Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig3 CaoProcess2018 6-5.png|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:A systematic framework for data management and integration in a continuous pharmaceutical manufacturing processing line|A systematic framework for data management and integration in a continuous pharmaceutical manufacturing processing line]]"''' | ||
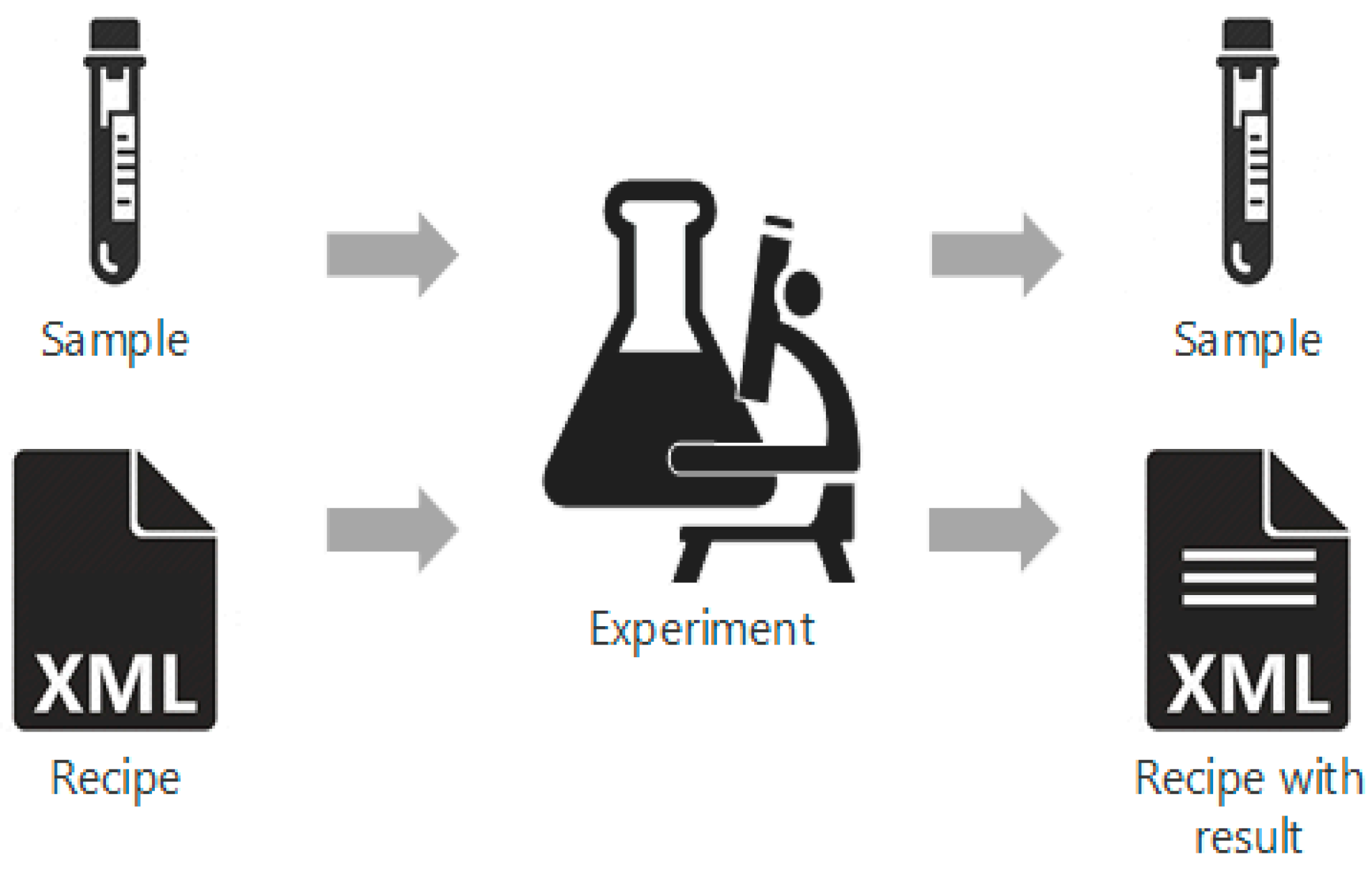
As the pharmaceutical industry seeks more efficient methods for the production of higher value therapeutics, the associated [[data analysis]], [[data visualization]], and predictive modeling require dependable data origination, management, transfer, and integration. As a result, the management and integration of data in a consistent, organized, and reliable manner is a big challenge for the pharmaceutical industry. In this work, an ontological [[information]] infrastructure is developed to integrate data within manufacturing plants and analytical [[Laboratory|laboratories]]. The ANSI/ISA-88 batch control standard has been adapted in this study to deliver a well-defined data structure that will improve the data communication inside the system architecture for continuous processing. All the detailed information of the lab-based experiment and process manufacturing—including equipment, samples, and parameters—are documented in the recipe. This recipe model is implemented into a process control system (PCS), data historian, and [[electronic laboratory notebook]] (ELN). ('''[[Journal:A systematic framework for data management and integration in a continuous pharmaceutical manufacturing processing line|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Unmet needs for analyzing biological big data: A survey of 704 NSF principal investigators|Unmet needs for analyzing biological big data: A survey of 704 NSF principal investigators]] | |||
: ▪ [[Journal:Big data as a driver for clinical decision support systems: A learning health systems perspective|Big data as a driver for clinical decision support systems: A learning health systems perspective]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Big data as a driver for clinical decision support systems: A learning health systems perspective|Big data as a driver for clinical decision support systems: A learning health systems perspective]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Implementation and use of cloud-based electronic lab notebook in a bioprocess engineering teaching laboratory|Implementation and use of cloud-based electronic lab notebook in a bioprocess engineering teaching laboratory | : ▪ [[Journal:Implementation and use of cloud-based electronic lab notebook in a bioprocess engineering teaching laboratory|Implementation and use of cloud-based electronic lab notebook in a bioprocess engineering teaching laboratory]] | ||
Revision as of 14:08, 2 July 2018
As the pharmaceutical industry seeks more efficient methods for the production of higher value therapeutics, the associated data analysis, data visualization, and predictive modeling require dependable data origination, management, transfer, and integration. As a result, the management and integration of data in a consistent, organized, and reliable manner is a big challenge for the pharmaceutical industry. In this work, an ontological information infrastructure is developed to integrate data within manufacturing plants and analytical laboratories. The ANSI/ISA-88 batch control standard has been adapted in this study to deliver a well-defined data structure that will improve the data communication inside the system architecture for continuous processing. All the detailed information of the lab-based experiment and process manufacturing—including equipment, samples, and parameters—are documented in the recipe. This recipe model is implemented into a process control system (PCS), data historian, and electronic laboratory notebook (ELN). (Full article...)
Recently featured:
- ▪ Unmet needs for analyzing biological big data: A survey of 704 NSF principal investigators
- ▪ Big data as a driver for clinical decision support systems: A learning health systems perspective
- ▪ Implementation and use of cloud-based electronic lab notebook in a bioprocess engineering teaching laboratory