Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Reisman EBioinformatics2016 12.jpg|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:A polyglot approach to bioinformatics data integration: A phylogenetic analysis of HIV-1|A polyglot approach to bioinformatics data integration: A phylogenetic analysis of HIV-1]]"''' | ||
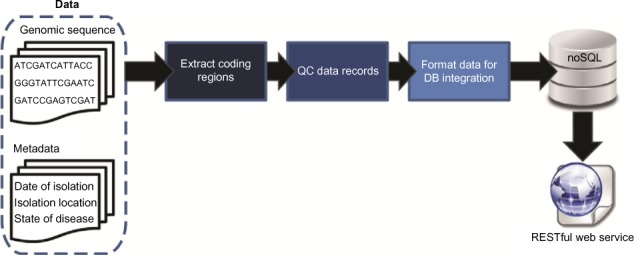
As [[sequencing]] technologies continue to drop in price and increase in throughput, new challenges emerge for the management and accessibility of genomic sequence data. We have developed a pipeline for facilitating the storage, retrieval, and subsequent analysis of molecular data, integrating both sequence and metadata. Taking a polyglot approach involving multiple languages, libraries, and persistence mechanisms, sequence data can be aggregated from publicly available and local repositories. Data are exposed in the form of a RESTful web service, formatted for easy querying, and retrieved for downstream analyses. As a proof of concept, we have developed a resource for annotated HIV-1 sequences. Phylogenetic analyses were conducted for >6,000 HIV-1 sequences revealing spatial and temporal factors influence the evolution of the individual genes uniquely. Nevertheless, signatures of origin can be extrapolated even despite increased globalization. The approach developed here can easily be customized for any species of interest. ('''[[Journal:A polyglot approach to bioinformatics data integration: A phylogenetic analysis of HIV-1|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:The systems biology format converter|The systems biology format converter]] | |||
: ▪ [[Journal:Chemozart: A web-based 3D molecular structure editor and visualizer platform|Chemozart: A web-based 3D molecular structure editor and visualizer platform]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Chemozart: A web-based 3D molecular structure editor and visualizer platform|Chemozart: A web-based 3D molecular structure editor and visualizer platform]] | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:Perceptions of pathology informatics by non-informaticist pathologists and trainees|Perceptions of pathology informatics by non-informaticist pathologists and trainees]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Perceptions of pathology informatics by non-informaticist pathologists and trainees|Perceptions of pathology informatics by non-informaticist pathologists and trainees]] | ||
Revision as of 15:18, 5 July 2016
"A polyglot approach to bioinformatics data integration: A phylogenetic analysis of HIV-1"
As sequencing technologies continue to drop in price and increase in throughput, new challenges emerge for the management and accessibility of genomic sequence data. We have developed a pipeline for facilitating the storage, retrieval, and subsequent analysis of molecular data, integrating both sequence and metadata. Taking a polyglot approach involving multiple languages, libraries, and persistence mechanisms, sequence data can be aggregated from publicly available and local repositories. Data are exposed in the form of a RESTful web service, formatted for easy querying, and retrieved for downstream analyses. As a proof of concept, we have developed a resource for annotated HIV-1 sequences. Phylogenetic analyses were conducted for >6,000 HIV-1 sequences revealing spatial and temporal factors influence the evolution of the individual genes uniquely. Nevertheless, signatures of origin can be extrapolated even despite increased globalization. The approach developed here can easily be customized for any species of interest. (Full article...)
Recently featured: