Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| (30 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Mandrioli Molecules2019 24-11.png|240px]]</div> | ||
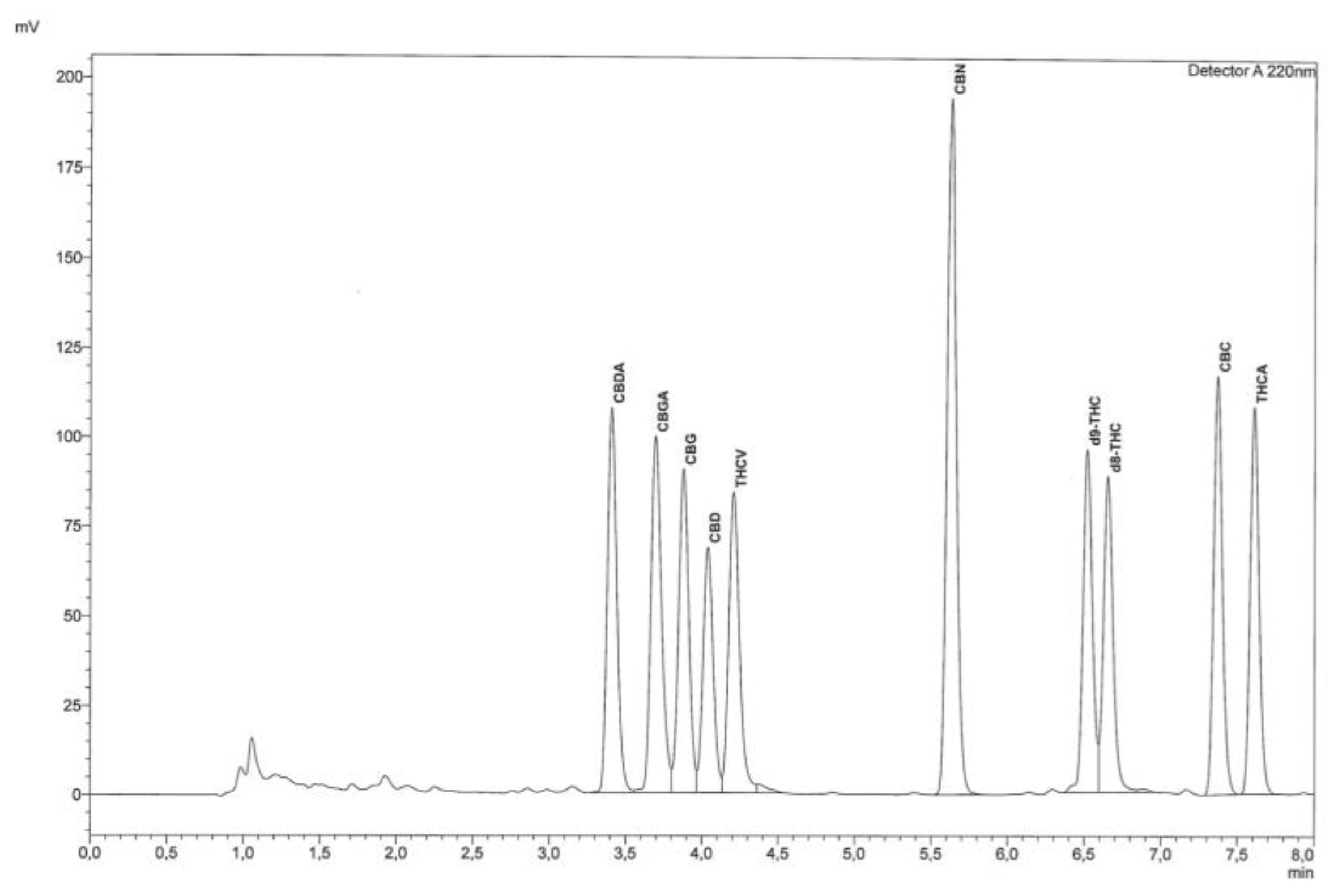
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Fast detection of 10 cannabinoids by RP-HPLC-UV method in Cannabis sativa L.|Fast detection of 10 cannabinoids by RP-HPLC-UV method in Cannabis sativa L.]]"''' | ||
[[wikipedia:Cannabis|Cannabis]] has regained much attention as a result of updated legislation authorizing many different uses, and it can be classified on the basis of the content of [[wikipedia:Tetrahydrocannabinol|Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol]] (Δ9-THC), a psychotropic substance for which there are legal limitations in many countries. For this purpose, accurate qualitative and quantitative determination is essential. The relationship between THC and [[wikipedia:Cannabidiol|cannabidiol]] (CBD) is also significant, as the latter substance is endowed with many specific and non-psychoactive proprieties. For these reasons, it becomes increasingly important and urgent to utilize fast, easy, validated, and harmonized procedures for determination of [[wikipedia:Cannabinoid|cannabinoids]]. The procedure described herein allows rapid determination of 10 cannabinoids from the [[wikipedia:Inflorescence|inflorescences]] of ''Cannabis sativa'' L. by extraction with organic solvents. Separation and subsequent detection are by [[wikipedia:Reversed-phase chromatography|reversed-phase]] [[high-performance liquid chromatography]] with ultraviolet detector (RP-HPLC-UV). ('''[[Journal:Fast detection of 10 cannabinoids by RP-HPLC-UV method in Cannabis sativa L.|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal: | : ▪ [[Journal:What is this sensor and does this app need access to it?|What is this sensor and does this app need access to it?]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal: | : ▪ [[Journal:AI meets exascale computing: Advancing cancer research with large-scale high-performance computing|AI meets exascale computing: Advancing cancer research with large-scale high-performance computing]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal: | : ▪ [[Journal:Building infrastructure for African human genomic data management|Building infrastructure for African human genomic data management]] | ||
Revision as of 16:43, 20 January 2020
"Fast detection of 10 cannabinoids by RP-HPLC-UV method in Cannabis sativa L."
Cannabis has regained much attention as a result of updated legislation authorizing many different uses, and it can be classified on the basis of the content of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC), a psychotropic substance for which there are legal limitations in many countries. For this purpose, accurate qualitative and quantitative determination is essential. The relationship between THC and cannabidiol (CBD) is also significant, as the latter substance is endowed with many specific and non-psychoactive proprieties. For these reasons, it becomes increasingly important and urgent to utilize fast, easy, validated, and harmonized procedures for determination of cannabinoids. The procedure described herein allows rapid determination of 10 cannabinoids from the inflorescences of Cannabis sativa L. by extraction with organic solvents. Separation and subsequent detection are by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detector (RP-HPLC-UV). (Full article...)
Recently featured: