Difference between revisions of "Journal:Sample identifiers and metadata to support data management and reuse in multidisciplinary ecosystem sciences"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Saving and adding more.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Saving and adding more.) |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
The study of natural ecosystems requires multidisciplinary science teams to understand and model processes from molecular to global scales.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Weart |first=Spencer |date=2013-02-26 |title=Rise of interdisciplinary research on climate |url=https://www.pnas.org/content/110/Supplement_1/3657 |journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences |volume=110 |issue=Supplement 1 |pages=3657–3664 |doi=10.1073/pnas.1107482109 |pmc=PMC3586608 |pmid=22778431}}</ref> Many research activities involve diverse collections of [[Sample (material)|samples]] and associated field or [[laboratory]] measurements.<ref name=":0">{{Cite journal |last=Devaraju, A.; Klump, J.; Cox, S.J.D. et al. |date=2016-11-01 |title=Representing and publishing physical sample descriptions |url=https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300416302023 |journal=Computers & Geosciences |language=en |volume=96 |pages=1–10 |doi=10.1016/j.cageo.2016.07.018 |issn=0098-3004}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Ponsero |first=Alise J |last2=Bomhoff |first2=Matthew |last3=Blumberg |first3=Kai |last4=Youens-Clark |first4=Ken |last5=Herz |first5=Nina M |last6=Wood-Charlson |first6=Elisha M |last7=Delong |first7=Edward F |last8=Hurwitz |first8=Bonnie L |date=2020-07-31 |title=Planet Microbe: a platform for marine microbiology to discover and analyze interconnected ‘omics and environmental data |url=https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/49/D1/D792/5879428 |journal=Nucleic Acids Research |volume=49 |issue=D1 |pages=D792–D802 |doi=10.1093/nar/gkaa637 |issn=0305-1048 |pmc=PMC7778950 |pmid=32735679}}</ref> For example, studies of organic matter cycling through plants and soil involves analysis of samples to represent soil biogeochemistry, microbial communities, plant structures, leaf gas exchange, and traits of the specific organisms involved.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Cordeiro |first=Amanda L. |last2=Norby |first2=Richard J. |last3=Andersen |first3=Kelly M. |last4=Valverde-Barrantes |first4=Oscar |last5=Fuchslueger |first5=Lucia |last6=Oblitas |first6=Erick |last7=Hartley |first7=Iain P. |last8=Iversen |first8=Colleen M. |last9=Gonçalves |first9=Nathan B. |last10=Takeshi |first10=Bruno |last11=Lapola |first11=David M. |date=2020 |title=Fine-root dynamics vary with soil depth and precipitation in a low-nutrient tropical forest in the Central Amazonia |url=https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/pei3.10010 |journal=Plant-Environment Interactions |language=en |volume=1 |issue=1 |pages=3–16 |doi=10.1002/pei3.10010 |issn=2575-6265}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Malik |first=Ashish A. |last2=Martiny |first2=Jennifer B. H. |last3=Brodie |first3=Eoin L. |last4=Martiny |first4=Adam C. |last5=Treseder |first5=Kathleen K. |last6=Allison |first6=Steven D. |date=2020-01 |title=Defining trait-based microbial strategies with consequences for soil carbon cycling under climate change |url=https://www.nature.com/articles/s41396-019-0510-0 |journal=The ISME Journal |language=en |volume=14 |issue=1 |pages=1–9 |doi=10.1038/s41396-019-0510-0 |issn=1751-7370 |pmc=PMC6908601 |pmid=31554911}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Treseder |first=Kathleen K. |last2=Balser |first2=Teri C. |last3=Bradford |first3=Mark A. |last4=Brodie |first4=Eoin L. |last5=Dubinsky |first5=Eric A. |last6=Eviner |first6=Valerie T. |last7=Hofmockel |first7=Kirsten S. |last8=Lennon |first8=Jay T. |last9=Levine |first9=Uri Y. |last10=MacGregor |first10=Barbara J. |last11=Pett-Ridge |first11=Jennifer |date=2011-09-03 |title=Integrating microbial ecology into ecosystem models: challenges and priorities |url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10533-011-9636-5 |journal=Biogeochemistry |volume=109 |issue=1-3 |pages=7–18 |doi=10.1007/s10533-011-9636-5 |issn=0168-2563}}</ref> Each scientific expert, project team, and discipline has a responsibility to ensure that others can interpret, integrate, and reuse their sample data to help solve emerging problems as our global environment continues to change.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Soranno |first=Patricia A. |last2=Schimel |first2=David S. |date=2014 |title=Macrosystems ecology: big data, big ecology |url=https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1890/1540-9295-12.1.3 |journal=Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment |language=en |volume=12 |issue=1 |pages=3–3 |doi=10.1890/1540-9295-12.1.3 |issn=1540-9309}}</ref> | The study of natural ecosystems requires multidisciplinary science teams to understand and model processes from molecular to global scales.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Weart |first=Spencer |date=2013-02-26 |title=Rise of interdisciplinary research on climate |url=https://www.pnas.org/content/110/Supplement_1/3657 |journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences |volume=110 |issue=Supplement 1 |pages=3657–3664 |doi=10.1073/pnas.1107482109 |pmc=PMC3586608 |pmid=22778431}}</ref> Many research activities involve diverse collections of [[Sample (material)|samples]] and associated field or [[laboratory]] measurements.<ref name=":0">{{Cite journal |last=Devaraju, A.; Klump, J.; Cox, S.J.D. et al. |date=2016-11-01 |title=Representing and publishing physical sample descriptions |url=https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300416302023 |journal=Computers & Geosciences |language=en |volume=96 |pages=1–10 |doi=10.1016/j.cageo.2016.07.018 |issn=0098-3004}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Ponsero |first=Alise J |last2=Bomhoff |first2=Matthew |last3=Blumberg |first3=Kai |last4=Youens-Clark |first4=Ken |last5=Herz |first5=Nina M |last6=Wood-Charlson |first6=Elisha M |last7=Delong |first7=Edward F |last8=Hurwitz |first8=Bonnie L |date=2020-07-31 |title=Planet Microbe: a platform for marine microbiology to discover and analyze interconnected ‘omics and environmental data |url=https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/49/D1/D792/5879428 |journal=Nucleic Acids Research |volume=49 |issue=D1 |pages=D792–D802 |doi=10.1093/nar/gkaa637 |issn=0305-1048 |pmc=PMC7778950 |pmid=32735679}}</ref> For example, studies of organic matter cycling through plants and soil involves analysis of samples to represent soil biogeochemistry, microbial communities, plant structures, leaf gas exchange, and traits of the specific organisms involved.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Cordeiro |first=Amanda L. |last2=Norby |first2=Richard J. |last3=Andersen |first3=Kelly M. |last4=Valverde-Barrantes |first4=Oscar |last5=Fuchslueger |first5=Lucia |last6=Oblitas |first6=Erick |last7=Hartley |first7=Iain P. |last8=Iversen |first8=Colleen M. |last9=Gonçalves |first9=Nathan B. |last10=Takeshi |first10=Bruno |last11=Lapola |first11=David M. |date=2020 |title=Fine-root dynamics vary with soil depth and precipitation in a low-nutrient tropical forest in the Central Amazonia |url=https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/pei3.10010 |journal=Plant-Environment Interactions |language=en |volume=1 |issue=1 |pages=3–16 |doi=10.1002/pei3.10010 |issn=2575-6265}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Malik |first=Ashish A. |last2=Martiny |first2=Jennifer B. H. |last3=Brodie |first3=Eoin L. |last4=Martiny |first4=Adam C. |last5=Treseder |first5=Kathleen K. |last6=Allison |first6=Steven D. |date=2020-01 |title=Defining trait-based microbial strategies with consequences for soil carbon cycling under climate change |url=https://www.nature.com/articles/s41396-019-0510-0 |journal=The ISME Journal |language=en |volume=14 |issue=1 |pages=1–9 |doi=10.1038/s41396-019-0510-0 |issn=1751-7370 |pmc=PMC6908601 |pmid=31554911}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Treseder |first=Kathleen K. |last2=Balser |first2=Teri C. |last3=Bradford |first3=Mark A. |last4=Brodie |first4=Eoin L. |last5=Dubinsky |first5=Eric A. |last6=Eviner |first6=Valerie T. |last7=Hofmockel |first7=Kirsten S. |last8=Lennon |first8=Jay T. |last9=Levine |first9=Uri Y. |last10=MacGregor |first10=Barbara J. |last11=Pett-Ridge |first11=Jennifer |date=2011-09-03 |title=Integrating microbial ecology into ecosystem models: challenges and priorities |url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10533-011-9636-5 |journal=Biogeochemistry |volume=109 |issue=1-3 |pages=7–18 |doi=10.1007/s10533-011-9636-5 |issn=0168-2563}}</ref> Each scientific expert, project team, and discipline has a responsibility to ensure that others can interpret, integrate, and reuse their sample data to help solve emerging problems as our global environment continues to change.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Soranno |first=Patricia A. |last2=Schimel |first2=David S. |date=2014 |title=Macrosystems ecology: big data, big ecology |url=https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1890/1540-9295-12.1.3 |journal=Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment |language=en |volume=12 |issue=1 |pages=3–3 |doi=10.1890/1540-9295-12.1.3 |issn=1540-9309}}</ref> | ||
Collaboration across disciplines requires a more unified approach to report basic information about key data entities, such as samples. One challenge in promoting a unified way of reporting sample data is that some research communities have already developed community-specific conventions, including those for [[omics]] samples<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Field |first=Dawn |last2=Amaral-Zettler |first2=Linda |last3=Cochrane |first3=Guy |last4=Cole |first4=James R. |last5=Dawyndt |first5=Peter |last6=Garrity |first6=George M. |last7=Gilbert |first7=Jack |last8=Glöckner |first8=Frank Oliver |last9=Hirschman |first9=Lynette |last10=Karsch-Mizrachi |first10=Ilene |last11=Klenk |first11=Hans-Peter |date=2011-06-21 |title=The Genomic Standards Consortium |url=https://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.1001088 |journal=PLOS Biology |language=en |volume=9 |issue=6 |pages=e1001088 |doi=10.1371/journal.pbio.1001088 |issn=1545-7885 |pmc=PMC3119656 |pmid=21713030}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Reddy |first=T.B.K. |last2=Thomas |first2=Alex D. |last3=Stamatis |first3=Dimitri |last4=Bertsch |first4=Jon |last5=Isbandi |first5=Michelle |last6=Jansson |first6=Jakob |last7=Mallajosyula |first7=Jyothi |last8=Pagani |first8=Ioanna |last9=Lobos |first9=Elizabeth A. |last10=Kyrpides |first10=Nikos C. |date=2014-10-27 |title=The Genomes OnLine Database (GOLD) v.5: a metadata management system based on a four level (meta)genome project classification |url=https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/43/D1/D1099/2439522 |journal=Nucleic Acids Research |volume=43 |issue=D1 |pages=D1099–D1106 |doi=10.1093/nar/gku950 |issn=1362-4962 |pmc=PMC4384021 |pmid=25348402}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Yilmaz |first=Pelin |last2=Kottmann |first2=Renzo |last3=Field |first3=Dawn |last4=Knight |first4=Rob |last5=Cole |first5=James R. |last6=Amaral-Zettler |first6=Linda |last7=Gilbert |first7=Jack A. |last8=Karsch-Mizrachi |first8=Ilene |last9=Johnston |first9=Anjanette |last10=Cochrane |first10=Guy |last11=Vaughan |first11=Robert |date=2011-05 |title=Minimum information about a marker gene sequence (MIMARKS) and minimum information about any (x) sequence (MIxS) specifications |url=https://www.nature.com/articles/nbt.1823 |journal=Nature Biotechnology |language=en |volume=29 |issue=5 |pages=415–420 |doi=10.1038/nbt.1823 |issn=1546-1696 |pmc=PMC3367316 |pmid=21552244}}</ref>, [[Biodiversity informatics|biodiversity records]]<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Wieczorek |first=John |last2=Bloom |first2=David |last3=Guralnick |first3=Robert |last4=Blum |first4=Stan |last5=Döring |first5=Markus |last6=Giovanni |first6=Renato |last7=Robertson |first7=Tim |last8=Vieglais |first8=David |date=2012-01-06 |title=Darwin Core: An Evolving Community-Developed Biodiversity Data Standard |url=https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0029715 |journal=PLOS ONE |language=en |volume=7 |issue=1 |pages=e29715 |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0029715 |issn=1932-6203 |pmc=PMC3253084 |pmid=22238640}}</ref>, and geoscience samples.<ref name=":0" /><ref>{{Cite journal |last=System For Earth Sample Registration (SESAR) |date=2020-02-06 |title=SESAR Batch Registration Quick Guide |url=https://zenodo.org/record/3874923 |language=en |doi=10.5281/ZENODO.3874923}}</ref> A larger challenge is that many researchers use no formal reporting conventions, or exclude [[information]] needed to interpret and reuse the data.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Roche |first=Dominique G. |last2=Kruuk |first2=Loeske E. B. |last3=Lanfear |first3=Robert |last4=Binning |first4=Sandra A. |date=2015-11-10 |title=Public Data Archiving in Ecology and Evolution: How Well Are We Doing? |url=https://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.1002295 |journal=PLOS Biology |language=en |volume=13 |issue=11 |pages=e1002295 |doi=10.1371/journal.pbio.1002295 |issn=1545-7885 |pmc=PMC4640582 |pmid=26556502}}</ref> More coordination is needed across these communities to develop a multidisciplinary reporting format for physical samples that is widely adopted, or to ensure that standards are interoperable. Common reporting would support effective discovery, integration, and reuse of sample data that spans scientific domains. | Collaboration across disciplines requires a more unified approach to report basic information about key data entities, such as samples. One challenge in promoting a unified way of reporting sample data is that some research communities have already developed community-specific conventions, including those for [[omics]] samples<ref name=":1">{{Cite journal |last=Field |first=Dawn |last2=Amaral-Zettler |first2=Linda |last3=Cochrane |first3=Guy |last4=Cole |first4=James R. |last5=Dawyndt |first5=Peter |last6=Garrity |first6=George M. |last7=Gilbert |first7=Jack |last8=Glöckner |first8=Frank Oliver |last9=Hirschman |first9=Lynette |last10=Karsch-Mizrachi |first10=Ilene |last11=Klenk |first11=Hans-Peter |date=2011-06-21 |title=The Genomic Standards Consortium |url=https://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.1001088 |journal=PLOS Biology |language=en |volume=9 |issue=6 |pages=e1001088 |doi=10.1371/journal.pbio.1001088 |issn=1545-7885 |pmc=PMC3119656 |pmid=21713030}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Reddy |first=T.B.K. |last2=Thomas |first2=Alex D. |last3=Stamatis |first3=Dimitri |last4=Bertsch |first4=Jon |last5=Isbandi |first5=Michelle |last6=Jansson |first6=Jakob |last7=Mallajosyula |first7=Jyothi |last8=Pagani |first8=Ioanna |last9=Lobos |first9=Elizabeth A. |last10=Kyrpides |first10=Nikos C. |date=2014-10-27 |title=The Genomes OnLine Database (GOLD) v.5: a metadata management system based on a four level (meta)genome project classification |url=https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/43/D1/D1099/2439522 |journal=Nucleic Acids Research |volume=43 |issue=D1 |pages=D1099–D1106 |doi=10.1093/nar/gku950 |issn=1362-4962 |pmc=PMC4384021 |pmid=25348402}}</ref><ref name=":2">{{Cite journal |last=Yilmaz |first=Pelin |last2=Kottmann |first2=Renzo |last3=Field |first3=Dawn |last4=Knight |first4=Rob |last5=Cole |first5=James R. |last6=Amaral-Zettler |first6=Linda |last7=Gilbert |first7=Jack A. |last8=Karsch-Mizrachi |first8=Ilene |last9=Johnston |first9=Anjanette |last10=Cochrane |first10=Guy |last11=Vaughan |first11=Robert |date=2011-05 |title=Minimum information about a marker gene sequence (MIMARKS) and minimum information about any (x) sequence (MIxS) specifications |url=https://www.nature.com/articles/nbt.1823 |journal=Nature Biotechnology |language=en |volume=29 |issue=5 |pages=415–420 |doi=10.1038/nbt.1823 |issn=1546-1696 |pmc=PMC3367316 |pmid=21552244}}</ref>, [[Biodiversity informatics|biodiversity records]]<ref name=":3">{{Cite journal |last=Wieczorek |first=John |last2=Bloom |first2=David |last3=Guralnick |first3=Robert |last4=Blum |first4=Stan |last5=Döring |first5=Markus |last6=Giovanni |first6=Renato |last7=Robertson |first7=Tim |last8=Vieglais |first8=David |date=2012-01-06 |title=Darwin Core: An Evolving Community-Developed Biodiversity Data Standard |url=https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0029715 |journal=PLOS ONE |language=en |volume=7 |issue=1 |pages=e29715 |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0029715 |issn=1932-6203 |pmc=PMC3253084 |pmid=22238640}}</ref>, and geoscience samples.<ref name=":0" /><ref name=":4">{{Cite journal |last=System For Earth Sample Registration (SESAR) |date=2020-02-06 |title=SESAR Batch Registration Quick Guide |url=https://zenodo.org/record/3874923 |language=en |doi=10.5281/ZENODO.3874923}}</ref> A larger challenge is that many researchers use no formal reporting conventions, or exclude [[information]] needed to interpret and reuse the data.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Roche |first=Dominique G. |last2=Kruuk |first2=Loeske E. B. |last3=Lanfear |first3=Robert |last4=Binning |first4=Sandra A. |date=2015-11-10 |title=Public Data Archiving in Ecology and Evolution: How Well Are We Doing? |url=https://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.1002295 |journal=PLOS Biology |language=en |volume=13 |issue=11 |pages=e1002295 |doi=10.1371/journal.pbio.1002295 |issn=1545-7885 |pmc=PMC4640582 |pmid=26556502}}</ref> More coordination is needed across these communities to develop a multidisciplinary reporting format for physical samples that is widely adopted, or to ensure that standards are interoperable. Common reporting would support effective discovery, integration, and reuse of sample data that spans scientific domains. | ||
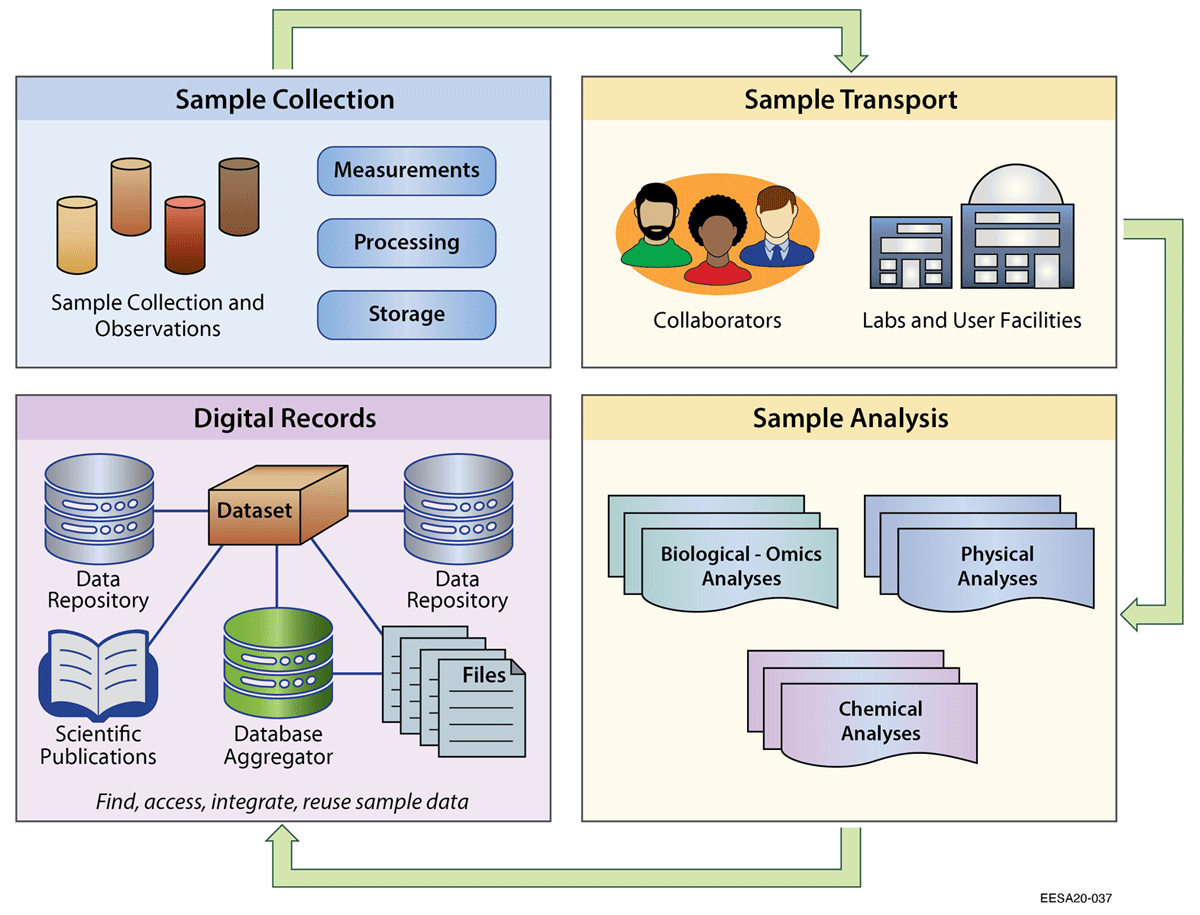
Sample identifiers are also needed to associate and manage important information describing a sample (i.e., [[metadata]]), such as the location, date, environmental context, and purpose of sample collection. For multidisciplinary studies, the task of generating and managing unique sample identifiers and associated metadata can be complicated, particularly as important contextual information is added throughout the data lifecycle.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Treloar |first=Andrew |last2=Klump |first2=Jens |date=2019-12-20 |title=Updating the Data Curation Continuum |url=http://www.ijdc.net/article/view/643 |journal=International Journal of Digital Curation |language=en |volume=14 |issue=1 |pages=87–101 |doi=10.2218/ijdc.v14i1.643 |issn=1746-8256}}</ref> Samples are sent to different collaborators, laboratories, and user facilities, and then combined into a variety of digital records and publications (Figure 1).<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Chase |first=John H. |last2=Bolyen |first2=Evan |last3=Rideout |first3=Jai Ram |last4=Caporaso |first4=J. Gregory |date=2015-12-22 |title=cual-id: Globally Unique, Correctable, and Human-Friendly Sample Identifiers for Comparative Omics Studies |url=https://journals.asm.org/doi/abs/10.1128/mSystems.00010-15 |journal=mSystems |language=EN |doi=10.1128/mSystems.00010-15 |pmc=PMC5069752 |pmid=27822516}}</ref> As a result, scientists face challenges with [[Information management|data management]], metadata management, tracking, or the ability to integrate and reuse valuable sample data. Without attention, these inefficiencies result in data and metadata loss and inhibit the potential of scientific discovery. | Sample identifiers are also needed to associate and manage important information describing a sample (i.e., [[metadata]]), such as the location, date, environmental context, and purpose of sample collection. For multidisciplinary studies, the task of generating and managing unique sample identifiers and associated metadata can be complicated, particularly as important contextual information is added throughout the data lifecycle.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Treloar |first=Andrew |last2=Klump |first2=Jens |date=2019-12-20 |title=Updating the Data Curation Continuum |url=http://www.ijdc.net/article/view/643 |journal=International Journal of Digital Curation |language=en |volume=14 |issue=1 |pages=87–101 |doi=10.2218/ijdc.v14i1.643 |issn=1746-8256}}</ref> Samples are sent to different collaborators, laboratories, and user facilities, and then combined into a variety of digital records and publications (Figure 1).<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Chase |first=John H. |last2=Bolyen |first2=Evan |last3=Rideout |first3=Jai Ram |last4=Caporaso |first4=J. Gregory |date=2015-12-22 |title=cual-id: Globally Unique, Correctable, and Human-Friendly Sample Identifiers for Comparative Omics Studies |url=https://journals.asm.org/doi/abs/10.1128/mSystems.00010-15 |journal=mSystems |language=EN |doi=10.1128/mSystems.00010-15 |pmc=PMC5069752 |pmid=27822516}}</ref> As a result, scientists face challenges with [[Information management|data management]], metadata management, tracking, or the ability to integrate and reuse valuable sample data. Without attention, these inefficiencies result in data and metadata loss and inhibit the potential of scientific discovery. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
==Methods== | ==Methods== | ||
===Review of existing sample identifiers, metadata conventions, and standards=== | |||
ESS-DIVE’s work on sample identifiers and metadata began in response to a specific problem with tracking multidisciplinary samples, as they are sent to different labs and user facilities, which DOE ESS scientists brought up during community meetings. As a community-focused data repository, our approach to this issue involved leading or participating in a variety of community discussions on sample identifiers and/or associated metadata. These included: | |||
*presenting identifier options in an ESS community webinar and whitepaper; | |||
*engaging in discussion with each pilot test participant; | |||
*holding several meetings with U.S. DOE user facilities and data systems representatives (Joint Genome Institute, National Microbiome Data Collaborative, Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory, and DOE Systems Biology Knowledgebase); | |||
*participating in broader community meetings on identifier and metadata practices for physical samples (Earth Science Information Partners [ESIP] and Research Data Alliance [RDA]]); | |||
*participating in a National Microbiome Data Collaborative (NMDC) Ontology workshop; | |||
*participating in a USGS workshop on sample collection metadata for the National Digital Catalogue; and | |||
*participating in the IGSN 2040 Steering Committee and business planning. | |||
After reviewing the scope and use of available persistent identifier (PID) options (Table 1) and community discussions, we focused additional identifier comparison on International GeoSample Numbers (IGSNs) and Archival Resource Keys (ARKs), which are most commonly used for a variety of sample types (Additional files, Supplemental Table 1). Considerations in the identifier assessment included association with a broader international community focused on sample identification and description, associated metadata to describe samples and their relationships, availability of user-friendly infrastructure to mint identifiers and validate metadata, general ease of use, and other technical identifier characteristics, listed in Additional files, Supplemental Table 1. | |||
{| | |||
| style="vertical-align:top;" | | |||
{| class="wikitable" border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" width="60%" | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="3" style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |'''Table 1.''' Examples of PIDs that have been used for samples, modified from Guralnick ''et al.''<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Guralnick |first=Robert P. |last2=Cellinese |first2=Nico |last3=Deck |first3=John |last4=Pyle |first4=Richard L. |last5=Kunze |first5=John |last6=Penev |first6=Lyubomir |last7=Walls |first7=Ramona |last8=Hagedorn |first8=Gregor |last9=Agosti |first9=Donat |last10=Wieczorek |first10=John |last11=Catapano |first11=Terry |date=2015-06-04 |title=Community Next Steps for Making Globally Unique Identifiers Work for Biocollections Data |url=https://zookeys.pensoft.net/article/5042/ |journal=ZooKeys |language=en |volume=494 |pages=133–154 |doi=10.3897/zookeys.494.9352 |issn=1313-2970 |pmc=PMC4400380 |pmid=25901117}}</ref><br /> <br /> ARK = Archival Resource Keys, URN = Uniform Resource Name, URI = Uniform Resource Identifier, DOI = Digital Object Identifier, UUID = Universally Unique Identifier, IGSN = International GeoSample Number, CETAF = Consortium of the European Taxonomic Facilities, RRID = Research Resource Identifier. | |||
|- | |||
! style="background-color:#e2e2e2; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |Identifier type | |||
! style="background-color:#e2e2e2; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |Identifier example | |||
! style="background-color:#e2e2e2; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |Scope | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |ARK | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |<nowiki>ark:/12148/btv1b8449691v</nowiki> | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |Flexible | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |URN | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |<nowiki>urn:catalog:UMMZ:Mammals:171041</nowiki> | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |Flexible | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |HTTP URI | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |<nowiki>http://data.rbge.org.uk/herb/E00115694</nowiki> | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |Flexible | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |DOI | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |<nowiki>10.7299/X7VQ32SJ</nowiki> | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |Flexible, mostly papers and datasets | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |UUID | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |<nowiki>EF0A4D3E-702F-4882-81B8- CA737AEB7B28</nowiki> | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |Flexible | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |IGSN | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |<nowiki>IGSN: IECUR0002</nowiki> | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |Geoscience, working to become general physical sample identifier | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |CETAF URI (based on HTTP URI) | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |<nowiki>http://data.rbge.org.uk/herb/E00421503</nowiki> | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |Species Occurrence, Specimens from CETAF institutions | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |RRID | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |<nowiki>RRID:MGI:5630441</nowiki> | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |Biomedical Research Resources | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |BioSample accession number | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |<nowiki>SAMN03983893</nowiki> | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" |Biological source materials used in experimental assays | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
|} | |||
We also reviewed existing metadata standards and templates that are relevant for samples collected by environmental scientists, including general digital object standards<ref>{{Cite journal |last=DataCite Metadata Working Group |date=2019 |others=Madeleine de Smaele, Amy Hatfield Hart, Jan Ashton, Isabel Bernal Martinez, Stefanie Dietiker, Jannean Elliot |title=DataCite Metadata Schema for the Publication and Citation of Research Data v4.2 |url=http://schema.datacite.org/meta/kernel-4.2/ |doi=10.5438/RV0G-AV03}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=DCMI Usage Board |date=20 January 2020 |title=DCMI Metadata Terms |work=Dublin Core Metadata Initiative |url=https://www.dublincore.org/specifications/dublin-core/dcmi-terms/ |publisher=DCMI |accessdate=16 September 2020}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Cox |first=Simon Jonathan David |date=2011 |title=ISO 19156:2011 - Geographic information -- Observations and measurements |url=http://rgdoi.net/10.13140/2.1.1142.3042 |language=en |publisher=International Organization for Standardization |doi=10.13140/2.1.1142.3042}}</ref>, biodiversity records<ref name=":3" /><ref>{{Citation |last=Group |first=Darwin Core Task |date=2014-11-08 |title=Darwin Core: 2014-11-08 |url=https://zenodo.org/record/12694 |work=Biodiversity Information Standards (TDWG) |publisher=Zenodo |doi=10.5281/zenodo.12694 |accessdate=}}</ref>, omics (e.g. [[genomics]], metagenomics) material<ref name=":1" /><ref name=":2" /><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Reddy |first=T.B.K. |last2=Thomas |first2=Alex D. |last3=Stamatis |first3=Dimitri |last4=Bertsch |first4=Jon |last5=Isbandi |first5=Michelle |last6=Jansson |first6=Jakob |last7=Mallajosyula |first7=Jyothi |last8=Pagani |first8=Ioanna |last9=Lobos |first9=Elizabeth A. |last10=Kyrpides |first10=Nikos C. |date=2014-10-27 |title=The Genomes OnLine Database (GOLD) v.5: a metadata management system based on a four level (meta)genome project classification |url=https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku950 |journal=Nucleic Acids Research |volume=43 |issue=D1 |pages=D1099–D1106 |doi=10.1093/nar/gku950 |issn=1362-4962 |pmc=PMC4384021 |pmid=25348402}}</ref>, and geoscience samples<ref name=":4" /><ref>{{Cite journal |last=System For Earth Sample Registration (SESAR) |date=2020-02-17 |title=SESAR XML Schema for samples |url=https://zenodo.org/record/3875531 |language=en |doi=10.5281/ZENODO.3875531}}</ref> (see Additional files, Supplemental Table 2). We created a translation table comparing 49 metadata elements (see Additional files, Supplemental Table 3) in human-readable format. The translation table depicts linkages where metadata elements were common across standards, as well as differences. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 22:14, 7 December 2021
| Full article title | Sample identifiers and metadata to support data management and reuse in multidisciplinary ecosystem sciences |
|---|---|
| Journal | Data Science Journal |
| Author(s) | Damerow, Joan E.; Varadharajan, Charuleka; Boye, Kristin; Brodie, Eoin L.; Burrus, Madison; Chadwick, K. Dana; Crystal-Ornelas, Robert; Elbashandy, Hesham; Alves, Ricardo J.E.; Ely, Kim S.; Goldman, Amy E.; Haberman, Ted; Hendrix, Valerie; Kakalia, Zarine; Kemner, Kenneth M.; Kersting, Annie B.; Merino, Nancy; O'Brien, Fianna; Perzan, Zach; Robles, Emily; Sorensen, Patrick; Stegen, James C.; Walls, Ramona L.; Weisenhorn, Pamela; Zavarin, Mavrik; Agarwal, Deborah |
| Author affiliation(s) | Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Stanford University, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Metadata Game Changers, Argonne National Laboratory, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, University of Arizona |
| Primary contact | Email: JoanDamerow at lbl dot gov |
| Year published | 2021 |
| Volume and issue | 20(1) |
| Article # | 11 |
| DOI | 10.5334/dsj-2021-011 |
| ISSN | 1683-1470 |
| Distribution license | Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International |
| Website | https://datascience.codata.org/articles/10.5334/dsj-2021-011/ |
| Download | https://datascience.codata.org/articles/10.5334/dsj-2021-011/galley/1055/download/ (PDF) |
|
|
This article should be considered a work in progress and incomplete. Consider this article incomplete until this notice is removed. |
Abstract
Physical samples are foundational entities for research across the biological, Earth, and environmental sciences. Data generated from sample-based analyses are not only the basis of individual studies, but can also be integrated with other data to answer new and broader-scale questions. Ecosystem studies increasingly rely on multidisciplinary team-based science to study climate and environmental changes. While there are widely adopted conventions within certain domains to describe sample data, these have gaps when applied in a multidisciplinary context.
In this study, we reviewed existing practices for identifying, characterizing, and linking related environmental samples. We then tested practicalities of assigning persistent identifiers to samples, with standardized metadata, in a pilot field test involving eight United States Department of Energy projects. Participants collected a variety of sample types, with analyses conducted across multiple facilities. We address terminology gaps for multidisciplinary research and make recommendations for assigning identifiers and metadata that supports sample tracking, integration, and reuse. Our goal is to provide a practical approach to sample management, geared towards ecosystem scientists who contribute and reuse sample data.
Keywords: International GeoSample Numbers (IGSN), physical samples, soil, water, plant, leaf, microbial communities, related identifiers, persistent identifiers
Introduction
The study of natural ecosystems requires multidisciplinary science teams to understand and model processes from molecular to global scales.[1] Many research activities involve diverse collections of samples and associated field or laboratory measurements.[2][3] For example, studies of organic matter cycling through plants and soil involves analysis of samples to represent soil biogeochemistry, microbial communities, plant structures, leaf gas exchange, and traits of the specific organisms involved.[4][5][6] Each scientific expert, project team, and discipline has a responsibility to ensure that others can interpret, integrate, and reuse their sample data to help solve emerging problems as our global environment continues to change.[7]
Collaboration across disciplines requires a more unified approach to report basic information about key data entities, such as samples. One challenge in promoting a unified way of reporting sample data is that some research communities have already developed community-specific conventions, including those for omics samples[8][9][10], biodiversity records[11], and geoscience samples.[2][12] A larger challenge is that many researchers use no formal reporting conventions, or exclude information needed to interpret and reuse the data.[13] More coordination is needed across these communities to develop a multidisciplinary reporting format for physical samples that is widely adopted, or to ensure that standards are interoperable. Common reporting would support effective discovery, integration, and reuse of sample data that spans scientific domains.
Sample identifiers are also needed to associate and manage important information describing a sample (i.e., metadata), such as the location, date, environmental context, and purpose of sample collection. For multidisciplinary studies, the task of generating and managing unique sample identifiers and associated metadata can be complicated, particularly as important contextual information is added throughout the data lifecycle.[14] Samples are sent to different collaborators, laboratories, and user facilities, and then combined into a variety of digital records and publications (Figure 1).[15] As a result, scientists face challenges with data management, metadata management, tracking, or the ability to integrate and reuse valuable sample data. Without attention, these inefficiencies result in data and metadata loss and inhibit the potential of scientific discovery.
|
Our overall goal was to address sample identification and metadata needs of ecosystem scientists, and was driven by the user community of the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) data repository for Earth and environmental sciences, the Environmental Systems Science Data Infrastructure for a Virtual Ecosystem (ESS-DIVE).[16] The DOE’s Environmental Systems Science (ESS) program relies on multidisciplinary, team-based science to study complex processes within terrestrial ecosystems, spanning from the bedrock through the rhizosphere and vegetation to the atmospheric surface layer.[17] This community is well-positioned to help address specific challenges in standardizing and integrating data and metadata about a variety of environmental samples (e.g., soil, water, plant, and associated biological material used for omics analyses), which applies broadly to environmental research.[18][19][20][21][22]
We focus on sample identifiers and metadata that support the FAIR Guiding Principles (findability, accessibility, interoperability, and reusability) from the multidisciplinary domain-science perspective.[23][24][25][26][27] We therefore use a community-focused approach to: a.) evaluate existing options for sample identifiers and metadata descriptions for ecosystem science samples; b.) pilot the process of standardizing sample information to evaluate practical issues from domain-science perspectives; and c.) outline practical recommendations for sample identifier allocation, tracking, and associated metadata.
Methods
Review of existing sample identifiers, metadata conventions, and standards
ESS-DIVE’s work on sample identifiers and metadata began in response to a specific problem with tracking multidisciplinary samples, as they are sent to different labs and user facilities, which DOE ESS scientists brought up during community meetings. As a community-focused data repository, our approach to this issue involved leading or participating in a variety of community discussions on sample identifiers and/or associated metadata. These included:
- presenting identifier options in an ESS community webinar and whitepaper;
- engaging in discussion with each pilot test participant;
- holding several meetings with U.S. DOE user facilities and data systems representatives (Joint Genome Institute, National Microbiome Data Collaborative, Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory, and DOE Systems Biology Knowledgebase);
- participating in broader community meetings on identifier and metadata practices for physical samples (Earth Science Information Partners [ESIP] and Research Data Alliance [RDA]]);
- participating in a National Microbiome Data Collaborative (NMDC) Ontology workshop;
- participating in a USGS workshop on sample collection metadata for the National Digital Catalogue; and
- participating in the IGSN 2040 Steering Committee and business planning.
After reviewing the scope and use of available persistent identifier (PID) options (Table 1) and community discussions, we focused additional identifier comparison on International GeoSample Numbers (IGSNs) and Archival Resource Keys (ARKs), which are most commonly used for a variety of sample types (Additional files, Supplemental Table 1). Considerations in the identifier assessment included association with a broader international community focused on sample identification and description, associated metadata to describe samples and their relationships, availability of user-friendly infrastructure to mint identifiers and validate metadata, general ease of use, and other technical identifier characteristics, listed in Additional files, Supplemental Table 1.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
We also reviewed existing metadata standards and templates that are relevant for samples collected by environmental scientists, including general digital object standards[29][30][31], biodiversity records[11][32], omics (e.g. genomics, metagenomics) material[8][10][33], and geoscience samples[12][34] (see Additional files, Supplemental Table 2). We created a translation table comparing 49 metadata elements (see Additional files, Supplemental Table 3) in human-readable format. The translation table depicts linkages where metadata elements were common across standards, as well as differences.
References
- ↑ Weart, Spencer (26 February 2013). "Rise of interdisciplinary research on climate". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 110 (Supplement 1): 3657–3664. doi:10.1073/pnas.1107482109. PMC PMC3586608. PMID 22778431. https://www.pnas.org/content/110/Supplement_1/3657.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Devaraju, A.; Klump, J.; Cox, S.J.D. et al. (1 November 2016). "Representing and publishing physical sample descriptions" (in en). Computers & Geosciences 96: 1–10. doi:10.1016/j.cageo.2016.07.018. ISSN 0098-3004. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300416302023.
- ↑ Ponsero, Alise J; Bomhoff, Matthew; Blumberg, Kai; Youens-Clark, Ken; Herz, Nina M; Wood-Charlson, Elisha M; Delong, Edward F; Hurwitz, Bonnie L (31 July 2020). "Planet Microbe: a platform for marine microbiology to discover and analyze interconnected ‘omics and environmental data". Nucleic Acids Research 49 (D1): D792–D802. doi:10.1093/nar/gkaa637. ISSN 0305-1048. PMC PMC7778950. PMID 32735679. https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/49/D1/D792/5879428.
- ↑ Cordeiro, Amanda L.; Norby, Richard J.; Andersen, Kelly M.; Valverde-Barrantes, Oscar; Fuchslueger, Lucia; Oblitas, Erick; Hartley, Iain P.; Iversen, Colleen M. et al. (2020). "Fine-root dynamics vary with soil depth and precipitation in a low-nutrient tropical forest in the Central Amazonia" (in en). Plant-Environment Interactions 1 (1): 3–16. doi:10.1002/pei3.10010. ISSN 2575-6265. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/pei3.10010.
- ↑ Malik, Ashish A.; Martiny, Jennifer B. H.; Brodie, Eoin L.; Martiny, Adam C.; Treseder, Kathleen K.; Allison, Steven D. (1 January 2020). "Defining trait-based microbial strategies with consequences for soil carbon cycling under climate change" (in en). The ISME Journal 14 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1038/s41396-019-0510-0. ISSN 1751-7370. PMC PMC6908601. PMID 31554911. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41396-019-0510-0.
- ↑ Treseder, Kathleen K.; Balser, Teri C.; Bradford, Mark A.; Brodie, Eoin L.; Dubinsky, Eric A.; Eviner, Valerie T.; Hofmockel, Kirsten S.; Lennon, Jay T. et al. (3 September 2011). "Integrating microbial ecology into ecosystem models: challenges and priorities". Biogeochemistry 109 (1-3): 7–18. doi:10.1007/s10533-011-9636-5. ISSN 0168-2563. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10533-011-9636-5.
- ↑ Soranno, Patricia A.; Schimel, David S. (2014). "Macrosystems ecology: big data, big ecology" (in en). Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 12 (1): 3–3. doi:10.1890/1540-9295-12.1.3. ISSN 1540-9309. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1890/1540-9295-12.1.3.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Field, Dawn; Amaral-Zettler, Linda; Cochrane, Guy; Cole, James R.; Dawyndt, Peter; Garrity, George M.; Gilbert, Jack; Glöckner, Frank Oliver et al. (21 June 2011). "The Genomic Standards Consortium" (in en). PLOS Biology 9 (6): e1001088. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001088. ISSN 1545-7885. PMC PMC3119656. PMID 21713030. https://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.1001088.
- ↑ Reddy, T.B.K.; Thomas, Alex D.; Stamatis, Dimitri; Bertsch, Jon; Isbandi, Michelle; Jansson, Jakob; Mallajosyula, Jyothi; Pagani, Ioanna et al. (27 October 2014). "The Genomes OnLine Database (GOLD) v.5: a metadata management system based on a four level (meta)genome project classification". Nucleic Acids Research 43 (D1): D1099–D1106. doi:10.1093/nar/gku950. ISSN 1362-4962. PMC PMC4384021. PMID 25348402. https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/43/D1/D1099/2439522.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Yilmaz, Pelin; Kottmann, Renzo; Field, Dawn; Knight, Rob; Cole, James R.; Amaral-Zettler, Linda; Gilbert, Jack A.; Karsch-Mizrachi, Ilene et al. (1 May 2011). "Minimum information about a marker gene sequence (MIMARKS) and minimum information about any (x) sequence (MIxS) specifications" (in en). Nature Biotechnology 29 (5): 415–420. doi:10.1038/nbt.1823. ISSN 1546-1696. PMC PMC3367316. PMID 21552244. https://www.nature.com/articles/nbt.1823.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Wieczorek, John; Bloom, David; Guralnick, Robert; Blum, Stan; Döring, Markus; Giovanni, Renato; Robertson, Tim; Vieglais, David (6 January 2012). "Darwin Core: An Evolving Community-Developed Biodiversity Data Standard" (in en). PLOS ONE 7 (1): e29715. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0029715. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC PMC3253084. PMID 22238640. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0029715.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 System For Earth Sample Registration (SESAR) (6 February 2020) (in en). SESAR Batch Registration Quick Guide. doi:10.5281/ZENODO.3874923. https://zenodo.org/record/3874923.
- ↑ Roche, Dominique G.; Kruuk, Loeske E. B.; Lanfear, Robert; Binning, Sandra A. (10 November 2015). "Public Data Archiving in Ecology and Evolution: How Well Are We Doing?" (in en). PLOS Biology 13 (11): e1002295. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1002295. ISSN 1545-7885. PMC PMC4640582. PMID 26556502. https://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.1002295.
- ↑ Treloar, Andrew; Klump, Jens (20 December 2019). "Updating the Data Curation Continuum" (in en). International Journal of Digital Curation 14 (1): 87–101. doi:10.2218/ijdc.v14i1.643. ISSN 1746-8256. http://www.ijdc.net/article/view/643.
- ↑ Chase, John H.; Bolyen, Evan; Rideout, Jai Ram; Caporaso, J. Gregory (22 December 2015). "cual-id: Globally Unique, Correctable, and Human-Friendly Sample Identifiers for Comparative Omics Studies" (in EN). mSystems. doi:10.1128/mSystems.00010-15. PMC PMC5069752. PMID 27822516. https://journals.asm.org/doi/abs/10.1128/mSystems.00010-15.
- ↑ Varadharajan, C.; Cholia, S.; Snavely, C. et al. (8 January 2019). "Launching an Accessible Archive of Environmental Data" (in en-US). Eos. doi:10.1029/2019eo111263. http://eos.org/science-updates/launching-an-accessible-archive-of-environmental-data.
- ↑ Biological and Environmental Research Advisory Committee (2017). "Grand Challenges for Biological and Environmental Research: Progress and Future Vision" (PDF). U.S. Department of Energy. https://genomicscience.energy.gov/BERfiles/BERAC-2017-Grand-Challenges-Report.pdf.
- ↑ Chadwick, K. Dana; Brodrick, Philip G.; Grant, Kathleen; Goulden, Tristan; Henderson, Amanda; Falco, Nicola; Wainwright, Haruko; Williams, Kenneth H. et al. (2020). "Integrating airborne remote sensing and field campaigns for ecology and Earth system science" (in en). Methods in Ecology and Evolution 11 (11): 1492–1508. doi:10.1111/2041-210X.13463. ISSN 2041-210X. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/2041-210X.13463.
- ↑ Serbin, Shawn P.; Wu, Jin; Ely, Kim S.; Kruger, Eric L.; Townsend, Philip A.; Meng, Ran; Wolfe, Brett T.; Chlus, Adam et al. (2019). "From the Arctic to the tropics: multibiome prediction of leaf mass per area using leaf reflectance" (in en). New Phytologist 224 (4): 1557–1568. doi:10.1111/nph.16123. ISSN 1469-8137. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/nph.16123.
- ↑ Stegen, James C.; Goldman, Amy E. (9 October 2018). "WHONDRS: a Community Resource for Studying Dynamic River Corridors" (in EN). mSystems. doi:10.1128/mSystems.00151-18. PMC PMC6178584. PMID 30320221. https://journals.asm.org/doi/abs/10.1128/mSystems.00151-18.
- ↑ Wu, Jin; Rogers, Alistair; Albert, Loren P.; Ely, Kim; Prohaska, Neill; Wolfe, Brett T.; Oliveira, Raimundo Cosme; Saleska, Scott R. et al. (2019). "Leaf reflectance spectroscopy captures variation in carboxylation capacity across species, canopy environment and leaf age in lowland moist tropical forests" (in en). New Phytologist 224 (2): 663–674. doi:10.1111/nph.16029. ISSN 1469-8137. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/nph.16029.
- ↑ Wu, Jin; Serbin, Shawn P.; Ely, Kim S.; Wolfe, Brett T.; Dickman, L. Turin; Grossiord, Charlotte; Michaletz, Sean T.; Collins, Adam D. et al. (2020). "The response of stomatal conductance to seasonal drought in tropical forests" (in en). Global Change Biology 26 (2): 823–839. doi:10.1111/gcb.14820. ISSN 1365-2486. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/gcb.14820.
- ↑ Beck, Marcus W.; O’Hara, Casey; Lowndes, Julia S. Stewart; Mazor, Raphael D.; Theroux, Susanna; Gillett, David J.; Lane, Belize; Gearheart, Gregory (20 July 2020). "The importance of open science for biological assessment of aquatic environments" (in en). PeerJ 8: e9539. doi:10.7717/peerj.9539. ISSN 2167-8359. PMC PMC7377246. PMID 32742805. https://peerj.com/articles/9539.
- ↑ Conze, Ronald; Lorenz, Henning; Ulbricht, Damian; Elger, Kirsten; Gorgas, Thomas (25 January 2017). "Utilizing the International Geo Sample Number Concept in Continental Scientific Drilling During ICDP Expedition COSC-1" (in en). Data Science Journal 16: 2. doi:10.5334/dsj-2017-002. ISSN 1683-1470. http://datascience.codata.org/articles/10.5334/dsj-2017-002/.
- ↑ Lehnert, Kerstin; Wyborn, Lesley; Klump, Jens (2019). "FAIR Geoscientific Samples and Data Need International Collaboration" (in en). Acta Geologica Sinica - English Edition 93 (S3): 32–33. doi:10.1111/1755-6724.14236. ISSN 1755-6724. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/1755-6724.14236.
- ↑ Stall, Shelley; Yarmey, Lynn; Cutcher-Gershenfeld, Joel; Hanson, Brooks; Lehnert, Kerstin; Nosek, Brian; Parsons, Mark; Robinson, Erin et al. (1 June 2019). "Make scientific data FAIR" (in en). Nature 570 (7759): 27–29. doi:10.1038/d41586-019-01720-7. https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-019-01720-7.
- ↑ Wilkinson, Mark D.; Dumontier, Michel; Aalbersberg, IJsbrand Jan; Appleton, Gabrielle; Axton, Myles; Baak, Arie; Blomberg, Niklas; Boiten, Jan-Willem et al. (15 March 2016). "The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship" (in en). Scientific Data 3 (1): 160018. doi:10.1038/sdata.2016.18. ISSN 2052-4463. PMC PMC4792175. PMID 26978244. https://www.nature.com/articles/sdata201618.
- ↑ Guralnick, Robert P.; Cellinese, Nico; Deck, John; Pyle, Richard L.; Kunze, John; Penev, Lyubomir; Walls, Ramona; Hagedorn, Gregor et al. (4 June 2015). "Community Next Steps for Making Globally Unique Identifiers Work for Biocollections Data" (in en). ZooKeys 494: 133–154. doi:10.3897/zookeys.494.9352. ISSN 1313-2970. PMC PMC4400380. PMID 25901117. https://zookeys.pensoft.net/article/5042/.
- ↑ DataCite Metadata Working Group (2019). DataCite Metadata Schema for the Publication and Citation of Research Data v4.2. Madeleine de Smaele, Amy Hatfield Hart, Jan Ashton, Isabel Bernal Martinez, Stefanie Dietiker, Jannean Elliot. doi:10.5438/RV0G-AV03. http://schema.datacite.org/meta/kernel-4.2/.
- ↑ DCMI Usage Board (20 January 2020). "DCMI Metadata Terms". Dublin Core Metadata Initiative. DCMI. https://www.dublincore.org/specifications/dublin-core/dcmi-terms/. Retrieved 16 September 2020.
- ↑ Cox, Simon Jonathan David (2011) (in en). ISO 19156:2011 - Geographic information -- Observations and measurements. International Organization for Standardization. doi:10.13140/2.1.1142.3042. http://rgdoi.net/10.13140/2.1.1142.3042.
- ↑ Group, Darwin Core Task (8 November 2014), "Darwin Core: 2014-11-08", Biodiversity Information Standards (TDWG) (Zenodo), doi:10.5281/zenodo.12694, https://zenodo.org/record/12694
- ↑ Reddy, T.B.K.; Thomas, Alex D.; Stamatis, Dimitri; Bertsch, Jon; Isbandi, Michelle; Jansson, Jakob; Mallajosyula, Jyothi; Pagani, Ioanna et al. (27 October 2014). "The Genomes OnLine Database (GOLD) v.5: a metadata management system based on a four level (meta)genome project classification". Nucleic Acids Research 43 (D1): D1099–D1106. doi:10.1093/nar/gku950. ISSN 1362-4962. PMC PMC4384021. PMID 25348402. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku950.
- ↑ System For Earth Sample Registration (SESAR) (17 February 2020) (in en). SESAR XML Schema for samples. doi:10.5281/ZENODO.3875531. https://zenodo.org/record/3875531.
Notes
This presentation is faithful to the original, with only a few minor changes to presentation. In some cases important information was missing from the references, and that information was added. The original article lists references in alphabetical order; however, this version lists them in order of appearance, by design.