Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| (23 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Duncan FrontBioengBiotech2019 7.jpg|240px]]</div> | ||
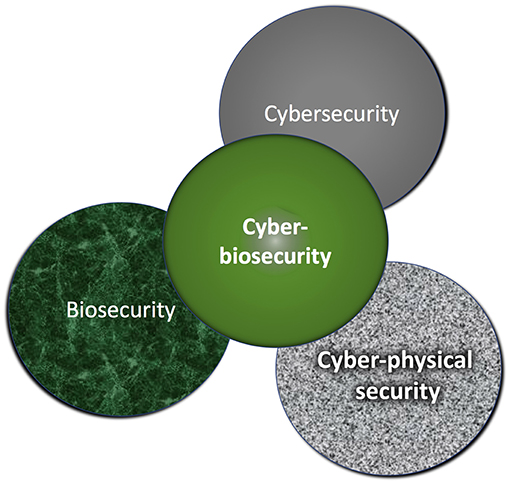
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Cyberbiosecurity: A new perspective on protecting U.S. food and agricultural system|Cyberbiosecurity: A new perspective on protecting U.S. food and agricultural system]]"''' | ||
Our national data and infrastructure security issues affecting the “bioeconomy” are evolving rapidly. Simultaneously, the conversation about cybersecurity of the U.S. [[Agriculture industry|food and agricultural system]] (cyber biosecurity) is incomplete and disjointed. The food and agricultural production sectors influence over 20% of the nation's economy ($6.7T) and 15% of U.S. employment (43.3M jobs). The food and agricultural sectors are immensely diverse, and they require advanced technologies and efficiencies that rely on computer technologies, big data, [[Cloud computing|cloud-based]] data storage, and internet accessibility. There is a critical need to safeguard the cyber biosecurity of our bioeconomy, but currently protections are minimal and do not broadly exist across the food and agricultural system. Using the food safety management Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) system concept as an introductory point of reference, we identify important features in broad food and agricultural production and food systems: dairy, food animals, row crops, fruits and vegetables, and environmental resources (water). ('''[[Journal:Cyberbiosecurity: A new perspective on protecting U.S. food and agricultural system|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal: | : ▪ [[Journal:DAQUA-MASS: An ISO 8000-61-based data quality management methodology for sensor data|DAQUA-MASS: An ISO 8000-61-based data quality management methodology for sensor data]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal: | : ▪ [[Journal:Security architecture and protocol for trust verifications regarding the integrity of files stored in cloud services|Security architecture and protocol for trust verifications regarding the integrity of files stored in cloud services]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal: | : ▪ [[Journal:What Is health information quality? Ethical dimension and perception by users|What Is health information quality? Ethical dimension and perception by users]] | ||
Revision as of 16:29, 20 May 2019
"Cyberbiosecurity: A new perspective on protecting U.S. food and agricultural system"
Our national data and infrastructure security issues affecting the “bioeconomy” are evolving rapidly. Simultaneously, the conversation about cybersecurity of the U.S. food and agricultural system (cyber biosecurity) is incomplete and disjointed. The food and agricultural production sectors influence over 20% of the nation's economy ($6.7T) and 15% of U.S. employment (43.3M jobs). The food and agricultural sectors are immensely diverse, and they require advanced technologies and efficiencies that rely on computer technologies, big data, cloud-based data storage, and internet accessibility. There is a critical need to safeguard the cyber biosecurity of our bioeconomy, but currently protections are minimal and do not broadly exist across the food and agricultural system. Using the food safety management Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) system concept as an introductory point of reference, we identify important features in broad food and agricultural production and food systems: dairy, food animals, row crops, fruits and vegetables, and environmental resources (water). (Full article...)
Recently featured: