Difference between revisions of "Main Page/Featured article of the week/2018"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Added last week's article of the week.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Added last week's article of the week.) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
<!-- Below this line begin pasting previous news --> | <!-- Below this line begin pasting previous news --> | ||
<h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: January 8–14:</h2> | <h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: January 15–21:</h2> | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Imborek JPathInfo2017 8.jpg|240px]]</div> | |||
'''"[[Journal:Preferred names, preferred pronouns, and gender identity in the electronic medical record and laboratory information system: Is pathology ready?|Preferred names, preferred pronouns, and gender identity in the electronic medical record and laboratory information system: Is pathology ready?]]"''' | |||
[[Electronic medical record]]s (EMRs) and [[laboratory information system]]s (LISs) commonly utilize patient identifiers such as legal name, sex, medical record number, and date of birth. There have been recommendations from some EMR working groups (e.g., the World Professional Association for Transgender Health) to include preferred name, pronoun preference, assigned sex at birth, and gender identity in the EMR. These practices are currently uncommon in the United States. There has been little published on the potential impact of these changes on pathology and LISs. We review the available literature and guidelines on the use of preferred name and gender identity on pathology, including data on changes in [[laboratory]] testing following gender transition treatments. We also describe pathology and clinical laboratory challenges in the implementation of preferred name at our institution. ('''[[Journal:Preferred names, preferred pronouns, and gender identity in the electronic medical record and laboratory information system: Is pathology ready?|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: January 8–14:</h2> | |||
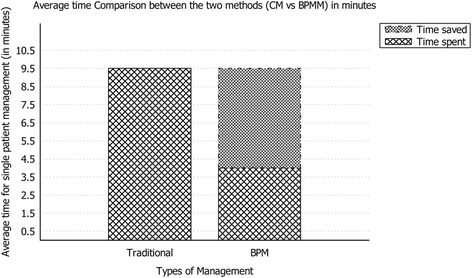
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig4 Andellini BMCMedInfoDecMak2017 17-1.gif|240px]]</div> | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig4 Andellini BMCMedInfoDecMak2017 17-1.gif|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal:Experimental application of business process management technology to manage clinical pathways: A pediatric kidney transplantation follow-up case|Experimental application of business process management technology to manage clinical pathways: A pediatric kidney transplantation follow-up case]]"''' | '''"[[Journal:Experimental application of business process management technology to manage clinical pathways: A pediatric kidney transplantation follow-up case|Experimental application of business process management technology to manage clinical pathways: A pediatric kidney transplantation follow-up case]]"''' | ||
Revision as of 17:11, 23 January 2018
|
|
If you're looking for other "Article of the Week" archives: 2014 - 2015 - 2016 - 2017 - 2018 |
Featured article of the week archive - 2018
Welcome to the LIMSwiki 2018 archive for the Featured Article of the Week.
Featured article of the week: January 15–21:Electronic medical records (EMRs) and laboratory information systems (LISs) commonly utilize patient identifiers such as legal name, sex, medical record number, and date of birth. There have been recommendations from some EMR working groups (e.g., the World Professional Association for Transgender Health) to include preferred name, pronoun preference, assigned sex at birth, and gender identity in the EMR. These practices are currently uncommon in the United States. There has been little published on the potential impact of these changes on pathology and LISs. We review the available literature and guidelines on the use of preferred name and gender identity on pathology, including data on changes in laboratory testing following gender transition treatments. We also describe pathology and clinical laboratory challenges in the implementation of preferred name at our institution. (Full article...)
|