Difference between revisions of "Journal:Understanding cybersecurity frameworks and information security standards: A review and comprehensive overview"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Saving and adding more.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Saving and adding more.) |
||
| Line 136: | Line 136: | ||
* ISO/IEC 27019:2017 ''Information technology — Security techniques — Information security controls for the energy utility industry'' | * ISO/IEC 27019:2017 ''Information technology — Security techniques — Information security controls for the energy utility industry'' | ||
===ISF's ''Standard of Good Practice for Information Security''=== | |||
the Information Security Forum (ISF), an international organization based in London, with staff in New York City, initially published the ''Standard of Good Practice for Information Security'' in 1996. The ISF is a non-profit and independent organization that concentrates on the development of best practices and benchmarking in the information security arena. [7] Companies and individuals in manufacturing, financial services, transportation, chemical/pharmaceutical, retail, government, telecommunications, media, transportation, energy, and professional services from all over the world can join the ISF. The standard—which includes best practices in cybersecurity—is also revised every two years to cover the most recent best practices in information security. The standard is mainly designed to concentrate on six major aspects, including installing computers, application of critical business processes, managing security and networks, developing systems, and securing the environment for the end user. [2] | |||
===BSI's ''IT-Grundschutz Compendium'' and 200-X Standards=== | |||
The German Federal Office for Information Security (Bundesamt für Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik or BSI) is responsible for managing the security of computers and communication for the German government, focusing on security of computer applications, cryptography, internet security, security products, and security test laboratories [10]. Through its focus on "IT baseline protection" or IT-Grundschutz, BSI has provided recommendations for approaches, processes, methods, and procedures that are related to cybersecurity in its ''IT-Grundschutz Compendium'', as well as its 200-X series of standards. It also covers key areas in information security that are required to be considered while setting approaches for companies and public authorities. [34] | |||
====BSI-Standard 200-1: Information Security Management Systems (ISMS)==== | |||
The first standard in the BSI Standards 200-X series is BSI-Standard 200-1, which describes the main requirements that should be followed to implement ISMSs. There is full compatibility between 200-1 and ISO/IEC 27001. Moreover, recommendations and solutions of ISO standards are taken into consideration in this standard. [10] This standard mainly concentrates on managing the challenges of planning the information technology implementation process described in the ISO/IEC 27001 standard.<ref name="BSI200-1_18">{{cite web |url=https://www.bsi.bund.de/SharedDocs/Downloads/EN/BSI/Grundschutz/International/bsi-standard-2001_en_pdf.html?nn=908032 |title=BSI-Standard 200-1: Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) |publisher=Bundesamt für Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik |date=07 May 2018}}</ref> | |||
====BSI-Standard 200-2: IT-Grundschutz-Methodology==== | |||
BSI-Standard 200-2 includes the employment of IT security management practices in a practical step-by-step manner, covering suggestions for the selection of appropriate measures in information technology security, the implementation of information technology security, and the intricacies of information technology security using the IT-Grundschutz methodologies of standard, basic, and core protection. Additionally, general requirements to employ ISO 27001, 27002 and 13335 standards are interpreted using notes and examples, which help facilitate the establishment of a successful ISMS. [34]<ref name="BSI200-2_18">{{cite web |url=https://www.bsi.bund.de/SharedDocs/Downloads/EN/BSI/Grundschutz/International/bsi-standard-2002_en_pdf.html?nn=908032 |title=BSI-Standard 200-2: IT-Grundschutz-Methodology |publisher=Bundesamt für Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik |date=07 May 2018}}</ref> | |||
====BSI-Standard 200-3: Risk Analysis based on IT-Grundschutz==== | |||
BSI-Standard 200-3 concentrates on risk analysis. Organizations apply this approach to promote their risk analysis while they implement the IT-Grundschutz methodologies. [34] The elementary threats described in the ''IT-Grundschutz Compendium'' form the basis of the recommended information security risk analysis procedures of 200-3.<ref name="BSI200-3_18">{{cite web |url=https://www.bsi.bund.de/SharedDocs/Downloads/EN/BSI/Grundschutz/International/bsi-standard-2003_en_pdf.html?nn=908032 |title=BSI-Standard 200-3: Risk Analysis based on IT-Grundschutz |publisher=Bundesamt für Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik |date=07 May 2018}}</ref> | |||
===Industry-related standards=== | |||
Apart from the general classification of cybersecurity standards, a class of cybersecurity standards focusing on their application to specific business industries—including ISA/IEC 62443, ISO/SAE 21434, ETSI EN 303 645, and FIPS 140-3—is also provided in this study. | |||
====ISA/IEC 62443 standards==== | |||
ISA/IEC 62443 is an international series of standards in cybersecurity that is focused on the employment of cybersecurity requirements for operating technology in systems used for industrial automation and control system (IACS) purposes. [35] This series of standards, initially established by the ISA99 committee, addresses current and future cybersecurity concerns in IACSs. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has adopted this standard and asks security experts in industrial automation and control systems from all over the world to help develop the standard. [35] Since the standard has divided cybersecurity topics into different categories, it is not limited to the technology sector, and it also considers mitigating cyber threats regarding processes, employees, and countermeasures. | |||
====ISO/SAE 21434:2021==== | |||
This standard is focused on cybersecurity risk management requirements in the engineering of electronic systems of road vehicles and includes production, operation, development, maintenance, etc. concepts in vehicular engineering. [36] It also expands into addressing both components and interfaces of road vehicles. The main aim of this standard is to ensure that cybersecurity concerns are addressed in the engineering of road vehicles and that they are protected against different cyberattacks. [36] | |||
====ETSI EN 303 645 V2.1.1==== | |||
Cybersecurity is becoming a growing challenge, as more devices are connected to the internet and more people are sharing their personal data using [[internet of things]] (IoT) technologies. This standard targets all parties that are involved in manufacturing and developing IoT products and appliances. [37] The standard has collected a wide range of best practices and requirements in internet-connected products and appliances to ensure the security of consumers’ data. The main focus of this standard is on the establishment of organizational policies and technical controls that are applicable to all IoT devices. [37] | |||
====FIPS 140-3==== | |||
The Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) are published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). This standard includes hardware and software requirements to protect cryptography modules. Cryptography modules include valuable information that should be secured with respect to integrity and confidentiality concerns. Four security levels, from the lowest to the highest, are defined in FIPS 140-3. This standard is established based on the joint collaboration of NIST and the Canadian Centre for Cyber Security to ensure that cryptographic modules meet validation requirements. Therefore, if a product meets FIPS 140-3 requirements, it is accepted by federal agencies of the United States and Canada at the same time. [38]<ref name="NISTFIPS1403_19">{{cite web |url=https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/FIPS/NIST.FIPS.140-3.pdf |format=PDF |title=FIPS PUB 140-3 Security Requirement for Cyptographic Modules |publisher=National Institute of Standards and Technology |date=22 March 2019}}</ref> | |||
==Cybersecurity and information security frameworks== | |||
| Line 142: | Line 173: | ||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
This presentation is faithful to the original, with only a few minor changes to presentation, grammar, and punctuation. In some cases important information was missing from the references, and that information was added. | This presentation is faithful to the original, with only a few minor changes to presentation, grammar, and punctuation. In some cases important information was missing from the references, and that information was added. The BSI standards discussed in the original refer to the old 100 standards, for some unknown reason; they were updated to the 200-X series of standards for this version. Additional references to those 200-X standards are also supplied in this version. Similarly, the author refers to FIPS 140-2 instead of 140-3, for some unknown reason, despite 140-3 being released in March 2019; 140-3 is used in this version, and an additional reference is supplied. | ||
<!--Place all category tags here--> | <!--Place all category tags here--> | ||
Revision as of 16:21, 15 March 2023
| Full article title | Understanding cybersecurity frameworks and information security standards: A review and comprehensive overview |
|---|---|
| Journal | Electronics |
| Author(s) | Taherdoost, Hamed |
| Author affiliation(s) | University Canada West |
| Primary contact | Email: hamed dot taherdoost at gmail dot com |
| Year published | 2022 |
| Volume and issue | 11(14) |
| Article # | 2181 |
| DOI | 10.3390/electronics11142181 |
| ISSN | 2079-9292 |
| Distribution license | Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International |
| Website | https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9292/11/14/2181 |
| Download | https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9292/11/14/2181/pdf (PDF) |
|
|
This article should be considered a work in progress and incomplete. Consider this article incomplete until this notice is removed. |
Abstract
Businesses are reliant on data to survive in the competitive market, and data is constantly in danger of loss or theft. Loss of valuable data leads to negative consequences for both individuals and organizations. Cybersecurity is the process of protecting sensitive data from damage or theft. To successfully achieve the objectives of implementing cybersecurity at different levels, a range of procedures and standards should be followed. Cybersecurity standards determine the requirements that an organization should follow to achieve cybersecurity objectives and minimize the impact of cybercrimes. Cybersecurity standards demonstrate whether an information management system can meet security requirements through a range of best practices and procedures. A range of standards has been established by various organizations to be employed in information management systems of different sizes and types. However, it is challenging for businesses to adopt the standard that is the most appropriate based on their cybersecurity demands. Reviewing the experiences of other businesses in the industry helps organizations to adopt the most relevant cybersecurity standards and frameworks.
This study presents a narrative review of the most frequently used cybersecurity standards and frameworks based on 1. existing papers in the cybersecurity field and 2. applications of these cybersecurity standards and frameworks in various fields to help organizations select the cybersecurity standard or framework that best fits their cybersecurity requirements.
Keywords: cybersecurity framework, cybersecurity standard, information security framework, information security standard, cybersecurity requirements, information security requirements, narrative review
Introduction
A standard is described as an ideal condition with a minimum achievement limit. [1] It also refers to technical specifications that are required to be applied by a service facility to enable service users to acquire the maximum function, purpose, or profit from the services. [2] Many international organizations, associations, and consortia have a vital role in the development of standards. [3,4] According to Standards Australia[1], standards are represented as documents which define specifications, procedures, and guidelines, aiming to ensure safety, consistency, and reliability of products, services, and systems. Moreover, based on the provided definition by the International Organization for Standardization/International Electrotechnical Commission (ISO/IEC), standards are documents or rules made based on a general agreement and validated by a legal entity, which help to achieve optimal results, as a guideline, model, or sample, in a particular context.[2] A standard practically meets user demands, considers the limitations of technology and resources, and also meets the verification requirements. [2]
The term "standard" most commonly refers to established documents by professional bodies to be used by other organizations (i.e., technical standards, program standards), or standards of technical practice (i.e., practical cybersecurity standards).
The sets of practices or technical methods that help organizations to secure their cyber environment are referred to as cybersecurity standards. [6] Cybersecurity standards include users, network infrastructure, software, hardware, processes, and information in system storage media that can be connected to the internet. [6] The scope of cybersecurity standards is broad in that it covers security features in applications and cryptographic algorithms that mainly provide perspective toward security controls, processes, procedures, guidelines, and baselines. [7] Security experts recommend implementing cybersecurity standards as a fundamentally essential element consisting of a collection of best practices to protect organizations from cybersecurity threats and risks. [8]
The main aim of cybersecurity standards is to prevent or mitigate cyberattacks and reduce the risk of cyber threats. [9] The implementation of such standards typically benefits the adopter by saving time, decreasing costs, increasing profits, improving user awareness, minimizing risks, and offering business continuity. [7] Additionally, using standards facilitates the compliance of an organization to industry best practices and procedures and provides the opportunity to compare a security system on an international level. [10] Hence, the application of cybersecurity standards has been established in different organizations or businesses to protect assets against cyber threats. [11,12] As a result, different cybersecurity standards have been developed by various organizations to ensure that organizations of different size and nature implement appropriate measures to prevent and mitigate cyber threats. [13] However, since a considerable number of standards have been developed to cover different aspects of cybersecurity in various organizations, it may be challenging for business owners to choose the appropriate standard that is the best match for their business. [14]
This study aims to provide an overview of the most frequently used cybersecurity standards based on existing papers in the cybersecurity field, clarifying their features and applications in different industries. A wide range of cybersecurity standards and frameworks are available to ensure the protection of data in different industries; however, this review paper aims to provide a comparative concept regarding cybersecurity standards and frameworks and facilitate the selection of the most appropriate standards and frameworks. This paper can be also helpful for academic purposes to determine the direction of further studies in this field.
In the next section, an overview of the most common cybersecurity standards and frameworks is provided. Following that is a narrative literature review that is the result of extracting and analyzing 17 papers published about cybersecurity standards between 2000 to 2022, and then considering the aim of each study, the main findings of the research, as well as relevant industry and employed standards. Finally, a concluding discussion is presented that clarifies the contribution of different standards for specific purposes.
Cybersecurity standards and frameworks
Cybersecurity standards are generally classified into two main categories: information security standards and information security governance standards. [15] Information security standards and frameworks such as the ISO/IEC 27000 series, ISF SOGP, NIST 800 series, SOX, and Risk IT mainly concentrate on security concerns. Selecting the most appropriate standard or framework is a serious decision that should be made based on the requirements of the organization to examine if it adequately suits the demands of the business. In some cases, employment of a single standard does not suffice to meet the expectations of a business. Thus, managers need to examine whether they need to consider more than one standard or framework. [2]
Open standards and frameworks are easily available and optional to be employed. Thus, organizations can use some parts or all of the guidelines, as required, or use them in combination, integrated with other standards, to complement and strengthen other requirements. [16] Performance standards can be a policy or law to be complied with by certain countries. They may also be required by the responsible organization, association, or regulatory body to be complied with by the implementing organization. [17] A country or company is authorized to reject rules or standards published by others, or to develop their own proprietary standards or local regulatory standards. [18]
The effective implementation of cybersecurity standards as guidelines or techniques which include best practices to be used in business or industry is not possible without the employment of the relevant cybersecurity framework. [19,20] Cybersecurity standards explain and provide methods one by one, specify what is expected to be done to complete the process, and clarify methods to coincide with the standard; a cybersecurity framework is a general guideline that covers many components or domains that can be adopted by businesses/companies/institutions, which doesn't necessarily specify the steps that are required to be taken. [21] Satisfactory cybersecurity protection can be achieved by adopting a cybersecurity framework that describes the scope, implementation, and evaluation processes, and also provides a general structure and methodology for protecting critical digital assets. [22] In fact, organizations can refer to cybersecurity frameworks to realize guidelines in the successful implementation of cybersecurity standards to be better equipped to identify, detect, and respond to cyberattacks. [23]
Cybersecurity frameworks are flexible and can provide users with the freedom to choose some parts or the whole model, methods, or technical practices, offering general and adoptable guidelines, as well as offering suggestions to be applied within the organization. [24] Implementation costs can be reduced as a result of the flexibility of cybersecurity frameworks. This can be effective to protect the infrastructure against cyber threats and secure critical sectors in the nation and economy. Therefore, cybersecurity frameworks have been developed by academic institutions, international organizations, countries, and corporations to ensure cyber resilience. [25] Businesses that seek to successfully implement cybersecurity standards are dependent on cybersecurity frameworks to harmonize policy, business, and technological approaches that are effective to mitigate cybersecurity issues and address cyber risks. [26] Thus, to ensure the protection of data and the infrastructure in organizations, businesses, and governments, cybersecurity standards and frameworks are required. [27]
The difference between a standard and a framework is summarized in Table 1.
| ||||||
Cybersecurity and information security standards
Cybersecurity standards, as key parts of IT governance, are consulted to ensure that an organization is following its policies and strategy in cybersecurity. [3] Therefore, by relying on cybersecurity standards, an organization can turn its cybersecurity policies into measurable actions. Cybersecurity standards clarify functional and assurance steps that should be taken to achieve the objectives of the organization in terms of cybersecurity. It may seem costly for a business to invest in the implementation of cybersecurity standards; however, the confidence and trust that it brings are more beneficial for the organization. [28]
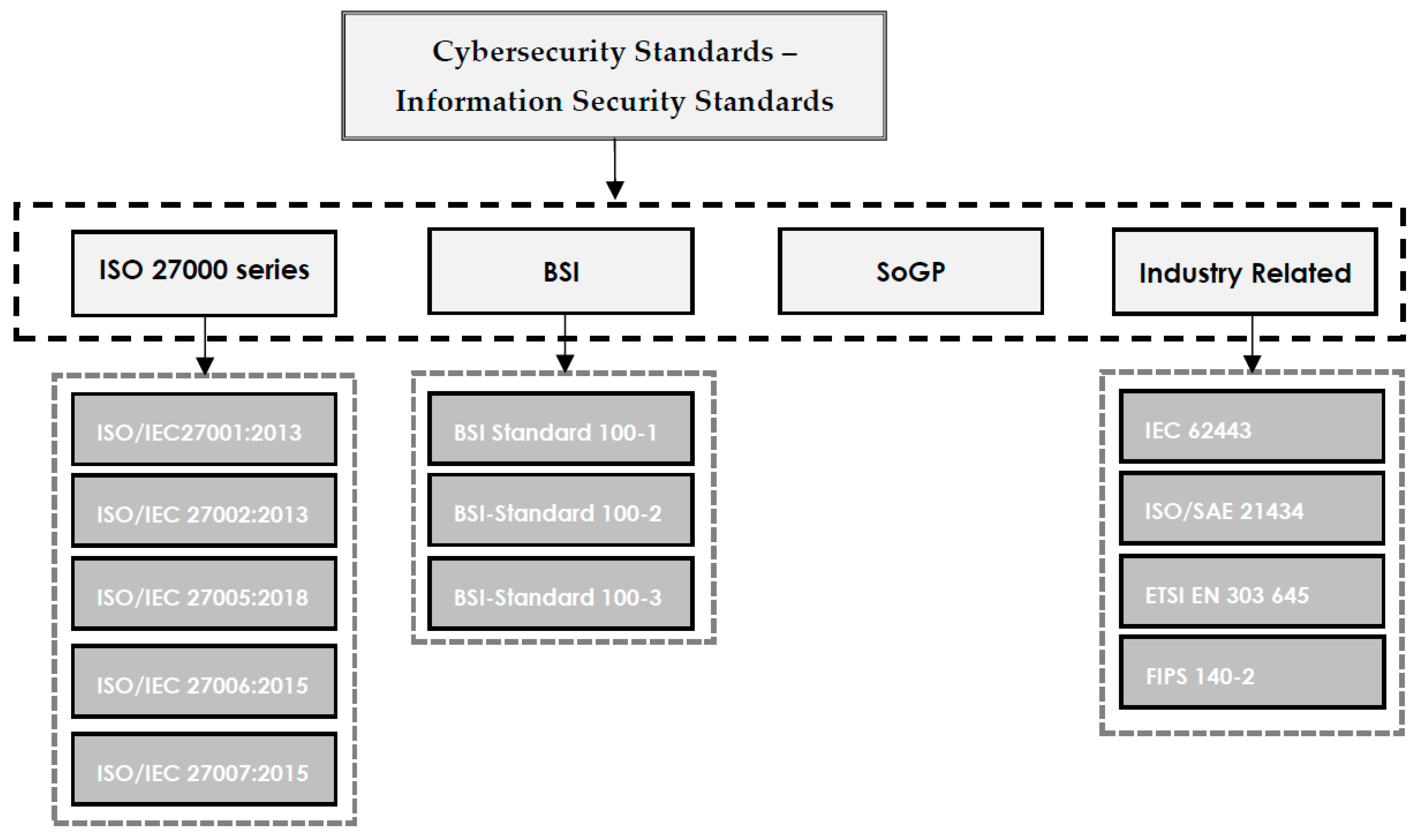
Written cybersecurity standard documents describe requirements to be respected by the organization and are easy to be controlled by stakeholders or relevant auditors. However, standards do not include how to achieve the standard requirements. The most popular and frequently used cybersecurity standards, referred to in this paper, are shown in Figure 1. It is important to note that cybersecurity frameworks may not be limited to what is presented in the scope of this study, since new frameworks are constantly being published based on demands. In a general classification, the ISO 27000 series, BSI, and SoGP are provided. Additionally, some standards that are common in industry are presented in the "Industry Related" category.
|
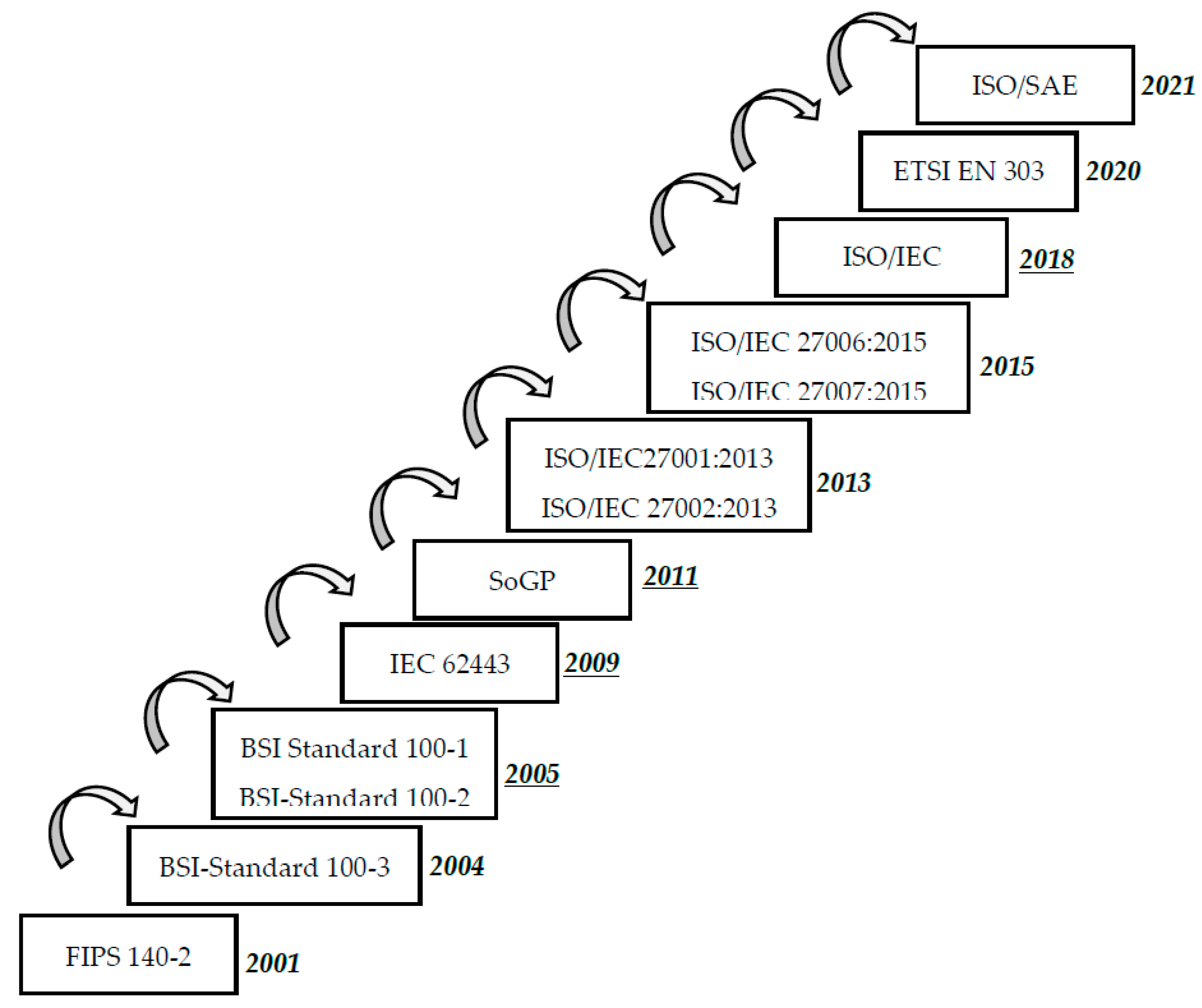
The evolution of cybersecurity standards over time is represented in Figure 2.
|
In the following subsections, the most popular cybersecurity standards—including the ISO 27000 series, SoGP, and BSI—are described to provide an overview and facilitate the process of decision-making.
ISO/IEC 27000 standards
The ISO/IEC 27000 series of standards concentrates on security in information systems management (ISM). [15] The family of ISO/IEC 27000 standards was initially recognized as BS7799 and then introduced as ISO standards as soon as the ISO added it to the information security management system (ISMS) standards. [29] Methods and practices to ensure effective implementation of information security in an organization are described in detail in ISO 27001, focusing on providing a secure and trustable exchange of data and communication channels. The main consideration of ISO 27001 in accomplishing managerial and organizational objectives and sub-objectives is through stressing the imporatance of risk management approaches. However, the ISO 27000 series has not been shown to successfully work as a complete information systems management (ISM) solution to be integrated into larger systems. ISO 27001, the first in the series of ISO/IEC 27000 standards, dates back to 2005. However, four standards, including 27001, 27002, 27005, and 27006, are currently published and widely used in organizations. [30]
ISO/IEC 27001:2013
ISO/IEC 27001:2013 is an internationally recognized standard that determines requirements to implement a certified ISMS for a business through seven key elements. [10] These steps include specifications for installation, performance, operation, controlling and monitoring, review, maintenance, and improvement of the system. General requirements for the treatment and assessment of risks that exist in the information system of the organizations are also included, regardless of the size, type, and nature of the business. ISO/IEC 27001 is commonly used along with ISO/IEC 27002, which clarifies security control objectives and recommendations, since it does not list specific security controls. Employment of ISO/IEC 27001 helps organizations to manage and protect the valuable information of employees and clients, manage information risks, and protect and develop their brands. [31] (Note that since the original publishing of this journal article, the standard was updated, in October 2022.)
ISO/IEC 27002:2013
ISO/IEC 27002:2013 is the code of practice for information security controls that lists a structured series of information security controls to comply with ISO/IEC 27001. However, security controls that are not specifically mentioned in this list are not mandatory to be employed by organizations. Best practice recommendations to be used by responsible individuals when they try to implement information security management are provided in ISO/IEC 27002. [32] This includes managing assets in an organization, securing human resources, managing operations and communications, securing environmental and physical aspects, managing business continuity, and managing compliance and information security incident areas. [25] (Note that since the original publishing of this journal article, the standard was updated, in February 2022.)
ISO/IEC 27005:2018
Guidelines for risk-based implementation of cybersecurity risk management are provided in ISO/IEC 27005:2018. The standard supports concepts and requirements that are specifically listed in ISO/IEC 27001. To completely understand ISO/IEC 27005, organizations need to gain knowledge about the processes and concepts of ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO/IEC 27002. ISO/IEC 27005 can be applicable to those implementing a satisfactory risk-based information system in organizations of different sizes and sectors. [33] ISO/IEC 27005 employs an information risk management process that consists of seven main elements, including installation of context, assessing risk, treating risk, accepting risk, communicating risk, consulting risk, as well as monitoring risk and reviewing risk. [25] (Note that since the original publishing of this journal article, the standard was updated, in October 2022.)
ISO/IEC 27006:2015
The main purpose of ISO/IEC 27006 is to determine formal processes and requirements that should be respected by third-party bodies that provide information security auditing and certifying services for other organizations. Conforming to ISO/IEC 27006 helps bodies to be recognized as trustable and reliable organizations operating ISMS. [10]
Other ISO/IEC standards
Other cybersecurity and information security standards put forth by the ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 27 technical committee include [25]:
- ISO/IEC 27000:2018 Information technology — Security techniques — Information security management systems — Overview and vocabulary
- ISO/IEC 27003:2017 Information technology — Security techniques — Information security management systems — Guidance
- ISO/IEC 27004:2016 Information technology — Security techniques — Information security management — Monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation
- ISO/IEC 27007:2020 Information security, cybersecurity and privacy protection — Guidelines for information security management systems auditing
- ISO/IEC TS 27008:2019 Information technology — Security techniques — Guidelines for the assessment of information security controls
- ISO/IEC 27009:2020 Information security, cybersecurity and privacy protection — Sector-specific application of ISO/IEC 27001 — Requirements
- ISO/IEC 27011:2016 Information technology — Security techniques — Code of practice for Information security controls based on ISO/IEC 27002 for telecommunications organizations
- ISO/IEC 27013:2021 Information security, cybersecurity and privacy protection — Guidance on the integrated implementation of ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO/IEC 20000-1
- ISO/IEC 27014:2020 Information security, cybersecurity and privacy protection — Governance of information security
- ISO/IEC TR 27016:2014 Information technology — Security techniques — Information security management — Organizational economics
- ISO/IEC 27017:2015 Information technology — Security techniques — Code of practice for information security controls based on ISO/IEC 27002 for cloud services
- ISO/IEC 27018:2019 Information technology — Security techniques — Code of practice for protection of personally identifiable information (PII) in public clouds acting as PII processors
- ISO/IEC 27019:2017 Information technology — Security techniques — Information security controls for the energy utility industry
ISF's Standard of Good Practice for Information Security
the Information Security Forum (ISF), an international organization based in London, with staff in New York City, initially published the Standard of Good Practice for Information Security in 1996. The ISF is a non-profit and independent organization that concentrates on the development of best practices and benchmarking in the information security arena. [7] Companies and individuals in manufacturing, financial services, transportation, chemical/pharmaceutical, retail, government, telecommunications, media, transportation, energy, and professional services from all over the world can join the ISF. The standard—which includes best practices in cybersecurity—is also revised every two years to cover the most recent best practices in information security. The standard is mainly designed to concentrate on six major aspects, including installing computers, application of critical business processes, managing security and networks, developing systems, and securing the environment for the end user. [2]
BSI's IT-Grundschutz Compendium and 200-X Standards
The German Federal Office for Information Security (Bundesamt für Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik or BSI) is responsible for managing the security of computers and communication for the German government, focusing on security of computer applications, cryptography, internet security, security products, and security test laboratories [10]. Through its focus on "IT baseline protection" or IT-Grundschutz, BSI has provided recommendations for approaches, processes, methods, and procedures that are related to cybersecurity in its IT-Grundschutz Compendium, as well as its 200-X series of standards. It also covers key areas in information security that are required to be considered while setting approaches for companies and public authorities. [34]
BSI-Standard 200-1: Information Security Management Systems (ISMS)
The first standard in the BSI Standards 200-X series is BSI-Standard 200-1, which describes the main requirements that should be followed to implement ISMSs. There is full compatibility between 200-1 and ISO/IEC 27001. Moreover, recommendations and solutions of ISO standards are taken into consideration in this standard. [10] This standard mainly concentrates on managing the challenges of planning the information technology implementation process described in the ISO/IEC 27001 standard.[3]
BSI-Standard 200-2: IT-Grundschutz-Methodology
BSI-Standard 200-2 includes the employment of IT security management practices in a practical step-by-step manner, covering suggestions for the selection of appropriate measures in information technology security, the implementation of information technology security, and the intricacies of information technology security using the IT-Grundschutz methodologies of standard, basic, and core protection. Additionally, general requirements to employ ISO 27001, 27002 and 13335 standards are interpreted using notes and examples, which help facilitate the establishment of a successful ISMS. [34][4]
BSI-Standard 200-3: Risk Analysis based on IT-Grundschutz
BSI-Standard 200-3 concentrates on risk analysis. Organizations apply this approach to promote their risk analysis while they implement the IT-Grundschutz methodologies. [34] The elementary threats described in the IT-Grundschutz Compendium form the basis of the recommended information security risk analysis procedures of 200-3.[5]
Apart from the general classification of cybersecurity standards, a class of cybersecurity standards focusing on their application to specific business industries—including ISA/IEC 62443, ISO/SAE 21434, ETSI EN 303 645, and FIPS 140-3—is also provided in this study.
ISA/IEC 62443 standards
ISA/IEC 62443 is an international series of standards in cybersecurity that is focused on the employment of cybersecurity requirements for operating technology in systems used for industrial automation and control system (IACS) purposes. [35] This series of standards, initially established by the ISA99 committee, addresses current and future cybersecurity concerns in IACSs. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has adopted this standard and asks security experts in industrial automation and control systems from all over the world to help develop the standard. [35] Since the standard has divided cybersecurity topics into different categories, it is not limited to the technology sector, and it also considers mitigating cyber threats regarding processes, employees, and countermeasures.
ISO/SAE 21434:2021
This standard is focused on cybersecurity risk management requirements in the engineering of electronic systems of road vehicles and includes production, operation, development, maintenance, etc. concepts in vehicular engineering. [36] It also expands into addressing both components and interfaces of road vehicles. The main aim of this standard is to ensure that cybersecurity concerns are addressed in the engineering of road vehicles and that they are protected against different cyberattacks. [36]
ETSI EN 303 645 V2.1.1
Cybersecurity is becoming a growing challenge, as more devices are connected to the internet and more people are sharing their personal data using internet of things (IoT) technologies. This standard targets all parties that are involved in manufacturing and developing IoT products and appliances. [37] The standard has collected a wide range of best practices and requirements in internet-connected products and appliances to ensure the security of consumers’ data. The main focus of this standard is on the establishment of organizational policies and technical controls that are applicable to all IoT devices. [37]
FIPS 140-3
The Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) are published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). This standard includes hardware and software requirements to protect cryptography modules. Cryptography modules include valuable information that should be secured with respect to integrity and confidentiality concerns. Four security levels, from the lowest to the highest, are defined in FIPS 140-3. This standard is established based on the joint collaboration of NIST and the Canadian Centre for Cyber Security to ensure that cryptographic modules meet validation requirements. Therefore, if a product meets FIPS 140-3 requirements, it is accepted by federal agencies of the United States and Canada at the same time. [38][6]
Cybersecurity and information security frameworks
References
- ↑ "What is a standard?". Standards Australia. 2022. https://www.standards.org.au/standards-development/what-is-standard. Retrieved 01 February 2022.
- ↑ "ISO/IEC Directives, Part 2: Rules for the structure and drafting of International Standards" (PDF). International Organization for Standardization, International Electrotechnical Commission. 2011. https://boss.cen.eu/media/yypjl3mn/iso_iec_directives_part2.pdf.
- ↑ "BSI-Standard 200-1: Information Security Management Systems (ISMS)". Bundesamt für Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik. 7 May 2018. https://www.bsi.bund.de/SharedDocs/Downloads/EN/BSI/Grundschutz/International/bsi-standard-2001_en_pdf.html?nn=908032.
- ↑ "BSI-Standard 200-2: IT-Grundschutz-Methodology". Bundesamt für Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik. 7 May 2018. https://www.bsi.bund.de/SharedDocs/Downloads/EN/BSI/Grundschutz/International/bsi-standard-2002_en_pdf.html?nn=908032.
- ↑ "BSI-Standard 200-3: Risk Analysis based on IT-Grundschutz". Bundesamt für Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik. 7 May 2018. https://www.bsi.bund.de/SharedDocs/Downloads/EN/BSI/Grundschutz/International/bsi-standard-2003_en_pdf.html?nn=908032.
- ↑ "FIPS PUB 140-3 Security Requirement for Cyptographic Modules" (PDF). National Institute of Standards and Technology. 22 March 2019. https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/FIPS/NIST.FIPS.140-3.pdf.
Notes
This presentation is faithful to the original, with only a few minor changes to presentation, grammar, and punctuation. In some cases important information was missing from the references, and that information was added. The BSI standards discussed in the original refer to the old 100 standards, for some unknown reason; they were updated to the 200-X series of standards for this version. Additional references to those 200-X standards are also supplied in this version. Similarly, the author refers to FIPS 140-2 instead of 140-3, for some unknown reason, despite 140-3 being released in March 2019; 140-3 is used in this version, and an additional reference is supplied.