User:Shawndouglas/sandbox/sublevel24
1. What is a cybersecurity plan and why do you need it?
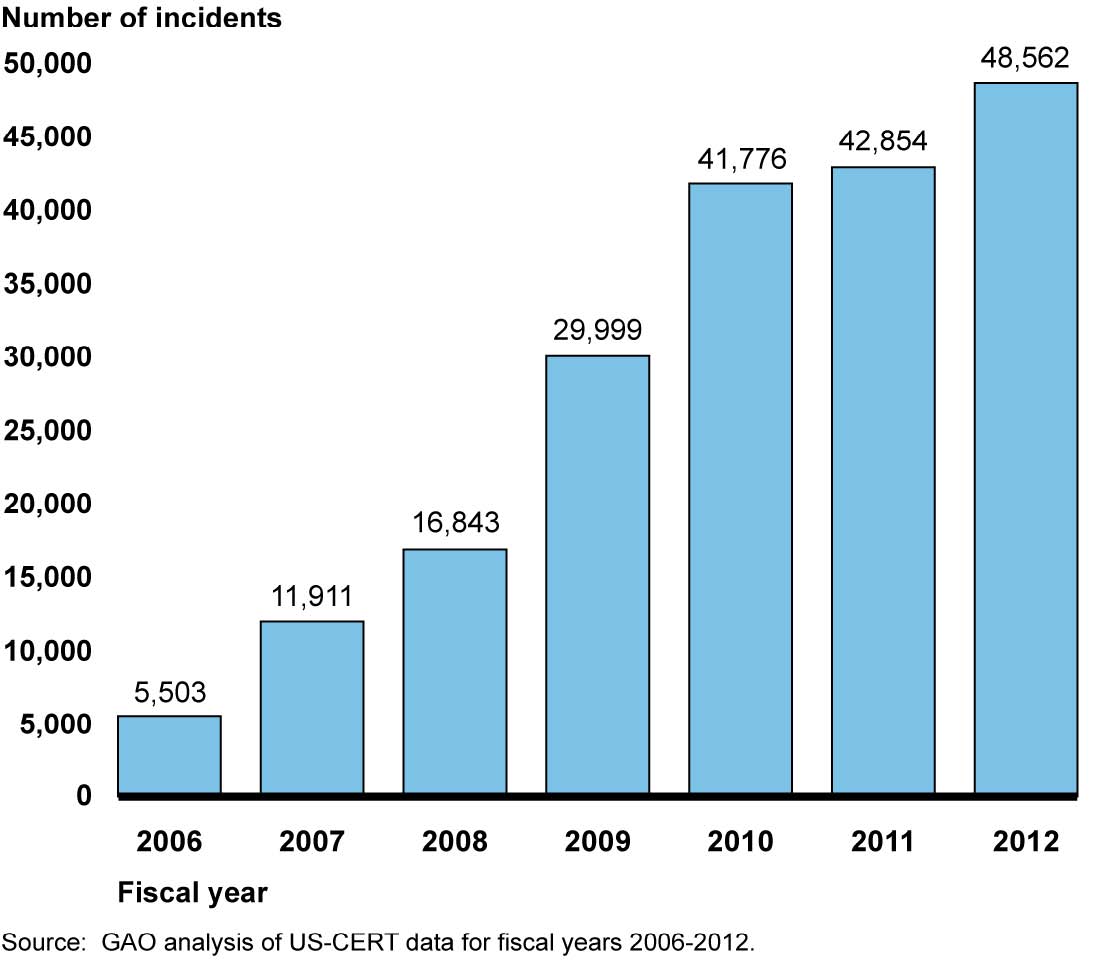
From law firms[1] to automotive manufacturers[2], the need to address cybersecurity is increasingly apparent. In 2018, the Center for Strategic & International Studies estimated that cybercrime causes close to $600 billion in damages to the global economy every year[3], though due to underreporting of crimes, that number may be much higher. That number also likely doesn't take into account lost business, fines, litigation, and intangible losses[4] In the end, businesses of all sizes average to about $200,000 in losses due to a cybersecurity incident[5], and nearly 60 percent of small and midsized businesses go bankrupt within six months because of it.[6]
It's not just large corporations at risk; small businesses of all types are also subject to cyber crimes. Juniper Research reports that despite small businesses making up over 99 percent of all companies, approximately 13 percent of overall cybersecurity spending came from those small businesses in 2018, amounting to about $500 per business.[7] Even the tiniest of businesses face cybersecurity risks today. The independent contractor with a WordPress-based website advertising their knowledge and skills must still ensure all website plugins and themes are updated and install security plugins to close potential vulnerabilities in the software. Without these precautions, hackers could spread malware, steal user data, add the website to a bot network, or hack it just for fun and learning.[8][9][10]
Unfortunately, roughly 60 to 70 percent of companies are still ill-prepared for cyber threats, either not having an up-to-date cybersecurity strategy or no plan at all.[6][10]
Developing a cybersecurity plan is not a simple process; it requires expertise, resources, and diligence. Even a simple plan may involve several months of development, more depending on the complexity involved. The time it takes to develop the plan may also be impacted by how much executive support is provided, the size of the development team (bigger is not always better), and how available required resources are.[11]
Keep in mind that while this guide has been written with intent to broadly cover multiple industries, it does have a slight lean towards laboratories, particularly those implementing information systems.
2. What are the major standard and regulations dictating cybersecurity action?
3. The NIST Cybersecurity Framework and its control families
4. Fitting a framework or specification into a cybersecurity plan
5. Develop and create the cybersecurity plan
https://www.limswiki.org/index.php/User:Shawndouglas/sandbox/sublevel28
6. Closing remarks
Appendix 1. A simplified description of NIST Cybersecurity Framework controls, with ties to LIMSpec
https://www.limswiki.org/index.php/User:Shawndouglas/sandbox/sublevel30
References
- ↑ Sobowale, J. (1 March 2017). "Law firms must manage cybersecurity risks". ABA Journal. American Bar Association. http://www.abajournal.com/magazine/article/managing_cybersecurity_risk/. Retrieved 14 December 2019.
- ↑ Watney, C.; Draffin, C. (November 2017). "Addressing new challenges in automotive cybersecurity" (PDF). R Street Policy Study No. 118. R Street Institute. https://www.rstreet.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/118-1.pdf. Retrieved 14 December 2019.
- ↑ Lewis, J.A. (21 February 2018). "Economic Impact of Cybercrime". Center for Strategic & International Studies. https://www.csis.org/analysis/economic-impact-cybercrime. Retrieved 14 December 2019.
- ↑ "BLOG: Cost of Cyber Crime to Small Businesses". Virginia SBDC Blog. Virginia SBDC. 30 May 2017. https://www.virginiasbdc.org/blog-cost-of-cyber-crime-to-small-businesses/. Retrieved 14 December 2019.
- ↑ "Hiscox Cyber Readiness Report 2019" (PDF). Hiscox Ltd. April 2019. https://www.hiscox.com/documents/2019-Hiscox-Cyber-Readiness-Report.pdf. Retrieved 14 December 2019.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Galvin, J. (7 May 2018). "60 Percent of Small Businesses Fold Within 6 Months of a Cyber Attack. Here's How to Protect Yourself". Inc.com. https://www.inc.com/joe-galvin/60-percent-of-small-businesses-fold-within-6-months-of-a-cyber-attack-heres-how-to-protect-yourself.html. Retrieved 14 December 2019.
- ↑ "Cybersecurity Breaches to Result in over 146 Billion Records Being Stolen by 2023". Juniper Research. 8 August 2018. https://www.juniperresearch.com/press/press-releases/cybersecurity-breaches-to-result-in-over-146-bn. Retrieved 14 December 2019.
- ↑ Grima, M. (14 November 2019). "Top reasons why WordPress websites get hacked (and how you can stop it)". WP White Security. https://www.wpwhitesecurity.com/why-malicious-hacker-target-wordpress/. Retrieved 14 December 2019.
- ↑ Moen, D. (19 April 2016). "What Hackers Do With Compromised WordPress Sites". Wordfence Blog. Defiant, Inc. https://www.wordfence.com/blog/2016/04/hackers-compromised-wordpress-sites/. Retrieved 14 December 2019.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Talaleve, A. (May 2019). "Website Hacking Statistics (Updated 2019)". WebARX. https://www.webarxsecurity.com/website-hacking-statistics-2018-february/. Retrieved 14 December 2019.
- ↑ Cadmus Group, LLC (30 October 2018). "Cybersecurity Strategy Development Guide" (PDF). National Association of Regulatory Utility Commissioners. https://pubs.naruc.org/pub/8C1D5CDD-A2C8-DA11-6DF8-FCC89B5A3204. Retrieved 29 November 2019.