Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Wang BMCBioinfo2019 20.png|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:CytoConverter: A web-based tool to convert karyotypes to genomic coordinates|CytoConverter: A web-based tool to convert karyotypes to genomic coordinates]]"''' | ||
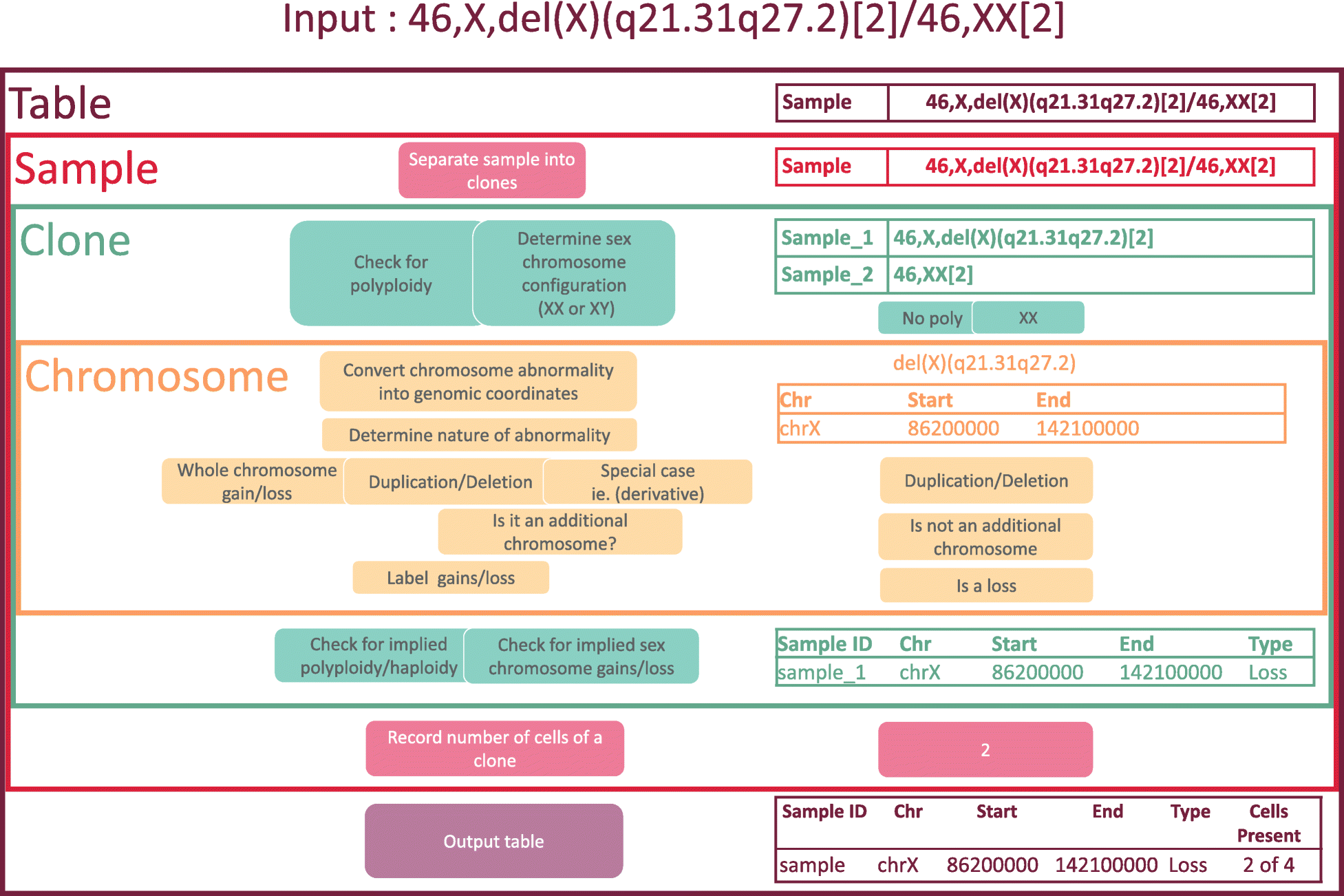
[[wikipedia:Cytogenetics|Cytogenetic]] nomenclature is used to describe chromosomal aberrations (or lack thereof) in a collection of cells, referred to as the cells’ [[wikipedia:Karyotype|karyotype]]. The nomenclature identifies locations on chromosomes using a system of cytogenetic bands, each with a unique name and region on a chromosome. Each band is microscopically visible after staining, and it encompasses a large portion of the chromosome. More modern analyses employ [[Genomics|genomic]] coordinates, which precisely specify a chromosomal location according to its distance from the end of the chromosome. Currently, there is no tool to convert cytogenetic nomenclature into genomic coordinates. Since locations of genes and other genomic features are usually specified by genomic coordinates, a conversion tool will facilitate the identification of the features that are harbored in the regions of chromosomal gain and loss that are implied by a karyotype. ('''[[Journal:CytoConverter: A web-based tool to convert karyotypes to genomic coordinates|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Implementing a novel quality improvement-based approach to data quality monitoring and enhancement in a multipurpose clinical registry|Implementing a novel quality improvement-based approach to data quality monitoring and enhancement in a multipurpose clinical registry]] | |||
: ▪ [[Journal:Fast detection of 10 cannabinoids by RP-HPLC-UV method in Cannabis sativa L.|Fast detection of 10 cannabinoids by RP-HPLC-UV method in Cannabis sativa L.]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Fast detection of 10 cannabinoids by RP-HPLC-UV method in Cannabis sativa L.|Fast detection of 10 cannabinoids by RP-HPLC-UV method in Cannabis sativa L.]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:What is this sensor and does this app need access to it?|What is this sensor and does this app need access to it?]] | : ▪ [[Journal:What is this sensor and does this app need access to it?|What is this sensor and does this app need access to it?]] | ||
Revision as of 16:22, 3 February 2020
"CytoConverter: A web-based tool to convert karyotypes to genomic coordinates"
Cytogenetic nomenclature is used to describe chromosomal aberrations (or lack thereof) in a collection of cells, referred to as the cells’ karyotype. The nomenclature identifies locations on chromosomes using a system of cytogenetic bands, each with a unique name and region on a chromosome. Each band is microscopically visible after staining, and it encompasses a large portion of the chromosome. More modern analyses employ genomic coordinates, which precisely specify a chromosomal location according to its distance from the end of the chromosome. Currently, there is no tool to convert cytogenetic nomenclature into genomic coordinates. Since locations of genes and other genomic features are usually specified by genomic coordinates, a conversion tool will facilitate the identification of the features that are harbored in the regions of chromosomal gain and loss that are implied by a karyotype. (Full article...)
Recently featured: