Difference between revisions of "Evolutionary informatics"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) m (Internal link.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Fixed date/year issues in citations) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
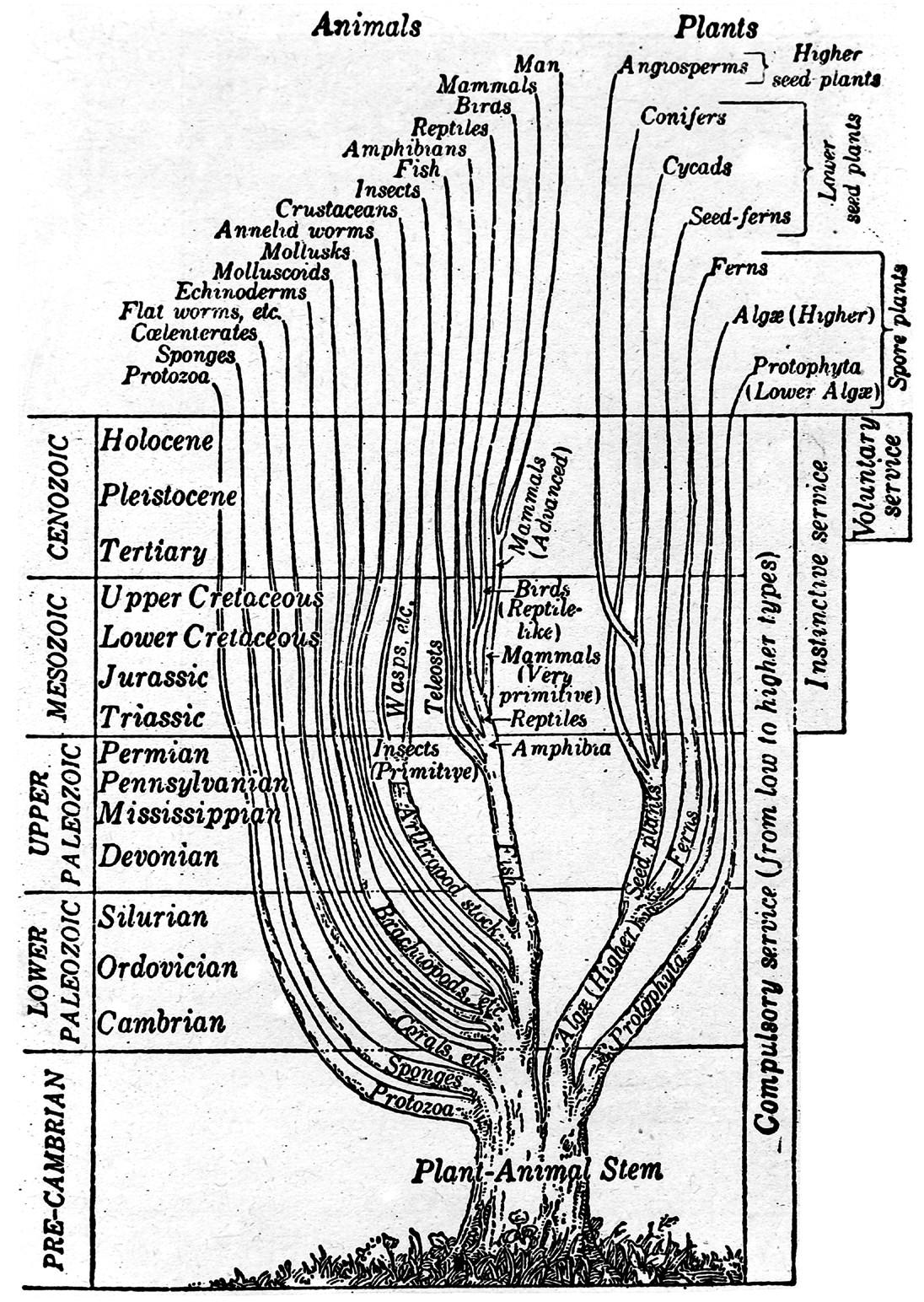
''( | [[File:Tree, plant and animal stem. Wellcome M0001295.jpg|right|thumb|360px|Phylogenomics and computational biology play important roles in evolutionary informatics, changing the way we view the Tree of Life.]]'''Evolutionary informatics''' is a sub-branch of [[informatics]] that addresses the algorithmic and technological tools (like information and analytical systems) needed to better manage data from research in ecology and evolutionary biology and answer evolutionary questions.<ref name="ParrEvoIn">{{cite journal |title=Evolutionary informatics: Unifying knowledge about the diversity of life |journal=Trends in Ecology and Evolution |author=Parr, C.S.; Guralnick, R.; Cellinese, N.; Page, R.D.M |volume=27 |issue=2 |year=2012 |pages=94–103 |doi=10.1016/j.tree.2011.11.001 |pmid=22154516}}</ref> | ||
As in [[bioinformatics]] and [[genomics]], scientists studying biological evolution have gathered an increasingly large volume of information, resulting in information management problems. Additionally, as bioinformatics and genomics are pertinent to the study of evolution, utilization of information from those areas is of concern in evolutionary informatics. | |||
== | ==History== | ||
Evolutionary informatics has evolved out of a wide variety of scientific, mathematical, and computational endeavors, including evolutionary biology, evolutionary computation, algorithmic and evolutionary algorithmic research, and software development.<ref name="ParrEvoIn" /> | |||
In 2006, the National Science Foundation-sponsored National Evolutionary Synthesis Center (NESCent) promoted the NESCent Evolutionary Informatics Working Group to "develop community cohesion on issues of standards and interoperability" of the infrastructure and tools used for "integrating evolutionary methodology into biological data analysis."<ref name="EvoInfoWG">{{cite web |url=https://evoinfo.nescent.org/Main_Page |title=Evolutionary Informatics (EvoInfo) Working Group |publisher=National Evolutionary Synthesis Center |date=14 April 2016 |accessdate=20 March 2020}}</ref> In subsequent years, NESCent became involved in creating the Hackathons, Interoperability, Phylogenies (HIP) working group and advancing several databases, libraries, and ontologies in the field of evolutionary biology.<ref name="HIP">{{cite web |url=http://www.evoio.org/wiki/HIP |title=HIP |publisher=National Evolutionary Synthesis Center |date=28 February 2014 |accessdate=13 January 2015}}</ref><ref name="NESCentInit">{{cite web |url=https://www.nescent.org/informatics/initiatives.php.html |title=Informatics Initiatives: Cyberinfrastructure for Evolutionary Biology |publisher=National Evolutionary Synthesis Center |accessdate=20 March 2020}}</ref> | |||
In | In 2007, Professor Robert Marks included the term "evolutionary informatics" in the title and content of his Baylor University-hosted website ''Evolutionary Informatics Laboratory'' (EIL). The university's administration subsequently took down the website for having "unapproved research," which reportedly included unpublished scholarly papers coauthored by Marks and intelligent design advocate William A. Dembski.<ref name="AmantEIL">{{cite web |url=http://www.baylor.edu/Lariat/news.php?action=story&story=46756 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20121003011642/http://www.baylor.edu/Lariat/news.php?action=story&story=46756 |title=New intelligent design conflict hits BU |author=St. Amant, Claire |work=The Lariat |publisher=Baylor University |date=11 September 2007 |archivedate=03 October 2012 |accessdate=12 January 2015}}</ref> Marks moved the content removed from Baylor servers to a new domain. Its front page stated the following concerning evolutionary informatics: | ||
<blockquote> | <blockquote>Evolutionary informatics merges theories of evolution and information, thereby wedding the natural, engineering, and mathematical sciences. Evolutionary informatics studies how evolving systems incorporate, transform, and export information. The Evolutionary Informatics Laboratory explores the conceptual foundations, mathematical development, and empirical application of evolutionary informatics. The principal theme of the lab’s research is teasing apart the respective roles of internally generated and externally applied information in the performance of evolutionary systems.<ref name="EILArch1">{{cite web |url=http://www.evolutionaryinformatics.org/ |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20070905131952/http://www.evolutionaryinformatics.org/ |title=The Evolutionary Informatics Lab |author=Marks, Robert |archivedate=05 September 2007 |accessdate=12 January 2015}}</ref></blockquote> | ||
In June 2010, the first ever Informatics for Phylogenetics, Evolution, and Biodiversity (iEvoBio) Conference took place in Portland, Oregon, with the goal of "both to catalyse the development of new tools, and to increase awareness of the possibilities offered by existing technologies."<ref name="iEvoBio10">{{cite web |url=http://www.ievobio.org/2010/about.html |title=iEvoBio: About the Conference |publisher=National Evolutionary Synthesis Center |date=08 March 2010 |accessdate=13 January 2015}}</ref> {{As of|2020}}, the conference still occurs. | |||
== | ==Application== | ||
Evolutionary informatics can help tackle problems and tasks such as the following<ref name="ParrEvoIn" />: | |||
* Connecting genomics data with scalable taxonomic concepts and data to reduce "the growing number of lineages that lack formal taxonomic names" | |||
* Leveraging legacy biodiversity data by digitizing it, semantically enhancing it, and making it more portable | |||
* Building "sustainable digital community repositories that provide access to rich data and metadata" in the field of evolutionary biology | |||
* Building "a semantic web for evolutionary biology" that uses data querying, mining, and integration tools | |||
* Developing algorithms to better model evolutionary changes | |||
==Informatics== | |||
The U.S. National Science Foundation-funded NESCent has been one of the key groups responsible for advancing the application of informatics to evolutionary biology problems in the twenty-first century. Started in 2004, NESCent has furthered several informatics goals in the field of evolutionary informatics by<ref name="NESCentInit" />: | |||
* contributing to the Generic Model Organism Database (GMOD) project "to further develop the data model for evolutionary datatypes (named organisms, georeferenced collections, genetic and phenotypic variability, and phylogenies), to develop web applications for accessing these types of data, and to provide user support for adoption of the GMOD platform for evolutionary model organisms." | |||
* promoting and contributing to several projects (Phenoscape, Phenex, OBO Foundry) that work with phenotype ontologies and their application to evolutionary morphologies. | |||
* promoting the integration of [[geoinformatics]] with evolutionary informatics so researcher may better "integrate population genetic and phylogenetic models of multiple taxa with data describing present and past environments and climate"; one such success has been GeoPhyloBuilder. | |||
* integrating the wide variety of existing tools to interoperate with each other through hack-a-thons and cooperation with open-source developers. | |||
* "working to establish a digital repository for published data" in the biosciences. | |||
===Application of algorithms to evolutionary biology=== | |||
== | The notion that information processing is essential to the evolutionary process predates the entry of the term "[[informatics]]" into the English language around 1967.<ref name="MWInfo">{{cite web |url=https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/informatics |title=Informatics |work=Merriam-Webster.com |publisher=Merriam-Webster, Inc |accessdate=20 March 2020}}</ref> Investigators were arguing as early as the 1940s that certain principles of information processing apply to both living and engineered systems, with much of their thinking encapsulated in Norbert Wiener's ''Cybernetics: or Control and Communication in the Animal and the Machine''.<ref name="Wiener48">{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=NnM-uISyywAC&printsec=frontcover |title=Cybernetics: or Control and Communication in the Animal and the Machine |author=Wiener, N. |publisher=The MIT Press |year=1965 |isbn=026273009X |accessdate=20 March 2020}}</ref> Wiener regarded evolution as "phylogenetic learning," or accrual of information in the genome.<ref name="Wiener48" /> | ||
Modern work has focused on evolution as more of an optimization of fitness functions, addressing the role of information in optimization. Work by researchers David Wolpert and William G. Macready in the mid-1990s established that evolutionary algorithms have average performance no better than that of random search. They argued that superior performance could be achieved only if algorithms incorporate prior knowledge of problems, and provided an information-geometric analysis of how algorithms and problems are matched (and mismatched).<ref name="NFLTech">{{cite book |url=http://delta.cs.cinvestav.mx/~ccoello/compevol/nfl.pdf |format=PDF |title=No Free Lunch Theorems for Search, Technical Report SFI-TR-95-02-010 |author=Wolpert, D.H.; Macready, W.G |publisher=Santa Fe Institute |year=1995 |accessdate=13 January 2015}}</ref><ref name="NFLTO">{{cite journal |title=No free lunch theorems for optimization |journal=IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation |author=Wolpert, D.H.; Macready, W.G. |volume=1 |issue=1 |pages=67–82 |year=1997 |doi=10.1109/4235.585893}}</ref> | |||
After reviewing Wolper and Macready's work on the "no free lunch" theorems, researcher Thomas M. English argued there was no free lunch due to an underlying "conservation of information," and that the duo's work "mistakes selection bias for prior information of the objective function."<ref name="EnglishOpti">{{cite journal |url=https://tmenglish.github.io/EP96.pdf |format=PDF |title=Evaluation of Evolutionary and Genetic Optimizers: No Free Lunch |journal=Evolutionary Programming V: Proceedings of the Fifth Annual Conference on Evolutionary Programming |author=English, T.M. |editor=Fogel, L.J.; Angeline, P.J.; Bäck, T. |pages=163–169 |year=1996 |accessdate=20 March 2020}}</ref> In 2000, English turned to Kolmogorov complexity as a measure of information in instances of fitness functions and optimization algorithms. He observed that almost all problems exhibit a high degree of Kolmogorov randomness, and thus those problems are easy for almost all optimization algorithms.<ref name="EnglishLearning">{{cite journal |title=Optimization is easy and learning is hard in the typical function |journal=Proceedings of the 2000 Congress on Evolutionary Computation |author=English, T.M. |volume=2 |pages=924–931 |year=2000 |doi=10.1109/CEC.2000.870741}}</ref> English later gave a new perspective on conservation by way of characterizing approximate satisfaction of a necessary and sufficient condition for "no free lunch."<ref name="EnglishNoMore">{{cite journal |title=No more lunch: Analysis of sequential search |journal=Congress on Evolutionary Computation, 2004 |author=English, T.M |volume=1 |pages=227–234 |year=2004 |doi=10.1109/CEC.2004.1330861}}</ref> | |||
Wolpert and Macready went on to prove the existence of coevolutionary "free lunches" in 2005.<ref name="WMCoev">{{cite journal |title=Coevolutionary free lunches |journal=IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation |author=Wolpert, D.H.; Macready, W.G |volume=9 |issue=6 |pages=721–735 |year=2005 |doi=10.1109/TEVC.2005.856205}}</ref> This may be interpreted as the discovery of a problem class for which some coevolutionary algorithms in biology are generally better informed than others of how to solve problems. | |||
==Further reading== | |||
== | * {{cite journal |title=Evolutionary informatics: Unifying knowledge about the diversity of life |journal=Trends in Ecology and Evolution |author=Parr, C.S.; Guralnick, R.; Cellinese, N.; Page, R.D.M |volume=27 |issue=2 |year=2012 |pages=94–103 |doi=10.1016/j.tree.2011.11.001 |pmid=22154516}} | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
* [http:// | * [https://ievobio.wordpress.com/ iEvoBio Conference] | ||
* [http://www.nescent.org/ NESCent] | |||
* [https://www.evoinfo.org/index.html Evolutionary Informatics Lab] | |||
==Notes== | |||
This article reuses some content from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evolutionary_informatics the Wikipedia article]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|colwidth=30em}} | |||
[[Category:Informatics]] | [[Category:Informatics]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:58, 4 January 2024
Evolutionary informatics is a sub-branch of informatics that addresses the algorithmic and technological tools (like information and analytical systems) needed to better manage data from research in ecology and evolutionary biology and answer evolutionary questions.[1]
As in bioinformatics and genomics, scientists studying biological evolution have gathered an increasingly large volume of information, resulting in information management problems. Additionally, as bioinformatics and genomics are pertinent to the study of evolution, utilization of information from those areas is of concern in evolutionary informatics.
History
Evolutionary informatics has evolved out of a wide variety of scientific, mathematical, and computational endeavors, including evolutionary biology, evolutionary computation, algorithmic and evolutionary algorithmic research, and software development.[1]
In 2006, the National Science Foundation-sponsored National Evolutionary Synthesis Center (NESCent) promoted the NESCent Evolutionary Informatics Working Group to "develop community cohesion on issues of standards and interoperability" of the infrastructure and tools used for "integrating evolutionary methodology into biological data analysis."[2] In subsequent years, NESCent became involved in creating the Hackathons, Interoperability, Phylogenies (HIP) working group and advancing several databases, libraries, and ontologies in the field of evolutionary biology.[3][4]
In 2007, Professor Robert Marks included the term "evolutionary informatics" in the title and content of his Baylor University-hosted website Evolutionary Informatics Laboratory (EIL). The university's administration subsequently took down the website for having "unapproved research," which reportedly included unpublished scholarly papers coauthored by Marks and intelligent design advocate William A. Dembski.[5] Marks moved the content removed from Baylor servers to a new domain. Its front page stated the following concerning evolutionary informatics:
Evolutionary informatics merges theories of evolution and information, thereby wedding the natural, engineering, and mathematical sciences. Evolutionary informatics studies how evolving systems incorporate, transform, and export information. The Evolutionary Informatics Laboratory explores the conceptual foundations, mathematical development, and empirical application of evolutionary informatics. The principal theme of the lab’s research is teasing apart the respective roles of internally generated and externally applied information in the performance of evolutionary systems.[6]
In June 2010, the first ever Informatics for Phylogenetics, Evolution, and Biodiversity (iEvoBio) Conference took place in Portland, Oregon, with the goal of "both to catalyse the development of new tools, and to increase awareness of the possibilities offered by existing technologies."[7] As of 2020[update], the conference still occurs.
Application
Evolutionary informatics can help tackle problems and tasks such as the following[1]:
- Connecting genomics data with scalable taxonomic concepts and data to reduce "the growing number of lineages that lack formal taxonomic names"
- Leveraging legacy biodiversity data by digitizing it, semantically enhancing it, and making it more portable
- Building "sustainable digital community repositories that provide access to rich data and metadata" in the field of evolutionary biology
- Building "a semantic web for evolutionary biology" that uses data querying, mining, and integration tools
- Developing algorithms to better model evolutionary changes
Informatics
The U.S. National Science Foundation-funded NESCent has been one of the key groups responsible for advancing the application of informatics to evolutionary biology problems in the twenty-first century. Started in 2004, NESCent has furthered several informatics goals in the field of evolutionary informatics by[4]:
- contributing to the Generic Model Organism Database (GMOD) project "to further develop the data model for evolutionary datatypes (named organisms, georeferenced collections, genetic and phenotypic variability, and phylogenies), to develop web applications for accessing these types of data, and to provide user support for adoption of the GMOD platform for evolutionary model organisms."
- promoting and contributing to several projects (Phenoscape, Phenex, OBO Foundry) that work with phenotype ontologies and their application to evolutionary morphologies.
- promoting the integration of geoinformatics with evolutionary informatics so researcher may better "integrate population genetic and phylogenetic models of multiple taxa with data describing present and past environments and climate"; one such success has been GeoPhyloBuilder.
- integrating the wide variety of existing tools to interoperate with each other through hack-a-thons and cooperation with open-source developers.
- "working to establish a digital repository for published data" in the biosciences.
Application of algorithms to evolutionary biology
The notion that information processing is essential to the evolutionary process predates the entry of the term "informatics" into the English language around 1967.[8] Investigators were arguing as early as the 1940s that certain principles of information processing apply to both living and engineered systems, with much of their thinking encapsulated in Norbert Wiener's Cybernetics: or Control and Communication in the Animal and the Machine.[9] Wiener regarded evolution as "phylogenetic learning," or accrual of information in the genome.[9]
Modern work has focused on evolution as more of an optimization of fitness functions, addressing the role of information in optimization. Work by researchers David Wolpert and William G. Macready in the mid-1990s established that evolutionary algorithms have average performance no better than that of random search. They argued that superior performance could be achieved only if algorithms incorporate prior knowledge of problems, and provided an information-geometric analysis of how algorithms and problems are matched (and mismatched).[10][11]
After reviewing Wolper and Macready's work on the "no free lunch" theorems, researcher Thomas M. English argued there was no free lunch due to an underlying "conservation of information," and that the duo's work "mistakes selection bias for prior information of the objective function."[12] In 2000, English turned to Kolmogorov complexity as a measure of information in instances of fitness functions and optimization algorithms. He observed that almost all problems exhibit a high degree of Kolmogorov randomness, and thus those problems are easy for almost all optimization algorithms.[13] English later gave a new perspective on conservation by way of characterizing approximate satisfaction of a necessary and sufficient condition for "no free lunch."[14]
Wolpert and Macready went on to prove the existence of coevolutionary "free lunches" in 2005.[15] This may be interpreted as the discovery of a problem class for which some coevolutionary algorithms in biology are generally better informed than others of how to solve problems.
Further reading
- Parr, C.S.; Guralnick, R.; Cellinese, N.; Page, R.D.M (2012). "Evolutionary informatics: Unifying knowledge about the diversity of life". Trends in Ecology and Evolution 27 (2): 94–103. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2011.11.001. PMID 22154516.
External links
Notes
This article reuses some content from the Wikipedia article.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Parr, C.S.; Guralnick, R.; Cellinese, N.; Page, R.D.M (2012). "Evolutionary informatics: Unifying knowledge about the diversity of life". Trends in Ecology and Evolution 27 (2): 94–103. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2011.11.001. PMID 22154516.
- ↑ "Evolutionary Informatics (EvoInfo) Working Group". National Evolutionary Synthesis Center. 14 April 2016. https://evoinfo.nescent.org/Main_Page. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- ↑ "HIP". National Evolutionary Synthesis Center. 28 February 2014. http://www.evoio.org/wiki/HIP. Retrieved 13 January 2015.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Informatics Initiatives: Cyberinfrastructure for Evolutionary Biology". National Evolutionary Synthesis Center. https://www.nescent.org/informatics/initiatives.php.html. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- ↑ St. Amant, Claire (11 September 2007). "New intelligent design conflict hits BU". The Lariat. Baylor University. Archived from the original on 03 October 2012. https://web.archive.org/web/20121003011642/http://www.baylor.edu/Lariat/news.php?action=story&story=46756. Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ↑ Marks, Robert. "The Evolutionary Informatics Lab". Archived from the original on 05 September 2007. https://web.archive.org/web/20070905131952/http://www.evolutionaryinformatics.org/. Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ↑ "iEvoBio: About the Conference". National Evolutionary Synthesis Center. 8 March 2010. http://www.ievobio.org/2010/about.html. Retrieved 13 January 2015.
- ↑ "Informatics". Merriam-Webster.com. Merriam-Webster, Inc. https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/informatics. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Wiener, N. (1965). Cybernetics: or Control and Communication in the Animal and the Machine. The MIT Press. ISBN 026273009X. https://books.google.com/books?id=NnM-uISyywAC&printsec=frontcover. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- ↑ Wolpert, D.H.; Macready, W.G (1995) (PDF). No Free Lunch Theorems for Search, Technical Report SFI-TR-95-02-010. Santa Fe Institute. http://delta.cs.cinvestav.mx/~ccoello/compevol/nfl.pdf. Retrieved 13 January 2015.
- ↑ Wolpert, D.H.; Macready, W.G. (1997). "No free lunch theorems for optimization". IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation 1 (1): 67–82. doi:10.1109/4235.585893.
- ↑ English, T.M. (1996). Fogel, L.J.; Angeline, P.J.; Bäck, T.. ed. "Evaluation of Evolutionary and Genetic Optimizers: No Free Lunch" (PDF). Evolutionary Programming V: Proceedings of the Fifth Annual Conference on Evolutionary Programming: 163–169. https://tmenglish.github.io/EP96.pdf. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- ↑ English, T.M. (2000). "Optimization is easy and learning is hard in the typical function". Proceedings of the 2000 Congress on Evolutionary Computation 2: 924–931. doi:10.1109/CEC.2000.870741.
- ↑ English, T.M (2004). "No more lunch: Analysis of sequential search". Congress on Evolutionary Computation, 2004 1: 227–234. doi:10.1109/CEC.2004.1330861.
- ↑ Wolpert, D.H.; Macready, W.G (2005). "Coevolutionary free lunches". IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation 9 (6): 721–735. doi:10.1109/TEVC.2005.856205.