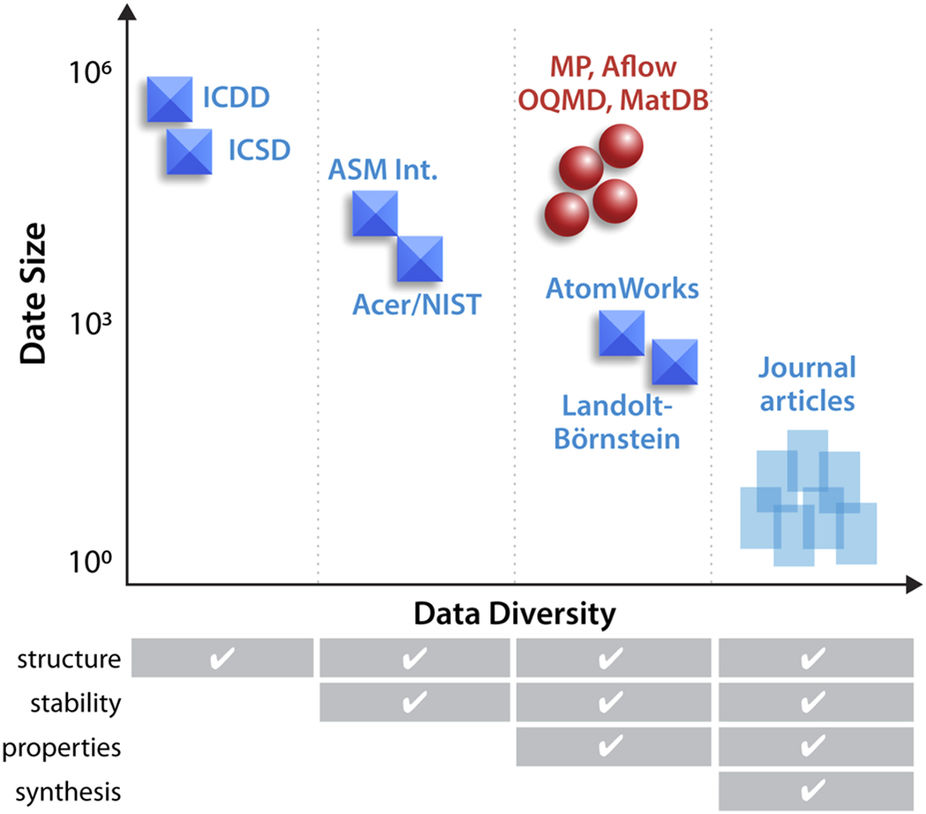
The use of advanced machine learning algorithms in experimental [[Materials informatics|materials science]] is limited by the lack of sufficiently large and diverse datasets amenable to data mining. If publicly open, such data resources would also enable materials research by scientists without access to expensive experimental equipment. Here, we report on our progress towards a publicly open High Throughput Experimental Materials (HTEM) Database (htem.nrel.gov). This database currently contains 140,000 sample entries, characterized by structural (100,000), synthetic (80,000), chemical (70,000), and optoelectronic (50,000) properties of inorganic thin film materials, grouped in >4,000 sample entries across >100 materials systems; more than a half of these data are publicly available. This article shows how the HTEM database may enable scientists to explore materials by browsing web-based user interface and an application programming interface. This paper also describes a HTE approach to generating materials data and discusses the [[laboratory information management system]] (LIMS) that underpins the HTEM database. Finally, this manuscript illustrates how advanced machine learning algorithms can be adopted to materials science problems using this open data resource. ('''[[Journal:An open experimental database for exploring inorganic materials|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Broad-scale genetic diversity of Cannabis for forensic applications|Broad-scale genetic diversity of Cannabis for forensic applications]] | |||
: ▪ [[Journal:Arkheia: Data management and communication for open computational neuroscience|Arkheia: Data management and communication for open computational neuroscience]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Arkheia: Data management and communication for open computational neuroscience|Arkheia: Data management and communication for open computational neuroscience]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Developing a bioinformatics program and supporting infrastructure in a biomedical library|Developing a bioinformatics program and supporting infrastructure in a biomedical library]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Developing a bioinformatics program and supporting infrastructure in a biomedical library|Developing a bioinformatics program and supporting infrastructure in a biomedical library]] | ||
Revision as of 17:46, 6 June 2018
"An open experimental database for exploring inorganic materials"
The use of advanced machine learning algorithms in experimental materials science is limited by the lack of sufficiently large and diverse datasets amenable to data mining. If publicly open, such data resources would also enable materials research by scientists without access to expensive experimental equipment. Here, we report on our progress towards a publicly open High Throughput Experimental Materials (HTEM) Database (htem.nrel.gov). This database currently contains 140,000 sample entries, characterized by structural (100,000), synthetic (80,000), chemical (70,000), and optoelectronic (50,000) properties of inorganic thin film materials, grouped in >4,000 sample entries across >100 materials systems; more than a half of these data are publicly available. This article shows how the HTEM database may enable scientists to explore materials by browsing web-based user interface and an application programming interface. This paper also describes a HTE approach to generating materials data and discusses the laboratory information management system (LIMS) that underpins the HTEM database. Finally, this manuscript illustrates how advanced machine learning algorithms can be adopted to materials science problems using this open data resource. (Full article...)
Recently featured: