Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Hatakeyama BMCBioinformatics2016 17.gif|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:SUSHI: An exquisite recipe for fully documented, reproducible and reusable NGS data analysis|SUSHI: An exquisite recipe for fully documented, reproducible and reusable NGS data analysis]]"''' | ||
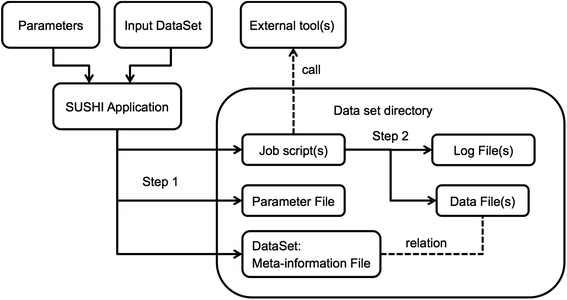
Next generation sequencing (NGS) produces massive datasets consisting of billions of reads and up to thousands of samples. Subsequent [[Bioinformatics|bioinformatic]] analysis is typically done with the help of open-source tools, where each application performs a single step towards the final result. This situation leaves the bioinformaticians with the tasks of combining the tools, managing the data files and meta-information, documenting the analysis, and ensuring reproducibility. | |||
We present SUSHI, an agile data analysis framework that relieves bioinformaticians from the administrative challenges of their data analysis. SUSHI lets users build reproducible data analysis workflows from individual applications and manages the input data, the parameters, meta-information with user-driven semantics, and the job scripts. As distinguishing features, SUSHI provides an expert command line interface as well as a convenient web interface to run bioinformatics tools. SUSHI datasets are self-contained and self-documented on the file system. This makes them fully reproducible and ready to be shared. With the associated meta-information being formatted as plain text tables, the datasets can be readily further analyzed and interpreted outside SUSHI. ('''[[Journal:SUSHI: An exquisite recipe for fully documented, reproducible and reusable NGS data analysis|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Open source data logger for low-cost environmental monitoring|Open source data logger for low-cost environmental monitoring]] | |||
: ▪ [[Journal:Evaluating health information systems using ontologies|Evaluating health information systems using ontologies]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Evaluating health information systems using ontologies|Evaluating health information systems using ontologies]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:From the desktop to the grid: Scalable bioinformatics via workflow conversion|From the desktop to the grid: Scalable bioinformatics via workflow conversion]] | : ▪ [[Journal:From the desktop to the grid: Scalable bioinformatics via workflow conversion|From the desktop to the grid: Scalable bioinformatics via workflow conversion]] | ||
Revision as of 15:31, 6 September 2016
"SUSHI: An exquisite recipe for fully documented, reproducible and reusable NGS data analysis"
Next generation sequencing (NGS) produces massive datasets consisting of billions of reads and up to thousands of samples. Subsequent bioinformatic analysis is typically done with the help of open-source tools, where each application performs a single step towards the final result. This situation leaves the bioinformaticians with the tasks of combining the tools, managing the data files and meta-information, documenting the analysis, and ensuring reproducibility.
We present SUSHI, an agile data analysis framework that relieves bioinformaticians from the administrative challenges of their data analysis. SUSHI lets users build reproducible data analysis workflows from individual applications and manages the input data, the parameters, meta-information with user-driven semantics, and the job scripts. As distinguishing features, SUSHI provides an expert command line interface as well as a convenient web interface to run bioinformatics tools. SUSHI datasets are self-contained and self-documented on the file system. This makes them fully reproducible and ready to be shared. With the associated meta-information being formatted as plain text tables, the datasets can be readily further analyzed and interpreted outside SUSHI. (Full article...)
Recently featured: