Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Anx1 WHO 2020 2020.5.png|240px]]</div> | ||
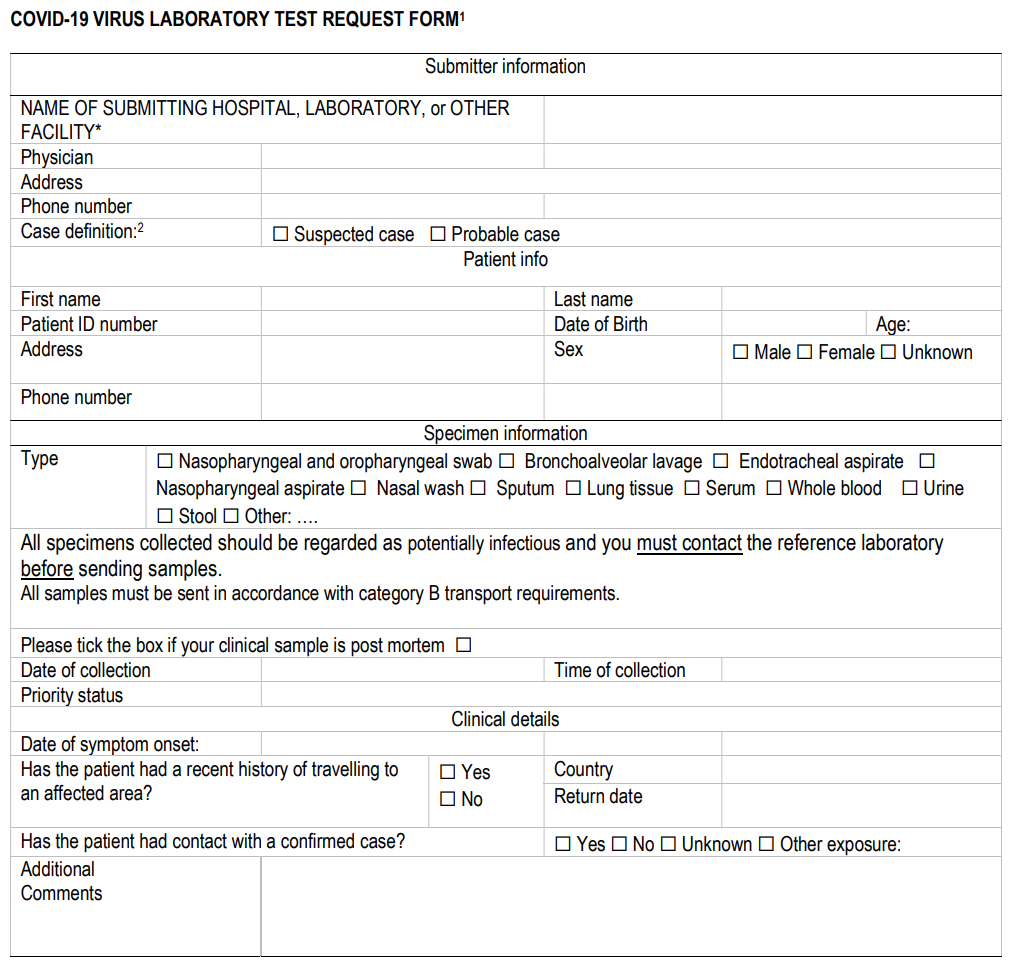
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Laboratory testing for coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in suspected human cases|Laboratory testing for coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in suspected human cases]]"''' | ||
This document provides interim guidance to [[Laboratory|laboratories]] and stakeholders involved in [[COVID-19]] virus laboratory testing of patients. It is based in part on the interim guidance on laboratory testing for [[Middle East respiratory syndrome]] (MERS) coronavirus. [[Information]] on human [[infection]] with the COVID-19 virus is evolving and the [[World Health Organization]] (WHO) continues to monitor developments and revise recommendations as necessary. This document will be revised as new information becomes available. Feedback is welcome and can be sent to WHElab@who.int. The virus has now been named SARS-CoV-2 by the International Committee of Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV)(2). This virus can cause the disease named coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). WHO refers to the virus as COVID-19 virus in its current documentation. ('''[[Journal:A security review of local government using NIST CSF: A case study|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal: | : ▪ [[Journal:One tool to find them all: A case of data integration and querying in a distributed LIMS platform|One tool to find them all: A case of data integration and querying in a distributed LIMS platform]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal: | : ▪ [[Journal:What is the "source" of open-source hardware?|What is the "source" of open-source hardware?]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal: | : ▪ [[Journal:From command-line bioinformatics to bioGUI|From command-line bioinformatics to bioGUI]] | ||
Revision as of 15:46, 23 March 2020
"Laboratory testing for coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in suspected human cases"
This document provides interim guidance to laboratories and stakeholders involved in COVID-19 virus laboratory testing of patients. It is based in part on the interim guidance on laboratory testing for Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) coronavirus. Information on human infection with the COVID-19 virus is evolving and the World Health Organization (WHO) continues to monitor developments and revise recommendations as necessary. This document will be revised as new information becomes available. Feedback is welcome and can be sent to WHElab@who.int. The virus has now been named SARS-CoV-2 by the International Committee of Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV)(2). This virus can cause the disease named coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). WHO refers to the virus as COVID-19 virus in its current documentation. (Full article...)
Recently featured: