Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig2 Rantos Computers2020 9-1.png|240px]]</div> | |||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Interoperability challenges in the cybersecurity information sharing ecosystem|Interoperability challenges in the cybersecurity information sharing ecosystem]]"''' | ||
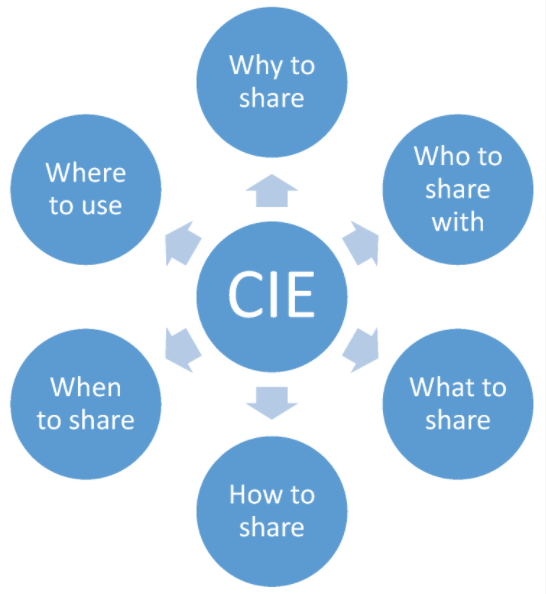
Threat intelligence helps businesses and organizations make the right decisions in their fight against cyber threats, and strategically design their digital defenses for an optimized and up-to-date security situation. Combined with advanced security analysis, threat intelligence helps reduce the time between the detection of an attack and its containment. This is achieved by continuously providing [[information]], accompanied by data, on existing and emerging cyber threats and vulnerabilities affecting corporate networks. This paper addresses challenges that organizations are bound to face when they decide to invest in effective and interoperable [[cybersecurity]] information sharing, and it categorizes them in a layered model. Based on this, it provides an evaluation of existing sources that share cybersecurity information. The aim of this research is to help organizations improve their cyber threat information exchange capabilities, to enhance their security posture and be more prepared against emerging threats. ('''[[Journal:Interoperability challenges in the cybersecurity information sharing ecosystem|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Data without software are just numbers|Data without software are just numbers]] | |||
: ▪ [[Journal:Persistent identification of instruments|Persistent identification of instruments]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Persistent identification of instruments|Persistent identification of instruments]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Cannabis contaminants limit pharmacological use of cannabidiol|Cannabis contaminants limit pharmacological use of cannabidiol]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Cannabis contaminants limit pharmacological use of cannabidiol|Cannabis contaminants limit pharmacological use of cannabidiol]] | ||
Revision as of 16:03, 11 October 2021
"Interoperability challenges in the cybersecurity information sharing ecosystem"
Threat intelligence helps businesses and organizations make the right decisions in their fight against cyber threats, and strategically design their digital defenses for an optimized and up-to-date security situation. Combined with advanced security analysis, threat intelligence helps reduce the time between the detection of an attack and its containment. This is achieved by continuously providing information, accompanied by data, on existing and emerging cyber threats and vulnerabilities affecting corporate networks. This paper addresses challenges that organizations are bound to face when they decide to invest in effective and interoperable cybersecurity information sharing, and it categorizes them in a layered model. Based on this, it provides an evaluation of existing sources that share cybersecurity information. The aim of this research is to help organizations improve their cyber threat information exchange capabilities, to enhance their security posture and be more prepared against emerging threats. (Full article...)
Recently featured: