Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
From LIMSWiki
Jump to navigationJump to searchShawndouglas (talk | contribs) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
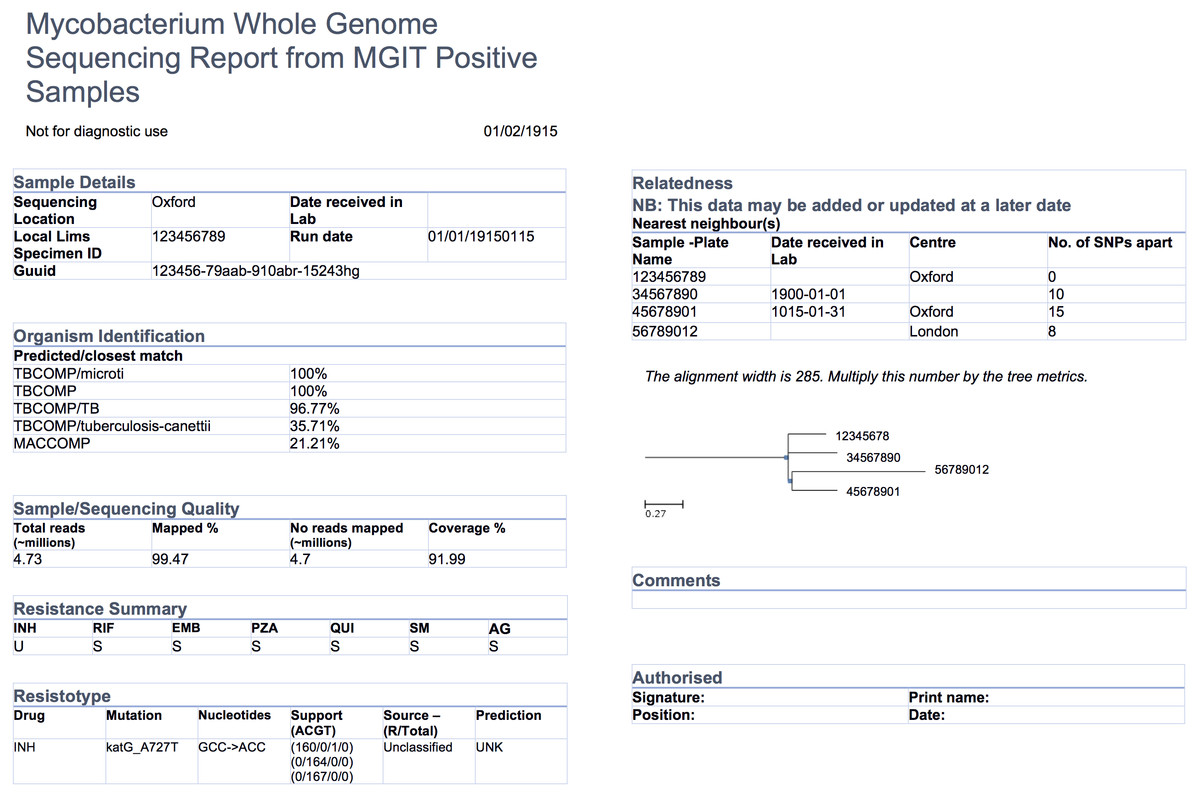
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Crisan PeerJ2018 6.jpg|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Evidence-based design and evaluation of a whole genome sequencing clinical report for the reference microbiology laboratory|Evidence-based design and evaluation of a whole genome sequencing clinical report for the reference microbiology laboratory]]"''' | ||
Microbial genome [[sequencing]] is now being routinely used in many [[Clinical laboratory|clinical]] and [[Public health laboratory|public health laboratories]]. Understanding how to [[Reporting|report]] complex genomic test results to stakeholders who may have varying familiarity with genomics — including clinicians, laboratorians, epidemiologists, and researchers — is critical to the successful and sustainable implementation of this new technology; however, there are no evidence-based guidelines for designing such a report in the pathogen genomics domain. Here, we describe an iterative, human-centered approach to creating a report template for communicating tuberculosis (TB) genomic test results. ('''[[Journal:Evidence-based design and evaluation of a whole genome sequencing clinical report for the reference microbiology laboratory|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Moving ERP systems to the cloud: Data security issues|Moving ERP systems to the cloud: Data security issues]] | |||
: ▪ [[Journal:Method-centered digital communities on protocols.io for fast-paced scientific innovation|Method-centered digital communities on protocols.io for fast-paced scientific innovation]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Method-centered digital communities on protocols.io for fast-paced scientific innovation|Method-centered digital communities on protocols.io for fast-paced scientific innovation]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Information management for enabling systems medicine|Information management for enabling systems medicine]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Information management for enabling systems medicine|Information management for enabling systems medicine]] | ||
Revision as of 14:39, 2 April 2018
Microbial genome sequencing is now being routinely used in many clinical and public health laboratories. Understanding how to report complex genomic test results to stakeholders who may have varying familiarity with genomics — including clinicians, laboratorians, epidemiologists, and researchers — is critical to the successful and sustainable implementation of this new technology; however, there are no evidence-based guidelines for designing such a report in the pathogen genomics domain. Here, we describe an iterative, human-centered approach to creating a report template for communicating tuberculosis (TB) genomic test results. (Full article...)
Recently featured: