Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig0 Cardenia JofFoodDrugAnal2018 26-4.jpg|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Development and validation of a fast gas chromatography–mass spectrometry method for the determination of cannabinoids in Cannabis sativa L|Development and validation of a fast gas chromatography–mass spectrometry method for the determination of cannabinoids in Cannabis sativa L]]"''' | ||
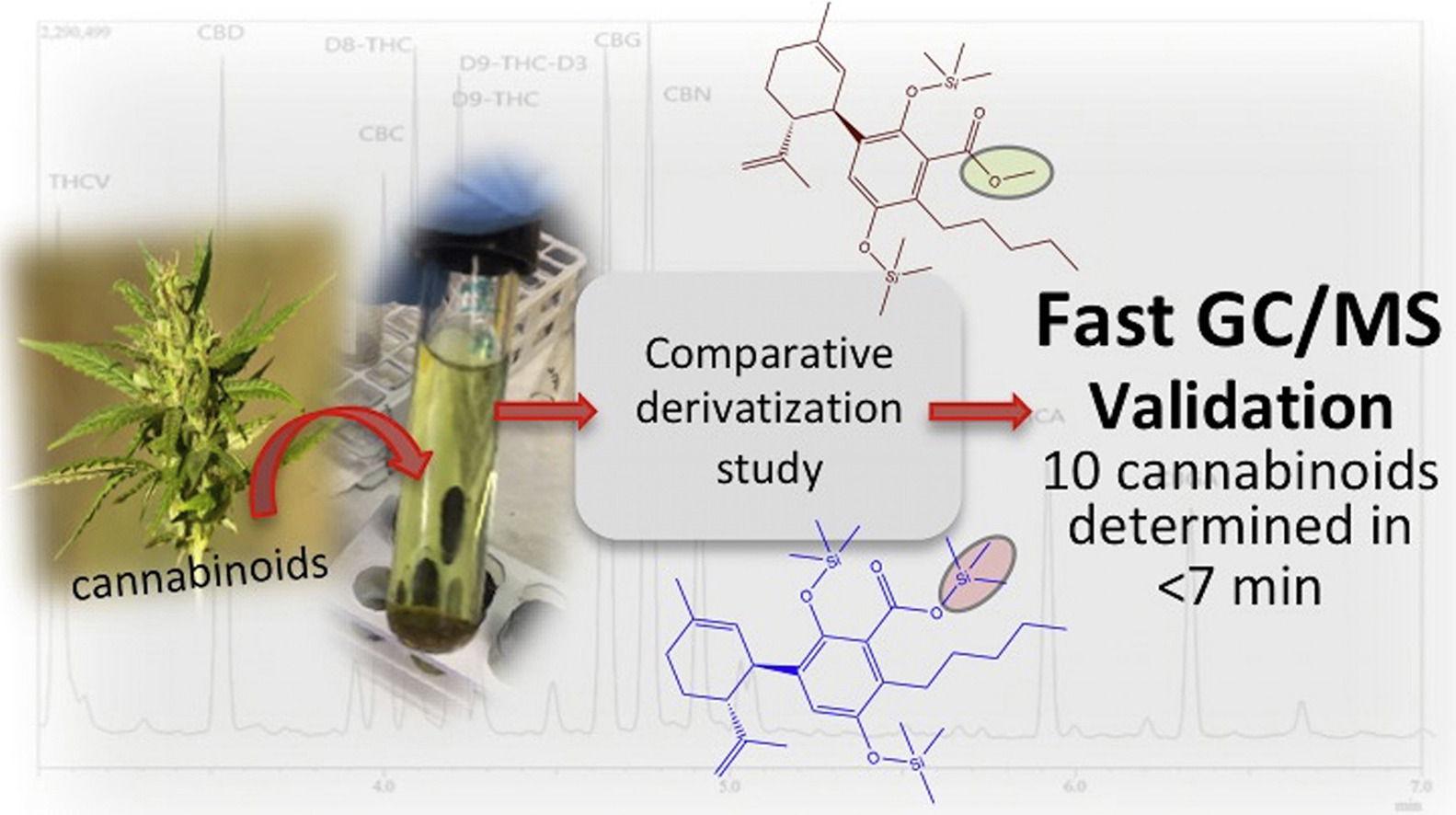
A routine method for determining [[wikipedia:Cannabinoid|cannabinoids]] in ''Cannabis sativa'' L. [[wikipedia:Inflorescence|inflorescence]], based on fast [[gas chromatography]] coupled to [[mass spectrometry]] (fast GC-MS), was developed and validated. To avoid the [[wikipedia:Decarboxylation|decarboxylation]] of the carboxyl group of cannabinoids, different derivatization approaches—i.e., silylation and esterification (diazomethane-mediated) reagents and solvents (pyridine or ethyl acetate)—were tested. The methylation significantly increased the signal-to-noise ratio of all carboxylic cannabinoids, except for cannabigerolic acid (CBGA). Since [[wikipedia:Diazomethane|diazomethane]] is not commercially available, is considered a hazardous reactive, and requires one-day synthesis by specialized chemical staff, the process of silylation was used along the entire validation of a routine method. The method gave a fast (total analysis time < 7.0 min) and satisfactory resolution (R > 1.1), with a good repeatability (intraday < 8.38%; interday < 11.10%) and sensitivity (LOD < 11.20 ng/mL). ('''[[Journal:Development and validation of a fast gas chromatography–mass spectrometry method for the determination of cannabinoids in Cannabis sativa L|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal: | : ▪ [[Journal:Design and refinement of a data quality assessment workflow for a large pediatric research network|Design and refinement of a data quality assessment workflow for a large pediatric research network]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal: | : ▪ [[Journal:Identification of Cannabis sativa L. (hemp) retailers by means of multivariate analysis of cannabinoids|Identification of Cannabis sativa L. (hemp) retailers by means of multivariate analysis of cannabinoids]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal: | : ▪ [[Journal:Data sharing at scale: A heuristic for affirming data cultures|Data sharing at scale: A heuristic for affirming data cultures]] | ||
Revision as of 17:13, 9 December 2019
A routine method for determining cannabinoids in Cannabis sativa L. inflorescence, based on fast gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (fast GC-MS), was developed and validated. To avoid the decarboxylation of the carboxyl group of cannabinoids, different derivatization approaches—i.e., silylation and esterification (diazomethane-mediated) reagents and solvents (pyridine or ethyl acetate)—were tested. The methylation significantly increased the signal-to-noise ratio of all carboxylic cannabinoids, except for cannabigerolic acid (CBGA). Since diazomethane is not commercially available, is considered a hazardous reactive, and requires one-day synthesis by specialized chemical staff, the process of silylation was used along the entire validation of a routine method. The method gave a fast (total analysis time < 7.0 min) and satisfactory resolution (R > 1.1), with a good repeatability (intraday < 8.38%; interday < 11.10%) and sensitivity (LOD < 11.20 ng/mL). (Full article...)
Recently featured: