Difference between revisions of "Journal:Definitions, components and processes of data harmonization in healthcare: A scoping review"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Saving and adding more.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Saving and adding more.) |
||
| Line 126: | Line 126: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" colspan="6"|'''Table 1.''' Characteristics of included studies (''n'' = 181)<br /> <br />CDE = clinical data exchange, CIE = clinical information exchange, DH = data harmonization, DL = data linkage, DS = data sharing, DW = data warehouse, EHR = electronic health record, HDE = health data exchange, HIE = health information exchange, IE = information exchange, IO = interoperability, LMICs = low-to-middle-income countries, RL = record linkage | | style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" colspan="6"|'''Table 1.''' Characteristics of included studies (''n'' = 181)<br /> <br />CDE = clinical data exchange, CIE = clinical information exchange, DH = data harmonization, DL = data linkage, DS = data sharing, DW = data warehouse, EHR = electronic health record, HDE = health data exchange, HIE = health information exchange, IE = information exchange, IO = interoperability, LMICs = low-to-middle-income countries, RL = record linkage | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="background-color:#e2e2e2; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Study name | ! style="background-color:#e2e2e2; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Study name | ||
| Line 392: | Line 390: | ||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: healthcare workers | | style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: healthcare workers | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"| | | style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Vest | ||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2010 | | style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2010 | ||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | | style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | ||
| Line 884: | Line 882: | ||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: healthcare workers | | style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: healthcare workers | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"| | | style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Mastebroek | ||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2017 | | style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2017 | ||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: qualitative | | style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: qualitative | ||
| Line 1,310: | Line 1,308: | ||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | | style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | ||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Research | | style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Research | ||
| | |- | ||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" colspan="6" align="left"|'''Study protocol''' | | style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" colspan="6" align="left"|'''Study protocol''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 1,416: | Line 1,414: | ||
|} | |} | ||
Of the 181 included studies, nine were not country-specific (these were global reviews), 151 were from the USA, and the rest were from other countries (specifically Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, Finland, Germany, Israel, Japan, Jordan, Korea, Malaysia, Netherlands, South Africa, and South Korea). In terms of the level of the health care system, 128 studies were on a DH intervention or activity that was concerned with the frontline level (health service providers), 48 studies were concerned with health system factors or policy-related activities at the managerial level, and five studies focused on DH interventions specifically for research purposes. Most studies (92%) used the term health information exchange (HIE), while the remaining studies (8%) used a variety of terms to describe various DH interventions and activities, specifically, record linkage, data mining, data linkage, data warehousing, data sharing, and data harmonization. | |||
===Definitions, components, and processes of data harmonization=== | |||
In this subsection, we first discuss the alternative terms and definitions of DH, and then we summarize key components and processes of DH using studies sampled from the 61 studies identified for the second and third objectives. Table 2 presents identifying details of the 61 studies, including the type of study design, the intervention terms, the country, the level of the health care system, and the purpose of the study. These studies were concerned with the challenges and opportunities of DH, the barriers and facilitators of DH, the various factors affecting DH (such as technical and financial factors), the outcomes of DH (such as patient safety and quality of care), and the privacy and security issues of patient information. | |||
{| | |||
| STYLE="vertical-align:top;"| | |||
{| class="wikitable" border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" width="70%" | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;" colspan="7"|'''Table 2.''' Characteristics of sampled studies (''n'' = 61)<br /> <br />CDE = clinical data exchange, CIE = clinical information exchange, DH = data harmonization, DL = data linkage, DS = data sharing, DW = data warehouse, EHR = electronic health record, HDE = health data exchange, HIE = health information exchange, IE = information exchange, IO = interoperability, LMICs = low-to-middle-income countries, RL = record linkage | |||
|- | |||
! style="background-color:#e2e2e2; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Study name | |||
! style="background-color:#e2e2e2; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Date | |||
! style="background-color:#e2e2e2; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Type of study | |||
! style="background-color:#e2e2e2; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Intervention term | |||
! style="background-color:#e2e2e2; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Country | |||
! style="background-color:#e2e2e2; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Level of the healthcare system | |||
! style="background-color:#e2e2e2; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Purpose of the study | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Akhlaq | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2016 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Review | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|LMICs | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management: countries | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Barriers and facilitators of HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Boyd | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2014 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|RL | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Australia | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Research | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Functions of record linkage | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Burris | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2017 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Commentary | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: hospitals | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Benefits of HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Campion | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2012 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: quantitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: healthcare workers | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Push and pull of HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Cimino | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2014 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Debates around consumer-mediated HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Dalan | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2010 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: qualitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|DM | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Research | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Possibilities for clinical data mining and research | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Dimitropoulos | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2009 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Privacy and security of interoperable HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Dixon | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2010 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Review | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Research | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Costs, effort and value of HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Downing | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2017 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: quantitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management: policies | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Relationship between HIE and organisational HIE policy decisions | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Downs | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2010 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Improving laboratory services through HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Dullabh | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2013 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: qualitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management: organizations | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Experience of HIE implementation | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Elysee | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2017 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: quantitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE, IO | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: hospitals | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Relationship between HIE, interoperability and medication reconciliation | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Esmaeilzadeh | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2016 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Review | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|n/a | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management: policies | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE assimilation and patterns for policy | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Esmaeilzadeh | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2017 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Review | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|n/a | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: patients | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Patients’ perceptions of HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Fontaine | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2010 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Review | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|n/a | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: primary healthcare | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE for primary healthcare practices | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Fontaine | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2010 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: qualitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: primary healthcare | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Barriers and facilitators of HIE in primary care practices | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frisse | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2010 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: patients, workers | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Impact of HIE on patient-provider relationships | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Gadd | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2011 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: quantitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: healthcare workers | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Users’ perspectives on the usability of a regional HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Gill | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2001 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: quantitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|DL | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|South Africa | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: patients, disease | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Linkage of non-communicable diseases data | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Greene | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2016 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Technical and financial aspects of HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Grossman | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2008 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Barriers to stakeholder participation in HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Haarbrandt | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2016 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|DW | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Approaches for a clinical data warehouse | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Herwehe | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2012 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: quantitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: healthcare workers | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Implementation of an electronic medical record and HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Hincapie | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2011 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: qualitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: healthcare workers | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Physicians’ opinions of HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Hopf | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2014 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Review | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|DL | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|n/a | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: healthcare workers | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Healthcare professionals’ views of linking routinely collected data | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Hu | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2007 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|DS | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Challenges in implementing an infectious disease information sharing and analysis system | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Hypponen | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2014 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: quantitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Finland | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: healthcare workers | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|User experiences with different regional HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Ji | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2017 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: quantitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Korea | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: hospitals | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Technology and policy changes for HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Jones | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2012 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|DS | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|An overview of electronic data sharing | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Kash | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2017 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Review | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|n/a | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: hospitals | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Hospital readmission reduction and the role of HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Kierkegaard | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2014 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: qualitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: healthcare workers | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Applications of HIE information to public health practice | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Kierkegaard | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2014 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: qualitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Health practitioners’ needs and HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Kuperman | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2013 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Potential unintended consequences of HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Liu | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2010 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: qualitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|DH | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|China | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Defining data elements for HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Maiorana | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2012 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: mixed | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: workers, disease | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Trust, confidentiality, and acceptability of sharing HIV data for HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Massoudi | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2016 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: qualitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: organizations | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE for clinical quality measures | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Mastebroek | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2014 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Review | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: disease, workers | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE in general care practice for people with disabilities | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Mastebroek | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2016 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: quantitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Netherlands | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: healthcare workers | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Priority setting and feasibility of HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Masterbroek | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2017 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: qualitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Netherlands | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: patients | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Experiences of people with intellectual disabilities in HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Matsumoto | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2017 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: qualitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: workers, hospitals | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE in managing hospital services | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Parker | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2016 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Review | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Research | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|The use of HIE in supporting clinical research | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Politi | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2014 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|n/a | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Use patterns of HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Rahurkar | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2015 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Review | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|n/a | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: hospitals | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Impact of HIE on cost, use and quality of care | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Ramos | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2016 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: mixed | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: patients | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE consent process in an HIV clinic | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Ranade-Kharkar | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2014 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Improving data quality integrity through HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Ross | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2010 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: qualitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: clinics | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Motivators, barriers, and potential facilitators of adoption of HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Rudin | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2014 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Review | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: clinical care | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Use and effect of HIE on clinical care | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Rundall | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2016 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: qualitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: policy makers, leaders | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Information-sharing needs and HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Sadoughi | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2018 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Review | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|n/a | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Quality and cost-effectiveness, and the rates of HIE adoption and participation | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Santos | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2017 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: quantitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Brazil | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: clinics, hospitals | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE for continuity of maternal and neonatal care | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Shade | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2012 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: quantitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: clinics, hospitals | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE for quality and continuity of HIV care | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Shapiro | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2016 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: workers, organizations | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE in emergency medicine | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Shapiro | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2006 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Approaches to patient HIE and their impact on emergency medicine | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Vest | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2010 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Challenges and strategies for HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Vest | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2012 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Review | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|n/a | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|National and international approaches of health information exchange | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Vest | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2015 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: qualitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: consumers, organizations | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE to change cost and utilisation outcomes | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Williams | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2012 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Strategies to advance HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Yaraghi | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2014 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Professional and geographical network effects on HIE growth | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Yeager | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2014 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: qualitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Frontline: consumers | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Factors related to HIE participation and use | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Zaidan | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2015 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Conceptual | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Malasia | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Management | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Security framework for nationwide HIE | |||
|- | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Zhu | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|2010 | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Primary: quantitative | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|HIE | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|USA | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Research | |||
| style="background-color:white; padding-left:10px; padding-right:10px;"|Facilitating clinical research through HIE | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
|} | |||
==Abbreviations== | ==Abbreviations== | ||
Revision as of 17:13, 2 November 2020
| Full article title | Definitions, components and processes of data harmonization in healthcare: A scoping review |
|---|---|
| Journal | BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making |
| Author(s) | Schmidt, Bey-Marrié; Colvin, Christopher J.; Hohlfeld, Ameer; Leon, Natalie |
| Author affiliation(s) | South African Medical Research Council, University of Cape Town, University of Virginia, Brown University |
| Primary contact | Online contact form |
| Year published | 2020 |
| Volume and issue | 20 |
| Page(s) | 222 |
| DOI | 10.1186/s12911-020-01218-7 |
| ISSN | 1472-6947 |
| Distribution license | Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International |
| Website | https://bmcmedinformdecismak.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12911-020-01218-7 |
| Download | https://bmcmedinformdecismak.biomedcentral.com/track/pdf/10.1186/s12911-020-01218-7 (PDF) |
|
|
This article should be considered a work in progress and incomplete. Consider this article incomplete until this notice is removed. |
Abstract
Background: Data harmonization (DH) has is increasingly being used by health managers, information technology specialists, and researchers as an important intervention for routine health information systems (RHISs). It is important to understand what DH is, how it is defined and conceptualized, and how it can lead to better health management decision-making. This scoping review identifies a range of definitions for DH, its characteristics (in terms of key components and processes), and common explanations of the relationship between DH and health management decision-making.
Methods: This scoping review identified more than 2,000 relevant studies (date filter) written in English and published in PubMed, Web of Science, and CINAHL. Two reviewers independently screened records for potential inclusion for the abstract and full-text screening stages. One reviewer did the data extraction, analysis, and synthesis, with built-in reliability checks from the rest of the team. We developed a narrative synthesis of definitions and explanations of the relationship between DH and health management decision-making.
Results: Of the 181 studies ultimately included in this scoping review, 61 included synthesis definitions and concepts of DH in detail. From these, we identified six common terms for data harmonization: "record linkage," "data linkage," "data warehousing," "data sharing," "data interoperability," and "health information exchange." We also identified nine key components or characteristics of data harmonization: it involves (a) multi-step processes; (b) integration and harmonization of different databases; (c) the use of two or more databases; (d) the use of electronic data; (e) pooling of data using unique patient identifiers; (f) different types of data; (g) data found within and across different departments and institutions at facility, district, regional, and national levels; (h) different types of technical activities; and (i) a specific scope. The relationship between DH and health management decision-making is not well-described in the literature. Several studies mentioned health providers’ concerns about data completeness, data quality, terminology, and coding of data elements as barriers to data use for clinical decision-making.
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this scoping review was the first to synthesize definitions and concepts of DH and address the causal relationship between DH and health management decision-making. Future research is required to assess the effectiveness of data harmonization on health management decision-making.
Keywords: data harmonization, health information exchange, health information system, scoping review
Background
Data harmonization (DH) in healthcare is a digital, technology-based innovation that can potentially help routine health information systems (RHISs) function at their best. It can help organize and integrate large databases containing routine health information.[1] Designing, developing, and implementing DH interventions has the potential to strengthen aspects of the health system, by enhancing RHISs to a state of high-quality and relevant information that can support decisions, actions, and changes across all components and levels of the health system.[2][3] When RHISs are functioning properly, they can help health practitioners and managers identify and close gaps in health service delivery, as well as inform their planning, implementation, and monitoring of interventions.[4][5] They can also help address problems related to using different variables and indicators for collecting, analyzing, and reporting health information across healthcare administration and management programs[6], which is common in low-and-middle-income (LMIC) settings. Other challenges to effective RHIS functioning include the production of poor-quality data that cannot easily be exchanged, as well as programmatic fragmentation across levels of the health system, which can result in the duplication and excessive production of data.[7]
Lack of standardized data production processes, fragmentation of databases, and errors and duplication in data production are only some of the challenges of RHISs, which may, at first glance be categorized as technical challenges.[3][8] Solutions to such apparently technical challenges include introducing new data forms, setting up warning systems to detect potential errors, and developing algorithms for integrating different databases.
However, DH interventions for RHISs may not be used effectively if data production and utilization processes are viewed as merely technical. Given that RHISs are embedded in complex health systems, DH interventions to improve RHIS functions are also influenced by the broader setting, in which dynamic and complex social and technical factors interact.[9][10][11] There is a need to consider the influence of social factors as well. These may include people’s competencies in dealing with new data production processes, institutional values about data utilization, and existing relationships between data producers and decision-makers.[8][12][13]
There is growing recognition that the development and implementation of DH interventions occurs in multiple technical and social contexts, and that DH interventions may differ in definition, purpose, and intended outcomes.[14] As such, various terms are used to describe interventions with similar aims and activities to data harmonization. For example, terms such as "record linkage," "data warehousing," "data sharing," and "health information exchange" are all used to describe data harmonization-type activities[15][16][17]; it is not always clear to which extent these interventions are similar in practice, scope, and relevance. The use of multiple terms may not be a problem in itself, but a common understanding of the components and processes will bring more clarity about what actually constitutes "data harmonization," and it will make it easier to compare and appraise the relevance and usefulness of DH interventions across settings.
Although DH has the potential to enhance RHISs, it is still unclear whether or how it affects health management decision-making. In some cases, DH interventions may not directly improve management decision-making, especially when interventions are more focused on the technical aspects of data production and less on the organizational and behavioral aspects of data use for decision-making.[18] The scope of this review is to therefore understand the different ways in which DH is defined, to identify its components and processes, and to describe whether or how DH can affect health management decision-making. Greater clarity about the range of definitions, components, and processes of DH interventions, as well as its intended outcomes, can help to better evaluate DH's relevance, usefulness, and impact.[12]
Methods
This scoping review was conducted according to the methods outlined by Arksey and O’Malley.[19] They recommend a process that is “not linear but, requiring researchers to engage with each stage in a reflexive way” to achieve both "in-depth and broad" results. This review followed the standard steps for systematic reviews: identifying the research question, identifying relevant studies, selecting studies for inclusion, extracting data, and synthesizing data. These are detailed in our published study protocol.[20]
Study objectives
This scoping review appraised the definitions, components, and processes of data harmonization activities, and it provided a broad explanation of the relationship between data harmonization interventions and health management decision-making. The specific objectives are:
- 1. to identify and provide an overview of the key components and processes of data harmonization studies;
- 2. to identify and synthesize the various definitions of data harmonization in healthcare; and
- 3. to describe the relationship between data harmonization interventions and health management decision-making.
We took a stepped approach in addressing these objectives. All included studies were used to address the first objective. To address the second objective, we sampled studies that were using alternative terms for DH interventions and used those to identify, synthesize, and compare similarities and differences in definitions. While executing these two objectives, we identified a smaller number of studies that contributed to the third objective.
Identifying relevant studies
Eligibility criteria
Peer-reviewed studies and gray literature were considered eligible for inclusion into the scoping review if they provided a definition or description of DH, and or, a more detailed conceptual explanation (in the form of a model, framework, or process) of a DH intervention. Additionally, studies were eligible if they provided an explanation of the causal relationship between DH and health management decision-making (such as through improved quality and accessibility of harmonized information for management and/or the use of harmonized health information for management decision-making). We considered any studies concerned with different technical activities of DH (such as linking, merging, cleaning and transferring). After screening, only studies for which we could access full-text articles were eligible for inclusion in the review.
Search strategy
A systematic literature search was conducted in PubMed, CINAHL, and Web of Science for eligible studies from January 1, 2000 to September 30, 2018. We limited our search to as far back as 2000, as digital technology-based innovations began during this period (such as health information exchange) in high-income countries (predominantly in the United States of America), and researchers and health system managers in LMICs became more interested in the integration of large digital databases.[21] We present the search strategy in the study protocol.[20] Based on preliminary searches, we anticipated that these databases would yield the highest results. The search strategies included a combination of keywords and Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) related to data harmonization (concept A) and health information systems (concept B). There were no geographic restrictions, but for logistical reasons of time and resources, we only searched for English studies.
Selecting studies for inclusion
Screening records
The first reviewer (BS) conducted all the searches with the help of a librarian and collated the records in the EndNote reference management program, where duplicates were removed. Two reviewers, (BS) and second reviewer (AH), then independently screened the records (titles and abstracts) to assess eligibility for full-text review. BS and AH resolved conflicts that emerged at this stage by talking through the inclusion criteria and arriving at a joint decision.
The full-texts of potentially eligible studies were retrieved and assessed by the two reviewers (BS and AH). Final inclusion into the review was based on whether at a minimum the study had a definition or description of a DH intervention or referred to its relationship with health management decision-making. The first reviewer read all full-texts and the second reviewer only read a sample (roughly a third) of the full-texts to verify the first reviewer’s decision about inclusion. BS and AH disagreed on four studies, and after discussion, agreed to exclude the studies.
After finalizing screening, the two reviewers then mapped out the characteristics of included studies in an Excel spreadsheet. They recorded the name of the first author; the date; the type of study (primary, review, conceptual, commentary); the term used for the intervention they described (DH or alternative); the country in which the study took place; the level at which the intervention was implemented (frontline, management, research); and indicated whether or not there was a conceptual model, framework, diagram, or process description of DH and health management decision-making. This detailed mapping of study characteristics was useful for informing sampling options for the second and third objectives.
Sampling of studies
A scoping review aims to map the literature on a particular topic rather than to provide an exhaustive explanation of a particular phenomenon of interest.[19][22] Thus, the number of included studies was expected to be high in the scoping reviews. To manage the high numbers for a scoping review such as this one (where the aim was to provide definitions and concepts), it was necessary to make use of a qualitative sampling approach. A qualitative sampling approach for this review aimed for variation and depth rather than an exhaustive sample; reviewing too large a number of studies can impair the quality of the analysis and synthesis.[23] We used two types of purposive sampling techniques called maximum variation sampling and theoretical sampling.[24] These techniques were used to identify both the range, variation, and similarities or differences in definitions and concepts and intervention descriptions (as per the second objective), and to provide a rich synthesis of explanations of causal relationships between DH and health management decision-making (as per the third objective). For the first objective, we did not apply a sampling strategy. Thus, we included all the studies that at a minimum provided a definition or description of a DH intervention.
Data extraction
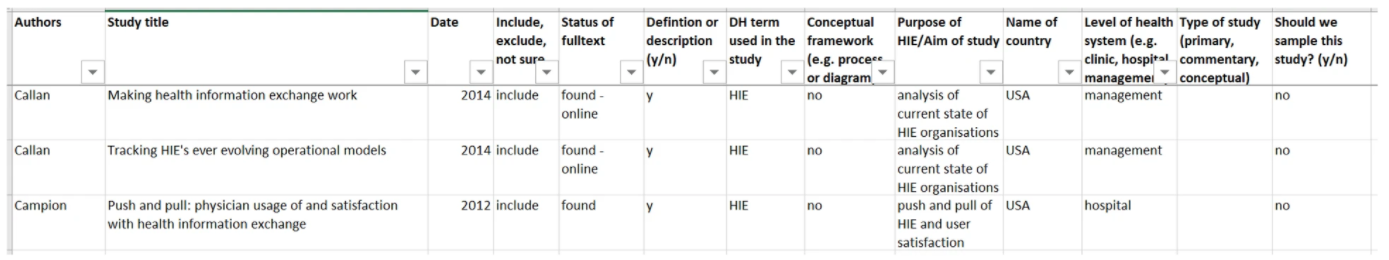
BS extracted data for the first objective from all the included studies (n = 181). AH independently extracted data from 81 (45%) of included studies to verify data extraction done by the first reviewer. We used an MS Excel spreadsheet for data extraction, as presented in Fig. 1. AH and BS extracted a few studies before clarifying the items in the spreadsheet. Once data extraction was complete, the reviewers were able to filter according to the individual items extracted in order to synthesize and compare the studies. Given the objectives of the scoping review, we did not extract any information relevant to conducting risk of bias or quality assessment. Not conducting risk of bias or quality assessment is consistent with scoping reviews of similar aims and methodological approaches.[19][22][25]
|
Data synthesis: Collating, summarizing, and reporting findings
The first reviewer (BS) conducted data analysis using manual coding and the filter option in MS Excel. Another reviewer (NL) reviewed the data analysis work on an ongoing basis as an additional quality check. For the first objective, we conducted a numerical analysis to provide an overview of the characteristics of all the included studies. For the second objective, we conducted a qualitative analysis to provide a narrative synthesis of the different DH definitions and concepts, and to identify different components or activities that are considered part of the DH processes. For the third objective, we reviewed data related to intentions, suggestions, and/or explanations of how DH may lead to improved health management decision-making. We extracted and analyzed data relevant to the second and third objectives at the same time. We first created a list of all the different terms used to describe DH interventions and then compared definitions across alternative terms by looking for similarities or differences in the definitions or descriptions of DH interventions. We then coded key components, processes, and outcomes of DH interventions and the factors reported as important in the relationship between DH and health management decision-making.
The findings are structured according to three themes matching the three study objectives: an overview of the key characteristics of included studies, alternative terms and definitions of DH, and a narrative synthesis of the relationship between DH and health management decision-making.
Reflexivity
Throughout the review, the authors were aware of their own positions and reflected on how these could influence the study design, search strategy, inclusion decisions, data extraction, and analysis, as well as the synthesis and interpretation of the findings.[23] The review authors are trained in anthropology, epidemiology, health systems, and evidence synthesis research. The first author was involved in participant observation of an innovative DH project in the Western Cape Department of Health in South Africa as part of her doctoral research, where she grappled with questions that informed the objectives of this review. Three of the authors (BS, AH, and NL) were involved in a Cochrane Collaboration systematic review on RHIS interventions when this scoping review was conceptualized, so they were familiar with some of the health information systems (HIS) literature and had some appreciation for the conceptual and methodological complexities of studying the field of health information management. This experience informed the way the first author developed the search strategy. She used an iterative approach to narrow down the search as much as possible because of her prior knowledge that it was difficult to balance sensitivity and specificity when developing a search strategy for HIS literature that is often multi-disciplinary in nature.
Results
Results of the search
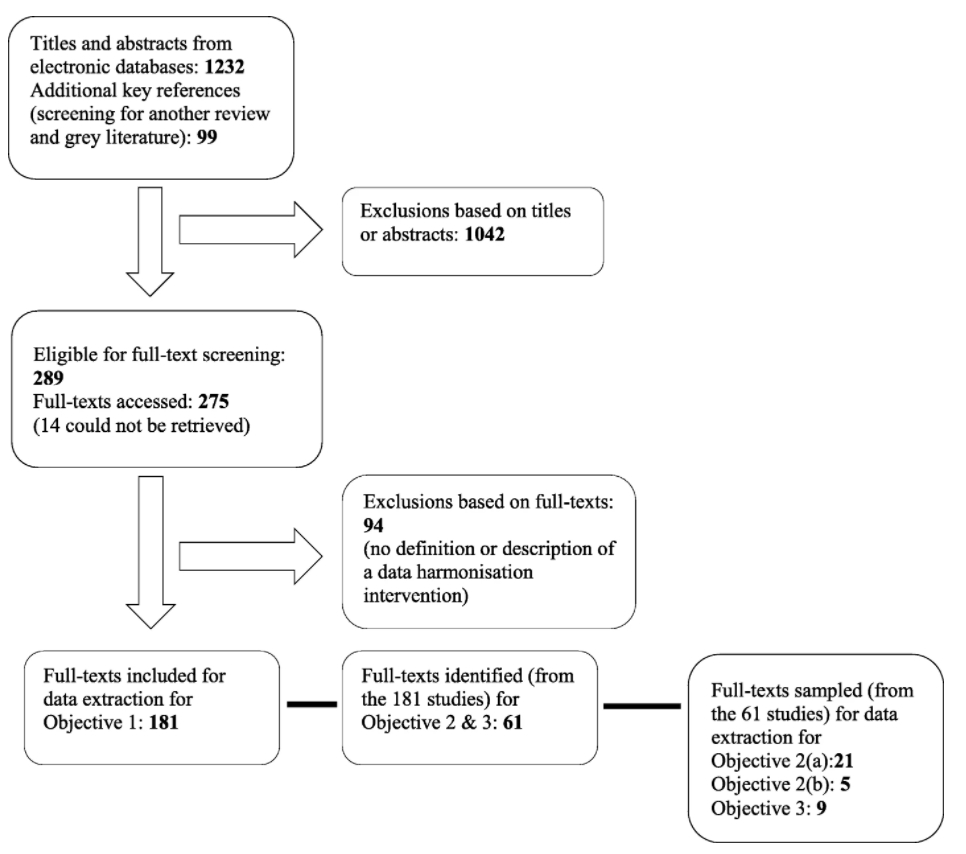
Figure 2 shows a PRISMA diagram of the search results. We screened a total of 1,331 records: 1,232 titles and abstracts identified from searching three electronic databases, and 99 from screening for a Cochrane Collaboration systematic review assessing the effectiveness of RHIS interventions on health systems management[26], as well as gray literature. Almost a quarter (289 of 1,331) were deemed potentially eligible for full-text screening. We accessed full-texts for 275 studies, and of those, 181 were included in the scoping review for the first objective. We excluded 94 full-text articles because they did not meet the minimum criteria; that is, they did not provide a definition or description of a DH intervention or activity. We sampled 61 studies from the 181 for the second and third objectives. We arrived at 61 studies by including all reviews (systematic or literature reviews) and all studies (irrespective of the type of study) that also had a process description, conceptual framework, or a theory of a DH intervention (that is, in addition to the minimum criteria for the first objective).
|
An overview of key characteristics of data harmonization studies
A total of 181 studies were included into this scoping review for the first objective (see Table 1). Given the high number of included studies, we decided to only map the following key characteristics of those studies: first author, date, type of study, intervention term (DH or alternative), country, and level of the health care system. Most included studies (126 of 181) were either primary studies assessing various aspects of developing and implementing DH interventions (quantitative studies n = 86), or patient, providers, or stakeholders’ perspectives (qualitative studies n = 34), or a combination of both (mixed methods studies n = 6).
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Of the 181 included studies, nine were not country-specific (these were global reviews), 151 were from the USA, and the rest were from other countries (specifically Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, Finland, Germany, Israel, Japan, Jordan, Korea, Malaysia, Netherlands, South Africa, and South Korea). In terms of the level of the health care system, 128 studies were on a DH intervention or activity that was concerned with the frontline level (health service providers), 48 studies were concerned with health system factors or policy-related activities at the managerial level, and five studies focused on DH interventions specifically for research purposes. Most studies (92%) used the term health information exchange (HIE), while the remaining studies (8%) used a variety of terms to describe various DH interventions and activities, specifically, record linkage, data mining, data linkage, data warehousing, data sharing, and data harmonization.
Definitions, components, and processes of data harmonization
In this subsection, we first discuss the alternative terms and definitions of DH, and then we summarize key components and processes of DH using studies sampled from the 61 studies identified for the second and third objectives. Table 2 presents identifying details of the 61 studies, including the type of study design, the intervention terms, the country, the level of the health care system, and the purpose of the study. These studies were concerned with the challenges and opportunities of DH, the barriers and facilitators of DH, the various factors affecting DH (such as technical and financial factors), the outcomes of DH (such as patient safety and quality of care), and the privacy and security issues of patient information.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Abbreviations
CDE = clinical data exchange
CIE = clinical information exchange
DH = data harmonization
DL = data linkage
DS = data sharing
DW = data warehouse
EHR = electronic health record
HDE = health data exchange
HIE = health information exchange
IE = information exchange
IO = interoperability
LMICs = low-to-middle-income countries
RL = record linkage
References
- ↑ Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Pan, F. et al. (2010). "Harmonization of health data at national level: a pilot study in China". International Journal of Medical Informatics 79 (6): 450–8. doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2010.03.002. PMID 20399139.
- ↑ Nutley, T.; Reynolds, H.W. (2013). "Improving the use of health data for health system strengthening". Global Health Action 6: 20001. doi:10.3402/gha.v6i0.20001. PMC PMC3573178. PMID 23406921. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3573178.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Lippeveld, T. (2001). "Routine health information systems: The glue of a unified health system". Keynote address at the Workshop on Issues and Innovation in Routine Health Information in Developing Countries. https://docplayer.net/3034875-Routine-health-information-systems-the-glue-of-a-unified-health-system.html.
- ↑ World Health Organization (2007). "Everybody's Business: Strengthening Health Systems to Improve Health Outcomes" (PDF). World Health Organization. pp. 44. ISBN 9789241596077. https://www.who.int/healthsystems/strategy/everybodys_business.pdf?ua=1.
- ↑ Health Metrics Network, World Health Organization (November 2012). "Country Health Information Systems Assessments: Overview and Lessons Learned - Working Paper 3" (PDF). World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 21 October 2014. https://web.archive.org/web/20141021202640/http://www.who.int/healthmetrics/resources/Working_Paper_3_HMN_Lessons_Learned.pdf.
- ↑ Heywood, A.; Boone, D. (February 2015). "Guidelines for Data Management Standards in Routine Health Information Systems". Measure Evaluation. pp. 93. https://www.measureevaluation.org/resources/publications/ms-15-99.
- ↑ Karuri, J.; Waiganjo, P.; Orwa, D. et al. (2014). "DHIS2: The Tool to Improve Health Data Demand and Use in Kenya". Journal of Health Informatics in Developing Countries 8 (1): 113. https://jhidc.org/index.php/jhidc/article/view/113.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Harrison, M.I.; Koppel, R.; Bar-Lev, S. (2007). "Unintended consequences of information technologies in health care--an interactive sociotechnical analysis". JAMIA 14 (5): 542–9. doi:10.1197/jamia.M2384. PMC PMC1975796. PMID 17600093. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1975796.
- ↑ van Olmen, J.; Criel, B.; Bhojani, U. et al. (2012). "The Health System Dynamics Framework: The introduction of an analytical model for health system analysis and its application to two case-studies". Health, Culture and Society 2 (1): 1–21. doi:10.5195/hcs.2012.71.
- ↑ Sittig, D.F.; Singh, H. (2010). "A new sociotechnical model for studying health information technology in complex adaptive healthcare systems". Quality & Safety in Healthcare 19 (Suppl. 3): i68–74. doi:10.1136/qshc.2010.042085. PMC PMC3120130. PMID 20959322. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3120130.
- ↑ Plsek, P. (27 January 2003). "Complexity and the Adoption of Innovation in Health Care" (PDF). Accelerating Quality Improvement in Health Care Strategies to Speed the Diffusion of Evidence-Based Innovations. https://www.nihcm.org/pdf/Plsek.pdf.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Cresswell, K.M.; Sheikh, A. (2014). "Undertaking sociotechnical evaluations of health information technologies". Informatics in Primary Care 21 (2): 78–83. doi:10.14236/jhi.v21i2.54. PMID 24841408.
- ↑ Cresswell, K.M.; Bates, D.W.; Sheikh, A. (2017). "Ten key considerations for the successful optimization of large-scale health information technology". JAMIA 24 (1): 182–7. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocw037. PMID 27107441.
- ↑ Fichtinger, A.; Rix, J.; Schäffler, U. et al. (2011). "Data Harmonisation Put into Practice by the HUMBOLDT Project". International Journal of Spatial Data Infrastructures Research 6: 234–60. doi:10.2902/1725-0463.2011.06.art11.
- ↑ Akhlaq, A.; McKinstry, B.; Muhammad, K.B.; Sheikh, A. (2016). "Barriers and facilitators to health information exchange in low- and middle-income country settings: A systematic review". Health Policy and Planning 31 (9): 1310–25. doi:10.1093/heapol/czw056. PMID 27185528.
- ↑ Boyd, J.H.; Randall, S.M.; Ferrante, A.M. et al. (2014). "Technical challenges of providing record linkage services for research". BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making 14: 23. doi:10.1186/1472-6947-14-23. PMC PMC3996173. PMID 24678656. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3996173.
- ↑ Hu, P.J.; Zeng, D.; Chen, H. et al. (2007). "System for infectious disease information sharing and analysis: Design and evaluation". IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine 11 (4): 483–92. doi:10.1109/titb.2007.893286. PMC PMC7186032. PMID 17674631. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7186032.
- ↑ Aqil, A.; Lippeveld, T.; Hozumi, D. (2009). "PRISM framework: A paradigm shift for designing, strengthening and evaluating routine health information systems". Health Policy and Planning 24 (3): 217–28. doi:10.1093/heapol/czp010. PMC PMC2670976. PMID 19304786. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2670976.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 Arksey, H.; O'Malley, L. (2005). "Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework". International Journal of Social Research Methodology 8 (1): 19–32. doi:10.1080/1364557032000119616.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Schmidt, B.-M.; Colvin, C.J.; Hohlfeld, A. et al. (2009). "Defining and conceptualising data harmonisation: A scoping review protocol". Health Policy and Planning 7 (1): 226. doi:10.1186/s13643-018-0890-7. PMC PMC6284298. PMID 30522527. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6284298.
- ↑ Cimino, J.J.; Frisse, M.E.; Halamka, J. et al. (2014). "Consumer-mediated health information exchanges: The 2012 ACMI debate". Journal of Biomedical Informatics 48: 5–15. doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2014.02.009. PMC PMC5514840. PMID 24561078. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5514840.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W. et al. (2016). "A scoping review on the conduct and reporting of scoping reviews". BMC Medical Research Methodology 16: 15. doi:10.1186/s12874-016-0116-4. PMC PMC4746911. PMID 26857112. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4746911.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Glenton, C.; Paulsen, L.; Bohren, M. et al. (2017). "Qualitative Evidence Synthesis template". Effective Practice and Organisation of Care. The Cochrane Collaboration. https://epoc.cochrane.org/news/qualitative-evidence-synthesis-template.
- ↑ Suri, H. (2011). "Purposeful Sampling in Qualitative Research Synthesis". Qualitative Research Journal 11 (2): 63–75. doi:10.3316/QRJ1102063.
- ↑ Popay, J.; Roberts, H.; Sowden, A. et al. (April 2006). "Guidance on the Conduct of Narrative Synthesis in Systematic Reviews: A Product from the ESRC Methods Programme". Lancaster University. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/233866356_Guidance_on_the_conduct_of_narrative_synthesis_in_systematic_reviews_A_product_from_the_ESRC_Methods_Programme.
- ↑ Leon, N.; Brady, L.; Kwamie, A. et al. (2015). "Routine Health Information System (RHIS) interventions to improve health systems management". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015 (12): CD012012. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012012.
Notes
This presentation is faithful to the original, with only a few minor changes to presentation. In some cases important information was missing from the references, and that information was added. The "Study objectives" section in the original only states two objectives, leading to confusion when encountering references to three objectives; the intended three objectives were inferred from the rest of the text and restated for this version. The original tables didn't include an abbreviation key; the meaning of the abbreviations was inferred from the rest of the text (and the cited papers) and added for this version. Additionally, the author has been contacted asking for clarification.