Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Talia JOfCloudComp2019 8.png|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:A view of programming scalable data analysis: From clouds to exascale|A view of programming scalable data analysis: From clouds to exascale]]"''' | ||
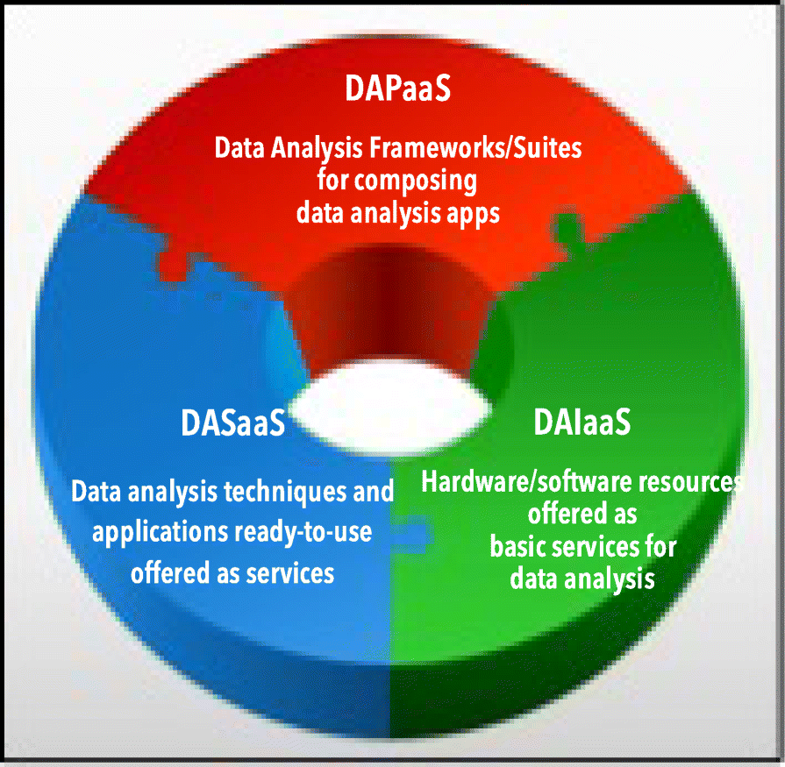
Scalability is a key feature for big data analysis and machine learning frameworks and for applications that need to analyze very large and real-time data available from data repositories, social media, sensor networks, smartphones, and the internet. Scalable big data analysis today can be achieved by parallel implementations that are able to exploit the computing and storage facilities of high-performance computing (HPC) systems and [[cloud computing]] systems, whereas in the near future exascale systems will be used to implement extreme-scale [[data analysis]]. Here is discussed how cloud computing currently supports the development of scalable data mining solutions and what the main challenges to be addressed and solved for implementing innovative data analysis applications on exascale systems currently are. ('''[[Journal:A view of programming scalable data analysis: From clouds to exascale|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Transferring exome sequencing data from clinical laboratories to healthcare providers: Lessons learned at a pediatric hospital|Transferring exome sequencing data from clinical laboratories to healthcare providers: Lessons learned at a pediatric hospital]] | |||
: ▪ [[Journal:Research on information retrieval model based on ontology|Research on information retrieval model based on ontology]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Research on information retrieval model based on ontology|Research on information retrieval model based on ontology]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Data to diagnosis in global health: A 3P approach|Data to diagnosis in global health: A 3P approach]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Data to diagnosis in global health: A 3P approach|Data to diagnosis in global health: A 3P approach]] | ||
Revision as of 15:13, 8 April 2019
"A view of programming scalable data analysis: From clouds to exascale"
Scalability is a key feature for big data analysis and machine learning frameworks and for applications that need to analyze very large and real-time data available from data repositories, social media, sensor networks, smartphones, and the internet. Scalable big data analysis today can be achieved by parallel implementations that are able to exploit the computing and storage facilities of high-performance computing (HPC) systems and cloud computing systems, whereas in the near future exascale systems will be used to implement extreme-scale data analysis. Here is discussed how cloud computing currently supports the development of scalable data mining solutions and what the main challenges to be addressed and solved for implementing innovative data analysis applications on exascale systems currently are. (Full article...)
Recently featured: