Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig2 Casey ForensicSciInt2020 316.jpg|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Digital transformation risk management in forensic science laboratories|Digital transformation risk management in forensic science laboratories]]"''' | ||
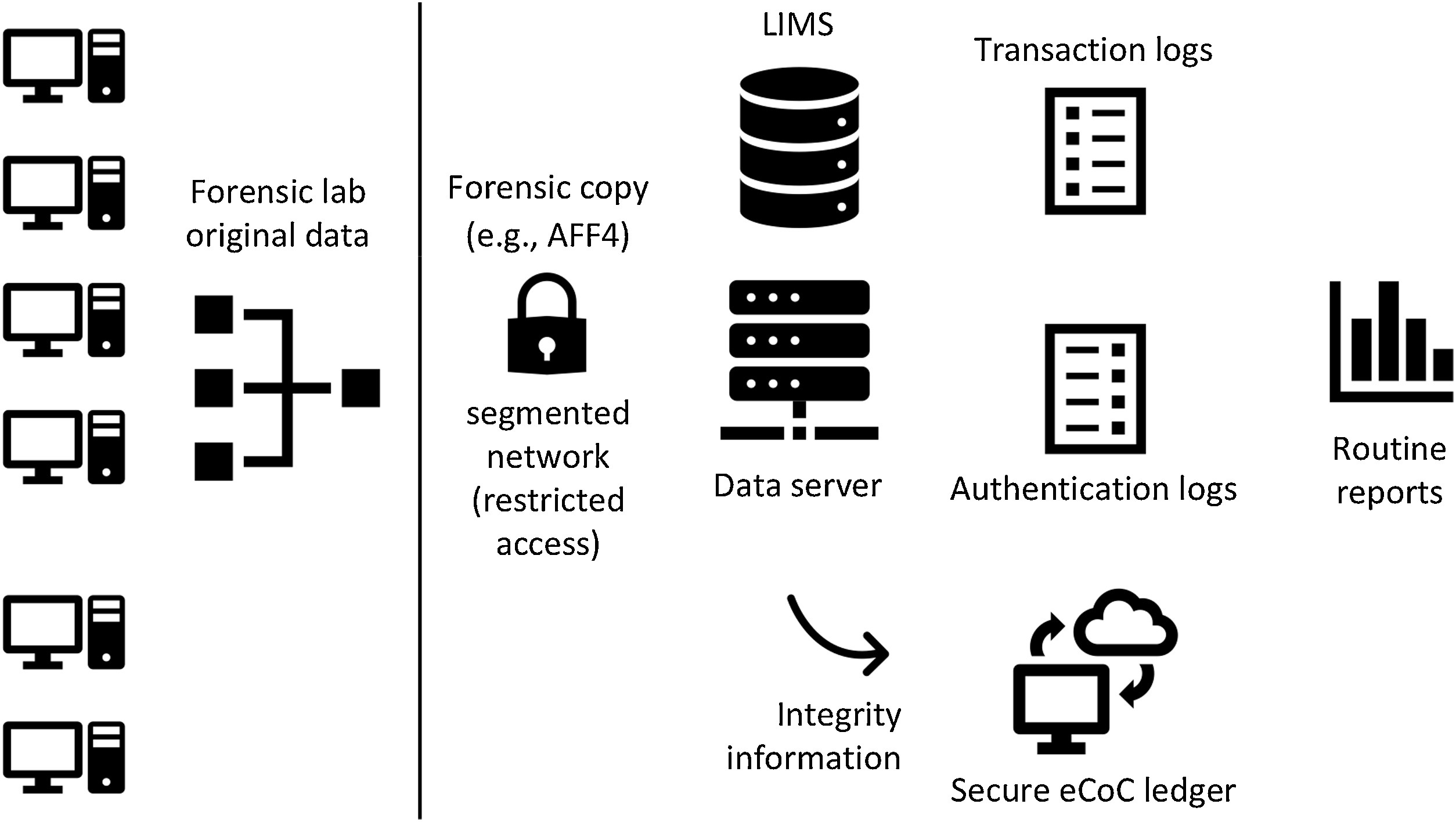
Technological advances are changing how [[Forensic laboratory|forensic laboratories]] operate in all [[Forensic science|forensic disciplines]], not only digital. Computers support [[workflow]] management and enable evidence analysis (physical and digital), while new technology enables previously unavailable forensic capabilities. Used properly, the integration of digital systems supports greater efficiency and reproducibility, and drives digital transformation of forensic laboratories. However, without the necessary preparations, these digital transformations can undermine the core principles and processes of forensic laboratories. Forensic preparedness concentrating on digital data reduces the cost and operational disruption of responding to various kinds of problems, including misplaced exhibits, allegations of employee misconduct, disclosure requirements, and information security breaches ... ('''[[Journal:Digital transformation risk management in forensic science laboratories|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
{{flowlist | | {{flowlist | | ||
* [[Journal:Named data networking for genomics data management and integrated workflows|Named data networking for genomics data management and integrated workflows]] | |||
* [[Journal:Implement an international interoperable PHR by FHIR: A Taiwan innovative application|Implement an international interoperable PHR by FHIR: A Taiwan innovative application]] | * [[Journal:Implement an international interoperable PHR by FHIR: A Taiwan innovative application|Implement an international interoperable PHR by FHIR: A Taiwan innovative application]] | ||
* [[Journal:Towards a risk catalog for data management plans|Towards a risk catalog for data management plans]] | * [[Journal:Towards a risk catalog for data management plans|Towards a risk catalog for data management plans]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 18:56, 17 January 2022
"Digital transformation risk management in forensic science laboratories"
Technological advances are changing how forensic laboratories operate in all forensic disciplines, not only digital. Computers support workflow management and enable evidence analysis (physical and digital), while new technology enables previously unavailable forensic capabilities. Used properly, the integration of digital systems supports greater efficiency and reproducibility, and drives digital transformation of forensic laboratories. However, without the necessary preparations, these digital transformations can undermine the core principles and processes of forensic laboratories. Forensic preparedness concentrating on digital data reduces the cost and operational disruption of responding to various kinds of problems, including misplaced exhibits, allegations of employee misconduct, disclosure requirements, and information security breaches ... (Full article...)
Recently featured: