Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| (281 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Tab1 Williamson F1000Res2023 10.png|240px]]</div> | ||
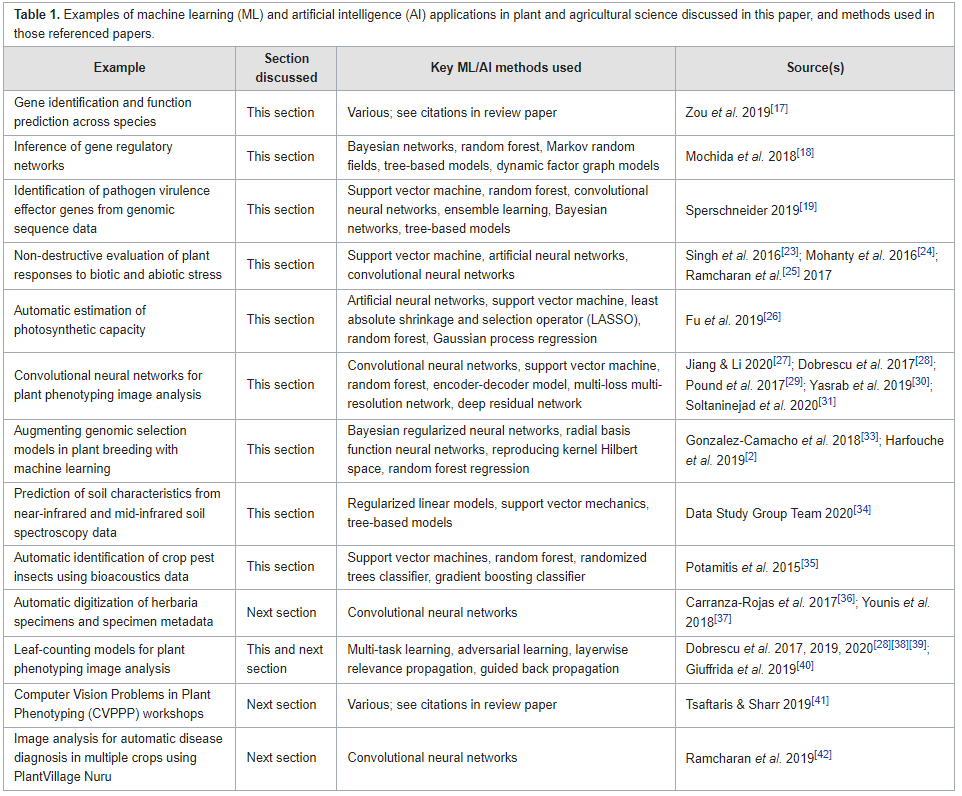
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Data management challenges for artificial intelligence in plant and agricultural research|Data management challenges for artificial intelligence in plant and agricultural research]]"''' | ||
[[Artificial intelligence]] (AI) is increasingly used within plant science, yet it is far from being routinely and effectively implemented in this domain. Particularly relevant to the development of novel food and agricultural technologies is the development of validated, meaningful, and usable ways to integrate, compare, and [[Data visualization|visualize]] large, multi-dimensional datasets from different sources and scientific approaches. After a brief summary of the reasons for the interest in data science and AI within plant science, the paper identifies and discusses eight key challenges in [[Information management|data management]] that must be addressed to further unlock the potential of AI in crop and agronomic research, and particularly the application of [[machine learning]] (ML), which holds much promise for this domain ... ('''[[Journal:Data management challenges for artificial intelligence in plant and agricultural research|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
''Recently featured'': | |||
{{flowlist | | |||
<br /> | * [[Journal:A blockchain-driven IoT-based food quality traceability system for dairy products using a deep learning model|A blockchain-driven IoT-based food quality traceability system for dairy products using a deep learning model]] | ||
''Recently featured'': | * [[Journal:Effect of good clinical laboratory practices (GCLP) quality training on knowledge, attitude, and practice among laboratory professionals: Quasi-experimental study|Effect of good clinical laboratory practices (GCLP) quality training on knowledge, attitude, and practice among laboratory professionals: Quasi-experimental study]] | ||
* [[Journal:GitHub as an open electronic laboratory notebook for real-time sharing of knowledge and collaboration|GitHub as an open electronic laboratory notebook for real-time sharing of knowledge and collaboration]] | |||
}} | |||
Revision as of 17:50, 15 April 2024
"Data management challenges for artificial intelligence in plant and agricultural research"
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly used within plant science, yet it is far from being routinely and effectively implemented in this domain. Particularly relevant to the development of novel food and agricultural technologies is the development of validated, meaningful, and usable ways to integrate, compare, and visualize large, multi-dimensional datasets from different sources and scientific approaches. After a brief summary of the reasons for the interest in data science and AI within plant science, the paper identifies and discusses eight key challenges in data management that must be addressed to further unlock the potential of AI in crop and agronomic research, and particularly the application of machine learning (ML), which holds much promise for this domain ... (Full article...)
Recently featured:
- A blockchain-driven IoT-based food quality traceability system for dairy products using a deep learning model
- Effect of good clinical laboratory practices (GCLP) quality training on knowledge, attitude, and practice among laboratory professionals: Quasi-experimental study
- GitHub as an open electronic laboratory notebook for real-time sharing of knowledge and collaboration