Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig4 Jofre ApplSci2021 11-15.png|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Cybersecurity and privacy risk assessment of point-of-care systems in healthcare: A use case approach|Cybersecurity and privacy risk assessment of point-of-care systems in healthcare: A use case approach]]"''' | ||
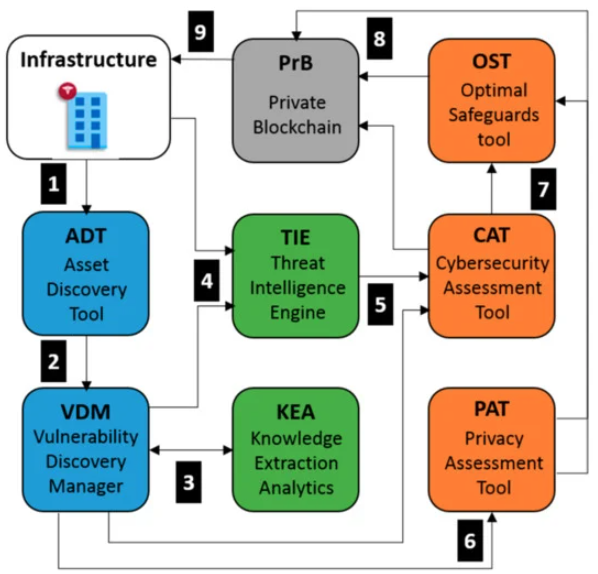
[[Point-of-care testing|Point-of-care]] (POC) systems are generally used in healthcare to respond rapidly and prevent critical health conditions. Hence, POC systems often handle personal [[Health informatics|health information]], and, consequently, their [[cybersecurity]] and [[Information privacy|privacy]] requirements are of crucial importance. However, assessing these requirements is a significant task. In this work, we propose a use-case approach to assess specifications of cybersecurity and privacy requirements of POC systems in a structured and self-contained form. Such an approach is appropriate since use cases are one of the most common means adopted by developers to derive requirements. As a result, we detail a use case approach in the framework of a real-based healthcare IT infrastructure that includes a [[Health information technology|health information system]], [[Message broker|integration engines]], application servers, web services, [[medical device]]s, smartphone apps, and medical modalities (all data simulated) together with the interaction with participants. Since our use case also sustains the analysis of cybersecurity and privacy risks in different threat scenarios, it also supports decision making and the analysis of compliance considerations. ('''[[Journal:Cybersecurity and privacy risk assessment of point-of-care systems in healthcare: A use case approach|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
{{flowlist | | {{flowlist | | ||
* [[Journal:Fostering reproducibility, reusability, and technology transfer in health informatics|Fostering reproducibility, reusability, and technology transfer in health informatics]] | |||
* [[Journal:Development of a core competency framework for clinical informatics|Development of a core competency framework for clinical informatics]] | * [[Journal:Development of a core competency framework for clinical informatics|Development of a core competency framework for clinical informatics]] | ||
* [[Journal:Strategies for laboratory professionals to drive laboratory stewardship|Strategies for laboratory professionals to drive laboratory stewardship]] | * [[Journal:Strategies for laboratory professionals to drive laboratory stewardship|Strategies for laboratory professionals to drive laboratory stewardship]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 18:04, 23 May 2022
Point-of-care (POC) systems are generally used in healthcare to respond rapidly and prevent critical health conditions. Hence, POC systems often handle personal health information, and, consequently, their cybersecurity and privacy requirements are of crucial importance. However, assessing these requirements is a significant task. In this work, we propose a use-case approach to assess specifications of cybersecurity and privacy requirements of POC systems in a structured and self-contained form. Such an approach is appropriate since use cases are one of the most common means adopted by developers to derive requirements. As a result, we detail a use case approach in the framework of a real-based healthcare IT infrastructure that includes a health information system, integration engines, application servers, web services, medical devices, smartphone apps, and medical modalities (all data simulated) together with the interaction with participants. Since our use case also sustains the analysis of cybersecurity and privacy risks in different threat scenarios, it also supports decision making and the analysis of compliance considerations. (Full article...)
Recently featured: