Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Navale F1000Research2020 8.gif|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Development of an informatics system for accelerating biomedical research|Development of an informatics system for accelerating biomedical research]]"''' | ||
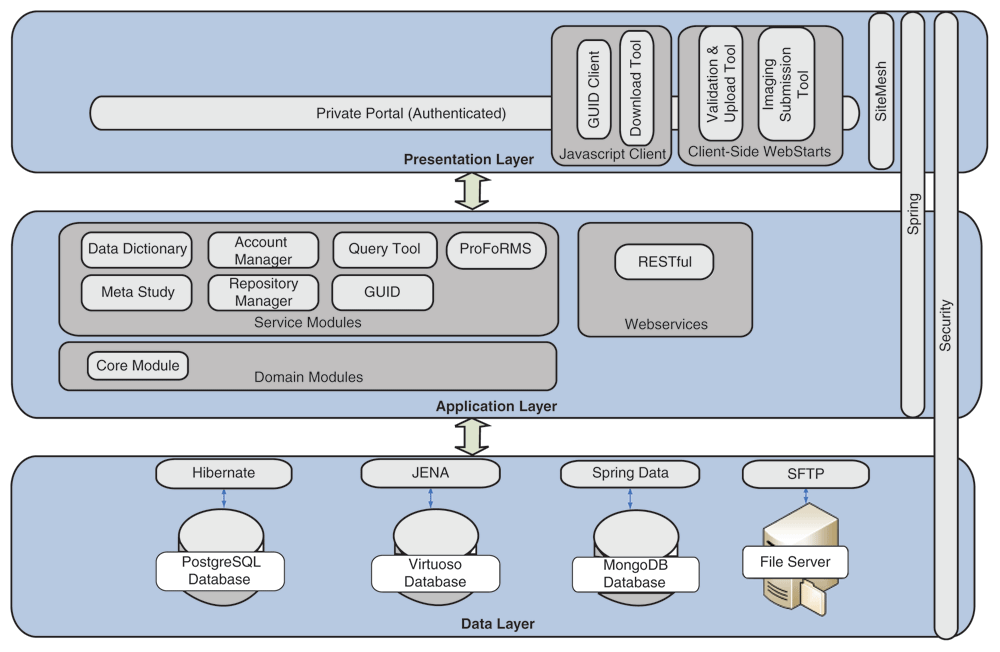
The Biomedical Research Informatics Computing System (BRICS) was developed to support multiple disease-focused research programs. Seven service modules are integrated together to provide a collaborative and extensible web-based environment. The modules—Data Dictionary, Account Management, Query Tool, Protocol and Form Research Management System, Meta Study, Data Repository, and Globally Unique Identifier—facilitate the management of research protocols, including the submission, processing, curation, access, and storage of clinical, imaging, and derived [[genomics]] data within the associated data repositories. Multiple instances of BRICS are deployed to support various biomedical research communities focused on accelerating discoveries for rare diseases, traumatic brain injuries, Parkinson’s disease, inherited eye diseases, and symptom science research. No personally identifiable [[information]] is stored within the data repositories. Digital object identifiers (DOIs) are associated with the research studies. ('''[[Journal:Development of an informatics system for accelerating biomedical research|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Mini-review of laboratory operations in biobanking: Building biobanking resources for translational research|Mini-review of laboratory operations in biobanking: Building biobanking resources for translational research]] | |||
: ▪ [[Journal:Extending an open-source tool to measure data quality: Case report on Observational Health Data Science and Informatics (OHDSI)|Extending an open-source tool to measure data quality: Case report on Observational Health Data Science and Informatics (OHDSI)]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Extending an open-source tool to measure data quality: Case report on Observational Health Data Science and Informatics (OHDSI)|Extending an open-source tool to measure data quality: Case report on Observational Health Data Science and Informatics (OHDSI)]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Advancing laboratory medicine in hospitals through health information exchange: A survey of specialist physicians in Canada|Advancing laboratory medicine in hospitals through health information exchange: A survey of specialist physicians in Canada]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Advancing laboratory medicine in hospitals through health information exchange: A survey of specialist physicians in Canada|Advancing laboratory medicine in hospitals through health information exchange: A survey of specialist physicians in Canada]] | ||
Revision as of 15:58, 13 September 2021
"Development of an informatics system for accelerating biomedical research"
The Biomedical Research Informatics Computing System (BRICS) was developed to support multiple disease-focused research programs. Seven service modules are integrated together to provide a collaborative and extensible web-based environment. The modules—Data Dictionary, Account Management, Query Tool, Protocol and Form Research Management System, Meta Study, Data Repository, and Globally Unique Identifier—facilitate the management of research protocols, including the submission, processing, curation, access, and storage of clinical, imaging, and derived genomics data within the associated data repositories. Multiple instances of BRICS are deployed to support various biomedical research communities focused on accelerating discoveries for rare diseases, traumatic brain injuries, Parkinson’s disease, inherited eye diseases, and symptom science research. No personally identifiable information is stored within the data repositories. Digital object identifiers (DOIs) are associated with the research studies. (Full article...)
Recently featured:
- ▪ Mini-review of laboratory operations in biobanking: Building biobanking resources for translational research
- ▪ Extending an open-source tool to measure data quality: Case report on Observational Health Data Science and Informatics (OHDSI)
- ▪ Advancing laboratory medicine in hospitals through health information exchange: A survey of specialist physicians in Canada