Difference between revisions of "Journal:Data science as an innovation challenge: From big data to value proposition"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Saving and adding more.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Saving and adding more.) |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
Here, we propose an exact configuration and series of steps to guide a big data analytics project. The lack of specified requirements and defined project goals in a big data analytics project (compared to a classic analytics project) make it challenging to structure the analytics process. Therefore, the linear innovation process serves as reference and orientation.<ref name="CooperStage90">{{cite journal |title=Stage-gate systems: A new tool for managing new products |journal=Business Horizons |author=Cooper, R.G. |volume=33 |issue=3 |pages=44–54 |year=1990 |doi=10.1016/0007-6813(90)90040-I}}</ref> As Braganza and colleagues<ref name="BraganzaResource17">{{cite journal |title=Resource management in big data initiatives: Processes and dynamic capabilities |journal=Journal of Business Research |author=Braganza, A.; Brooks, L.; Nepelski, D. et al. |volume=70 |pages=328–37 |year=2017 |doi=10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.08.006}}</ref> describe, for big data to be successfully integrated and implemented in an organization, clear and repeatable processes are required. Nevertheless, each analytics initiative is different and the process needs to flexible. Unfortunately, the literature rarely combines challenges in the analytics process with concepts from innovation management. Nevertheless, an integration of the concepts from innovation management could guide the analytics work of formulating digital strategies, organizational anchoring of the analytics units and their functions, and designing the analytics portfolio, as well as the underlying working principles (e.g., rapid prototyping, ideation techniques). | Here, we propose an exact configuration and series of steps to guide a big data analytics project. The lack of specified requirements and defined project goals in a big data analytics project (compared to a classic analytics project) make it challenging to structure the analytics process. Therefore, the linear innovation process serves as reference and orientation.<ref name="CooperStage90">{{cite journal |title=Stage-gate systems: A new tool for managing new products |journal=Business Horizons |author=Cooper, R.G. |volume=33 |issue=3 |pages=44–54 |year=1990 |doi=10.1016/0007-6813(90)90040-I}}</ref> As Braganza and colleagues<ref name="BraganzaResource17">{{cite journal |title=Resource management in big data initiatives: Processes and dynamic capabilities |journal=Journal of Business Research |author=Braganza, A.; Brooks, L.; Nepelski, D. et al. |volume=70 |pages=328–37 |year=2017 |doi=10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.08.006}}</ref> describe, for big data to be successfully integrated and implemented in an organization, clear and repeatable processes are required. Nevertheless, each analytics initiative is different and the process needs to flexible. Unfortunately, the literature rarely combines challenges in the analytics process with concepts from innovation management. Nevertheless, an integration of the concepts from innovation management could guide the analytics work of formulating digital strategies, organizational anchoring of the analytics units and their functions, and designing the analytics portfolio, as well as the underlying working principles (e.g., rapid prototyping, ideation techniques). | ||
Thus, in this article, we will concentrate on the question of what the practical discourse and work on analytics respectively implementing big data in organizations can learn from innovation management. A process for analytics innovation is introduced to guide the process from ideation to value generation. Emphasis is put on challenges during this process as well as different entry points. Thereby, we build on experience and insights from a number of analytics projects for different sectors and domains to derive recommendations for successfully implementing analytics solutions. | |||
We begin with a definition of big data and analytics. Next, we propose a process for a structured approach to retrieving value from data. Finally, we discuss the results and outline directions for future research. | |||
==Big data and analytics== | |||
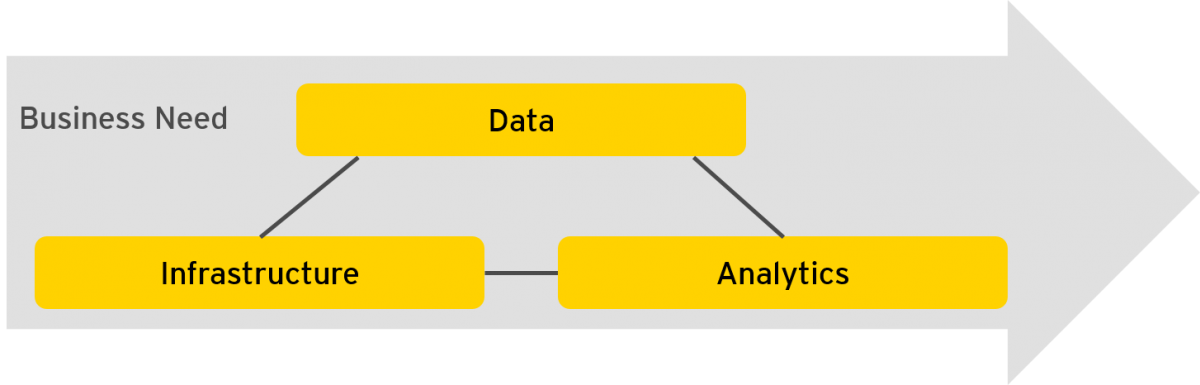
In this section, we address the elementary angles from which the analytics value chain should be looked at (Figure 1): data, infrastructure, and analytics–and the business need as the driver. According to our understanding, value is generated by analyzing data within a certain context, with a problem statement related to a business requirement driving the need for innovation. Besides expertise in conducting data and analytics projects, this process requires a working infrastructure, especially when volume, velocity, or variety of data to be analyzed exceeds certain limits. Below, we describe the three technical angles in more detail. | |||
[[File:Fig1 Kayser TechInnoManRev2018 8-3.png|600px]] | |||
{{clear}} | |||
{| | |||
| STYLE="vertical-align:top;"| | |||
{| border="0" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" width="600px" | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"| <blockquote>'''Figure 1.''' Framework of data, infrastructure, analytics and business need</blockquote> | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
|} | |||
===Data=== | |||
Big data is often defined with volume (how much data), velocity (speed of data generation), and variety as the diversity of data types.<ref name="PhilipData14">{{cite journal |title=Data-intensive applications, challenges, techniques and technologies: A survey on Big Data |journal=Information Sciences |author=Philip Chen, C.L.; Zhang, C.Y. |volume=275 |pages=314-347 |year=2014 |doi=10.1016/j.ins.2014.01.015}}</ref><ref name="GandomiBeyond15">{{cite journal |title=Beyond the hype: Big data concepts, methods, and analytics |journal=International Journal of Information Management |author=Gandomi, A.; Haider, M. |volume=35 |issue=2 |pages=137–44 |year=2015 |doi=10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2014.10.007}}</ref> Big data describes data collections of a size difficult to process with traditional data management techniques. While many definitions of big data concentrate on the aspect of volume referring to the scale of data available, big data brings in particular heterogeneous formats and a broad spectrum of possible data sources. Examples are structured numeric data or unstructured data such as text, images, or videos. This variety and broad landscape of data sources offers many opportunities for generating insights. Moreover, the speed of data creation enables rapid insights in ongoing developments. | |||
Recent technical improvements (e.g., [[cloud computing]], big data architectures) enable data to be analyzed and stored on a large scale. For many (new) types of data, their exact business value is unclear so far and requires systematic exploration. Available data is often messy, and even when cleaned up can be overwhelming and too complex to be easily understood, even by professional data scientists. The contribution of data is, of course, context specific and varies among business cases and applications. One key challenge is to identify data that best meets the business requirement. | |||
===Analytics=== | |||
Data science is concerned with knowledge generation from data. Analytics or data science addresses the exploration of data sets with different quantitative methods motivated from statistical modelling<ref name="JamesAnInto15">{{cite book |title=An Introduction to Statistical Learning with Applications in R |author=James, G.; Witten, D.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. |publisher=Springer |edition=6th |year=2015 |doi=9781461471387}}</ref> or machine learning.<ref name="MitchellMachine97">{{cite book |title=Machine Learning |author=Mitchell, T.M. |publisher=McGraw-Hill Education |edition=1st |year=1997 |doi=9780070428072}}</ref> Methods from different disciplines such as statistics, economics, or computer science find application to identify patterns, influence factors, or dependencies. In contrast to business intelligence, analytics reaches further than descriptive analytics (based on SQL) and often has a predictive component. Which method to apply depends on the exact business case. Analyzing data is restricted, for example, by a company’s internal policies as well as legal restrictions and guidelines that vary among countries. Data quality and reliability are further issues. Data understanding and domain knowledge are key prerequisites in the analysis process (e.g., Waller & Fawcett<ref name="WallerData13">{{cite journal |title=Data Science, Predictive Analytics, and Big Data: A Revolution That Will Transform Supply Chain Design and Management |journal=Journal of Business Logistics |author=Waller, M.A.; Fawcett, S.E. |volume=34 |issue=2 |pages=77–84 |year=2013 |doi=10.1111/jbl.12010}}</ref>), especially when model assumptions are made. | |||
Concerning data analysis, there are primarily the following opportunities for organizations: | |||
* Improved analysis of internal data: One example is forecasting methods that enhance expert-based planning approaches by additional figures. These methods build on existing databases such as business intelligence systems, and they contribute new or further insights to internal firm processes. | |||
* Putting data together in new ways: New combinations of data sets offer new insights, for example, through the combination of sensor data and user profiles. | |||
* Opening up to new or (so far) unused data sources (e.g., websites, open data) to identify potential for generating new insights: However, a context or application is necessary to use the data. One example is social media data used for market observation. | |||
However, the core problem of analytics is to work out the guiding question and achieve a match between business need, data source, and analysis as discussed later in the article. | |||
===IT infrastructure=== | |||
Relevant for the successful implementation of analytics is the adaption of the IT infrastructure to embed analytics solutions and integrate different data sources. The core layers of an IT infrastructure are the: | |||
# '''Data ingestion layer''': This layer covers the data transfer from a source system to an analytics environment. Therefore, a toolset and a corresponding process need to be defined. Traditional extract, transform, load (ETL) tools and relational databases are combined with Hadoop/big data setups covering, in particular, scenarios caused by less structured, high-volume, or streamed data. Analytics use cases build on data from data warehouses to fully unstructured data. This breadth challenges classic architectures and requires adaptable schemes. Which data sources to integrate depends on the specific application. | |||
# '''Data value exploration layer''': Based on the business need and corresponding use case, data is investigated, tested, and sampled in this layer. Depending on the complexity and business question, an appropriate analytics scheme is developed. Business and explorative analysis based on online analytical processing (OLAP) models in memory technologies are supplemented or expanded by using advanced analytics methods and integrating (e.g., R or Python plugins). | |||
# '''Data consumption layer''': Here, the results are used for visualization, for example. The end user can consume the data or service without deep technical understanding (e.g., for self-service business intelligence). | |||
Modern approaches require structures that are adaptable and scalable to different requirements and data sources. Factors such as system performance, cost efficiency, and overall enterprise infrastructure strategy must be taken into consideration. | |||
==From data to value: Turning ideas into applications== | |||
Organizations still struggle to use data meaningfully or lack the right competencies. One of the key challenges in analytics projects is identifying the business need and the guiding questions. Principally, different types of analytics problems arise in an organizational context ranging from precise requests that only lack specific capabilities to a principal interest in working with big data (e.g., no own infrastructure, expert-based approaches). This approach implies different starting points for the analytics process and different innovation pathways, both of which are described later in this article. | |||
===What is the starting point?=== | |||
The starting point for each analytics initiative varies. According to the four points mentioned above, the “state of the art” for each one needs to be assessed individually to estimate the analytics maturity: | |||
Revision as of 18:06, 24 July 2018
| Full article title | Data science as an innovation challenge: From big data to value proposition |
|---|---|
| Journal | Technology Innovation Management Review |
| Author(s) | Kayser, Victoria; Nehrke, Bastian; Zubovic, Damir |
| Author affiliation(s) | Ernst & Young |
| Year published | 2018 |
| Volume and issue | 8(3) |
| Page(s) | 16–25 |
| DOI | 10.22215/timreview/1143 |
| ISSN | 1927-0321 |
| Distribution license | Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported |
| Website | https://timreview.ca/article/1143 |
| Download | https://timreview.ca/sites/default/files/article_PDF/Kayser_et_al_TIMReview_March2018.pdf (PDF) |
|
|
This article should not be considered complete until this message box has been removed. This is a work in progress. |
Abstract
Analyzing “big data” holds huge potential for generating business value. The ongoing advancement of tools and technology over recent years has created a new ecosystem full of opportunities for data-driven innovation. However, as the amount of available data rises to new heights, so too does complexity. Organizations are challenged to create the right contexts, by shaping interfaces and processes, and by asking the right questions to guide the data analysis. Lifting the innovation potential requires teaming and focus to efficiently assign available resources to the most promising initiatives. With reference to the innovation process, this article will concentrate on establishing a process for analytics projects from first ideas to realization (in most cases, a running application). The question we tackle is: what can the practical discourse on big data and analytics learn from innovation management? The insights presented in this article are built on our practical experiences in working with various clients. We will classify analytics projects as well as discuss common innovation barriers along this process.
Keywords: analytics, big data, digital innovation, idea generation, innovation process
Introduction
Understandably, much effort is being expended into analyzing “big data” to unleash its potentially enormous business value.[1][2] New data sources evolve, and new techniques for storing and analyzing large data sets are enabling many new applications, but the exact business value of any one big data application is often unclear. From a practical viewpoint, organizations still struggle to use data meaningfully or they lack the right competencies. Different types of analytics problems arise in an organizational context, depending on whether the starting point is a precise request from a department that only lacks required skills or capabilities (e.g., machine learning) or rather it stems from a principal interest in working with big data (e.g., no own infrastructure, no methodical experience). So far, clear strategies and process for value generation from data are often missing.
Much literature addresses the technical and methodical implementation, the transformative strength of big data[3], the enhancement of firm performance by building analytics capability[4], or other managerial issues[5][1] Little work covers the transformation process from first ideas to ready analytics applications or in building analytics competence. This article seeks to address this gap.
Analytics initiatives have several unique features. First, they require an exploratory approach—the analysis does not start with specific requirements as in other projects but rather with an idea or data set. To assess the contribution, ideation techniques and rapid prototyping are applied. This exploration plays a key role in developing a shared understanding and giving a big data initiative a strategic direction. Second, analytics projects in their early phase are bound to a complex interplay between different stakeholder interests, competencies, and viewpoints. Learning is an integral part of these projects to build experience and competence with analytics. Third, analytics projects run in parallel to the existing information technology (IT) infrastructure and deliver short scripts or strategic insights, which are then installed in larger IT projects. Due to a missing end-to-end target, data is not only to be extracted, transformed, and loaded, but also needs to be identified, classified, and partly structured. So, a general process for value generation needs to be established to guide analytics projects and address these issues.
Here, we propose an exact configuration and series of steps to guide a big data analytics project. The lack of specified requirements and defined project goals in a big data analytics project (compared to a classic analytics project) make it challenging to structure the analytics process. Therefore, the linear innovation process serves as reference and orientation.[6] As Braganza and colleagues[7] describe, for big data to be successfully integrated and implemented in an organization, clear and repeatable processes are required. Nevertheless, each analytics initiative is different and the process needs to flexible. Unfortunately, the literature rarely combines challenges in the analytics process with concepts from innovation management. Nevertheless, an integration of the concepts from innovation management could guide the analytics work of formulating digital strategies, organizational anchoring of the analytics units and their functions, and designing the analytics portfolio, as well as the underlying working principles (e.g., rapid prototyping, ideation techniques).
Thus, in this article, we will concentrate on the question of what the practical discourse and work on analytics respectively implementing big data in organizations can learn from innovation management. A process for analytics innovation is introduced to guide the process from ideation to value generation. Emphasis is put on challenges during this process as well as different entry points. Thereby, we build on experience and insights from a number of analytics projects for different sectors and domains to derive recommendations for successfully implementing analytics solutions.
We begin with a definition of big data and analytics. Next, we propose a process for a structured approach to retrieving value from data. Finally, we discuss the results and outline directions for future research.
Big data and analytics
In this section, we address the elementary angles from which the analytics value chain should be looked at (Figure 1): data, infrastructure, and analytics–and the business need as the driver. According to our understanding, value is generated by analyzing data within a certain context, with a problem statement related to a business requirement driving the need for innovation. Besides expertise in conducting data and analytics projects, this process requires a working infrastructure, especially when volume, velocity, or variety of data to be analyzed exceeds certain limits. Below, we describe the three technical angles in more detail.
|
Data
Big data is often defined with volume (how much data), velocity (speed of data generation), and variety as the diversity of data types.[8][9] Big data describes data collections of a size difficult to process with traditional data management techniques. While many definitions of big data concentrate on the aspect of volume referring to the scale of data available, big data brings in particular heterogeneous formats and a broad spectrum of possible data sources. Examples are structured numeric data or unstructured data such as text, images, or videos. This variety and broad landscape of data sources offers many opportunities for generating insights. Moreover, the speed of data creation enables rapid insights in ongoing developments.
Recent technical improvements (e.g., cloud computing, big data architectures) enable data to be analyzed and stored on a large scale. For many (new) types of data, their exact business value is unclear so far and requires systematic exploration. Available data is often messy, and even when cleaned up can be overwhelming and too complex to be easily understood, even by professional data scientists. The contribution of data is, of course, context specific and varies among business cases and applications. One key challenge is to identify data that best meets the business requirement.
Analytics
Data science is concerned with knowledge generation from data. Analytics or data science addresses the exploration of data sets with different quantitative methods motivated from statistical modelling[10] or machine learning.[11] Methods from different disciplines such as statistics, economics, or computer science find application to identify patterns, influence factors, or dependencies. In contrast to business intelligence, analytics reaches further than descriptive analytics (based on SQL) and often has a predictive component. Which method to apply depends on the exact business case. Analyzing data is restricted, for example, by a company’s internal policies as well as legal restrictions and guidelines that vary among countries. Data quality and reliability are further issues. Data understanding and domain knowledge are key prerequisites in the analysis process (e.g., Waller & Fawcett[12]), especially when model assumptions are made.
Concerning data analysis, there are primarily the following opportunities for organizations:
- Improved analysis of internal data: One example is forecasting methods that enhance expert-based planning approaches by additional figures. These methods build on existing databases such as business intelligence systems, and they contribute new or further insights to internal firm processes.
- Putting data together in new ways: New combinations of data sets offer new insights, for example, through the combination of sensor data and user profiles.
- Opening up to new or (so far) unused data sources (e.g., websites, open data) to identify potential for generating new insights: However, a context or application is necessary to use the data. One example is social media data used for market observation.
However, the core problem of analytics is to work out the guiding question and achieve a match between business need, data source, and analysis as discussed later in the article.
IT infrastructure
Relevant for the successful implementation of analytics is the adaption of the IT infrastructure to embed analytics solutions and integrate different data sources. The core layers of an IT infrastructure are the:
- Data ingestion layer: This layer covers the data transfer from a source system to an analytics environment. Therefore, a toolset and a corresponding process need to be defined. Traditional extract, transform, load (ETL) tools and relational databases are combined with Hadoop/big data setups covering, in particular, scenarios caused by less structured, high-volume, or streamed data. Analytics use cases build on data from data warehouses to fully unstructured data. This breadth challenges classic architectures and requires adaptable schemes. Which data sources to integrate depends on the specific application.
- Data value exploration layer: Based on the business need and corresponding use case, data is investigated, tested, and sampled in this layer. Depending on the complexity and business question, an appropriate analytics scheme is developed. Business and explorative analysis based on online analytical processing (OLAP) models in memory technologies are supplemented or expanded by using advanced analytics methods and integrating (e.g., R or Python plugins).
- Data consumption layer: Here, the results are used for visualization, for example. The end user can consume the data or service without deep technical understanding (e.g., for self-service business intelligence).
Modern approaches require structures that are adaptable and scalable to different requirements and data sources. Factors such as system performance, cost efficiency, and overall enterprise infrastructure strategy must be taken into consideration.
From data to value: Turning ideas into applications
Organizations still struggle to use data meaningfully or lack the right competencies. One of the key challenges in analytics projects is identifying the business need and the guiding questions. Principally, different types of analytics problems arise in an organizational context ranging from precise requests that only lack specific capabilities to a principal interest in working with big data (e.g., no own infrastructure, expert-based approaches). This approach implies different starting points for the analytics process and different innovation pathways, both of which are described later in this article.
What is the starting point?
The starting point for each analytics initiative varies. According to the four points mentioned above, the “state of the art” for each one needs to be assessed individually to estimate the analytics maturity:
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 McAfee, A.; Byrnjolfsson, E. (2012). "Big data: The management revolution". Harvard Business Review 90 (10): 60–8. PMID 23074865.
- ↑ Wamba, S.F.; Gunasekaran, A.; Akter, S. et al. (2017). "Big data analytics and firm performance: Effects of dynamic capabilities". Journal of Business Research 70: 356–65. doi:10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.08.009.
- ↑ Wamba, S.F.; Akter, S.; Edwards, A. et al. (2015). "How ‘big data’ can make big impact: Findings from a systematic review and a longitudinal case study". International Journal of Production Economics 165: 234-46. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2014.12.031.
- ↑ Akter, S.; Wamba, S.F.; Gunasekaran, A. et al. (2016). "How to improve firm performance using big data analytics capability and business strategy alignment?". International Journal of Production Economics 182: 113–31. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2016.08.018.
- ↑ Devenport, T.H.; Harris, J.G. (2007). Competing on Analytics: The New Science of Winning. Harvard Business School Press. pp. 240. ISBN 9781422103326.
- ↑ Cooper, R.G. (1990). "Stage-gate systems: A new tool for managing new products". Business Horizons 33 (3): 44–54. doi:10.1016/0007-6813(90)90040-I.
- ↑ Braganza, A.; Brooks, L.; Nepelski, D. et al. (2017). "Resource management in big data initiatives: Processes and dynamic capabilities". Journal of Business Research 70: 328–37. doi:10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.08.006.
- ↑ Philip Chen, C.L.; Zhang, C.Y. (2014). "Data-intensive applications, challenges, techniques and technologies: A survey on Big Data". Information Sciences 275: 314-347. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2014.01.015.
- ↑ Gandomi, A.; Haider, M. (2015). "Beyond the hype: Big data concepts, methods, and analytics". International Journal of Information Management 35 (2): 137–44. doi:10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2014.10.007.
- ↑ James, G.; Witten, D.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. (2015). An Introduction to Statistical Learning with Applications in R (6th ed.). Springer. doi:9781461471387.
- ↑ Mitchell, T.M. (1997). Machine Learning (1st ed.). McGraw-Hill Education. doi:9780070428072.
- ↑ Waller, M.A.; Fawcett, S.E. (2013). "Data Science, Predictive Analytics, and Big Data: A Revolution That Will Transform Supply Chain Design and Management". Journal of Business Logistics 34 (2): 77–84. doi:10.1111/jbl.12010.
Notes
This presentation is faithful to the original, with only a few minor changes to presentation and grammar. In some cases important information was missing from the references, and that information was added. The original article lists references alphabetically, but this version — by design — lists them in order of appearance.