Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| (472 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Scroggie DigDisc2023 2.gif|240px]]</div> | ||
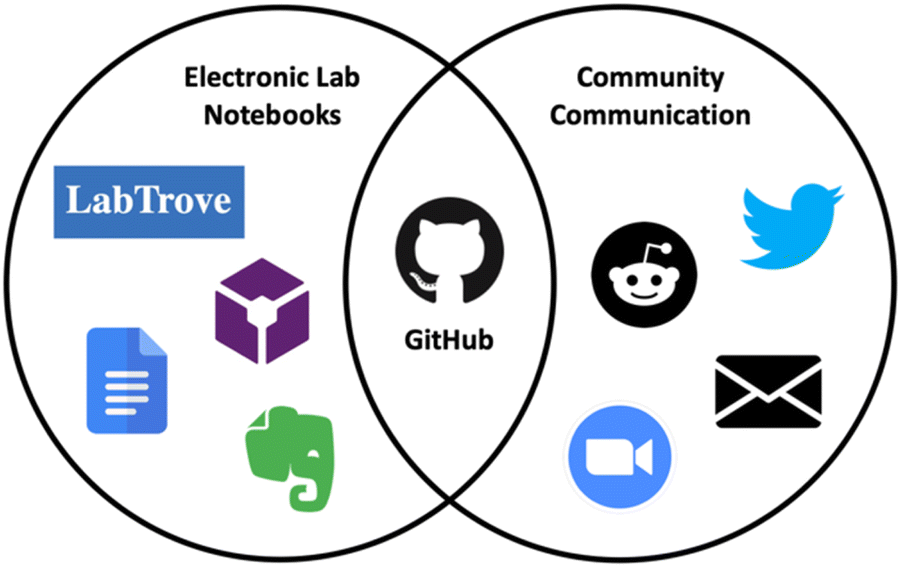
'''"[[Journal:GitHub as an open electronic laboratory notebook for real-time sharing of knowledge and collaboration|GitHub as an open electronic laboratory notebook for real-time sharing of knowledge and collaboration]]"''' | |||
[[Electronic laboratory notebook]]s (ELNs) have expanded the utility of the paper [[laboratory notebook]] beyond that of a simple record keeping tool. Open ELNs offer additional benefits to the scientific community, including increased transparency, reproducibility, and [[Data integrity|integrity]]. A key element underpinning these benefits is facile and expedient knowledge sharing which aids communication and collaboration. In previous projects, we have used [[LabTrove]] and [[LabArchives, LLC|LabArchives]] as open ELNs, in partnership with GitHub (an open-source web-based platform originally developed for collaborative coding) for communication and discussion. Here we present our personal experiences using GitHub as the central platform for many aspects of the scientific process ... ('''[[Journal:GitHub as an open electronic laboratory notebook for real-time sharing of knowledge and collaboration|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | ''Recently featured'': | ||
''Recently featured'': [[ | {{flowlist | | ||
* [[Journal:SODAR: Managing multiomics study data and metadata|SODAR: Managing multiomics study data and metadata]] | |||
* [[Journal:Benefits of information technology in healthcare: Artificial intelligence, internet of things, and personal health records|Benefits of information technology in healthcare: Artificial intelligence, internet of things, and personal health records]] | |||
* [[Journal:A quality assurance discrimination tool for the evaluation of satellite laboratory practice excellence in the context of European regulatory meat inspection for Trichinella spp.|A quality assurance discrimination tool for the evaluation of satellite laboratory practice excellence in the context of European regulatory meat inspection for ''Trichinella spp.'']] | |||
}} | |||
Revision as of 16:20, 26 March 2024
Electronic laboratory notebooks (ELNs) have expanded the utility of the paper laboratory notebook beyond that of a simple record keeping tool. Open ELNs offer additional benefits to the scientific community, including increased transparency, reproducibility, and integrity. A key element underpinning these benefits is facile and expedient knowledge sharing which aids communication and collaboration. In previous projects, we have used LabTrove and LabArchives as open ELNs, in partnership with GitHub (an open-source web-based platform originally developed for collaborative coding) for communication and discussion. Here we present our personal experiences using GitHub as the central platform for many aspects of the scientific process ... (Full article...)
Recently featured:
- SODAR: Managing multiomics study data and metadata
- Benefits of information technology in healthcare: Artificial intelligence, internet of things, and personal health records
- A quality assurance discrimination tool for the evaluation of satellite laboratory practice excellence in the context of European regulatory meat inspection for Trichinella spp.