Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| (28 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Niszczota EconBusRev23 9-2.png|240px]]</div> | ||
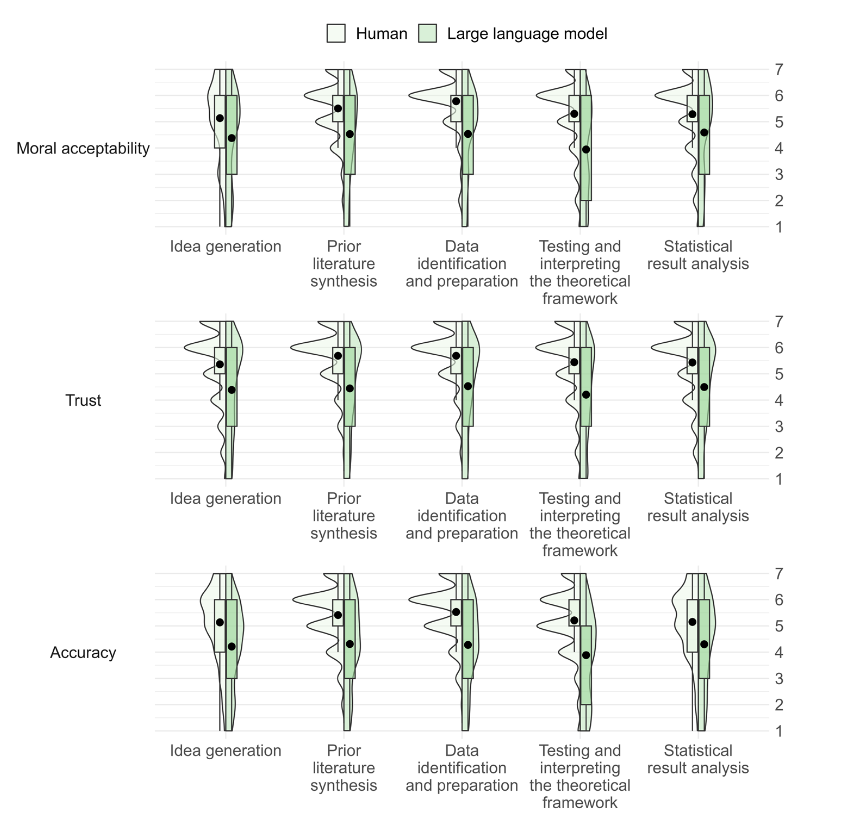
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Judgements of research co-created by generative AI: Experimental evidence|Judgements of research co-created by generative AI: Experimental evidence]]"''' | ||
The introduction of [[ChatGPT]] has fuelled a public debate on the appropriateness of using generative [[artificial intelligence]] (AI) ([[large language model]]s or LLMs) in work, including a debate on how they might be used (and abused) by researchers. In the current work, we test whether delegating parts of the research process to LLMs leads people to distrust researchers and devalues their scientific work. Participants (''N'' = 402) considered a researcher who delegates elements of the research process to a PhD student or LLM and rated three aspects of such delegation. Firstly, they rated whether it is morally appropriate to do so. Secondly, they judged whether—after deciding to delegate the research process—they would trust the scientist (who decided to delegate) to oversee future projects ... ('''[[Journal:Judgements of research co-created by generative AI: Experimental evidence|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
{{flowlist | | {{flowlist | | ||
* [[Journal: | * [[Journal:Geochemical biodegraded oil classification using a machine learning approach|Geochemical biodegraded oil classification using a machine learning approach]] | ||
* [[Journal: | * [[Journal:Knowledge of internal quality control for laboratory tests among laboratory personnel working in a biochemistry department of a tertiary care center: A descriptive cross-sectional study|Knowledge of internal quality control for laboratory tests among laboratory personnel working in a biochemistry department of a tertiary care center: A descriptive cross-sectional study]] | ||
* [[Journal: | * [[Journal:Sigma metrics as a valuable tool for effective analytical performance and quality control planning in the clinical laboratory: A retrospective study|Sigma metrics as a valuable tool for effective analytical performance and quality control planning in the clinical laboratory: A retrospective study]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:26, 20 May 2024
"Judgements of research co-created by generative AI: Experimental evidence"
The introduction of ChatGPT has fuelled a public debate on the appropriateness of using generative artificial intelligence (AI) (large language models or LLMs) in work, including a debate on how they might be used (and abused) by researchers. In the current work, we test whether delegating parts of the research process to LLMs leads people to distrust researchers and devalues their scientific work. Participants (N = 402) considered a researcher who delegates elements of the research process to a PhD student or LLM and rated three aspects of such delegation. Firstly, they rated whether it is morally appropriate to do so. Secondly, they judged whether—after deciding to delegate the research process—they would trust the scientist (who decided to delegate) to oversee future projects ... (Full article...)
Recently featured:
- Geochemical biodegraded oil classification using a machine learning approach
- Knowledge of internal quality control for laboratory tests among laboratory personnel working in a biochemistry department of a tertiary care center: A descriptive cross-sectional study
- Sigma metrics as a valuable tool for effective analytical performance and quality control planning in the clinical laboratory: A retrospective study