Difference between revisions of "Main Page/Featured article of the week/2015"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Added last week's article of the week.) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) m (Red link fixes) |
||
| (45 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ombox | {{ombox | ||
| type = notice | | type = notice | ||
| text = If you're looking for the 2014 | | text = If you're looking for other "Article of the Week" archives: [[Main Page/Featured article of the week/2014|2014]] - 2015 - [[Main Page/Featured article of the week/2016|2016]] - [[Main Page/Featured article of the week/2017|2017]] - [[Main Page/Featured article of the week/2018|2018]] - [[Main Page/Featured article of the week/2019|2019]] - [[Main Page/Featured article of the week/2020|2020]] - [[Main Page/Featured article of the week/2021|2021]] - [[Main Page/Featured article of the week/2022|2022]] - [[Main Page/Featured article of the week/2023|2023]] - [[Main Page/Featured article of the week/2024|2024]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
<!-- Below this line begin pasting previous news --> | <!-- Below this line begin pasting previous news --> | ||
<h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: April 20–26:</h2> | <h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: December 28—January 3:</h2> | ||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig3 Dander BMCBioinformatics2014 15.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
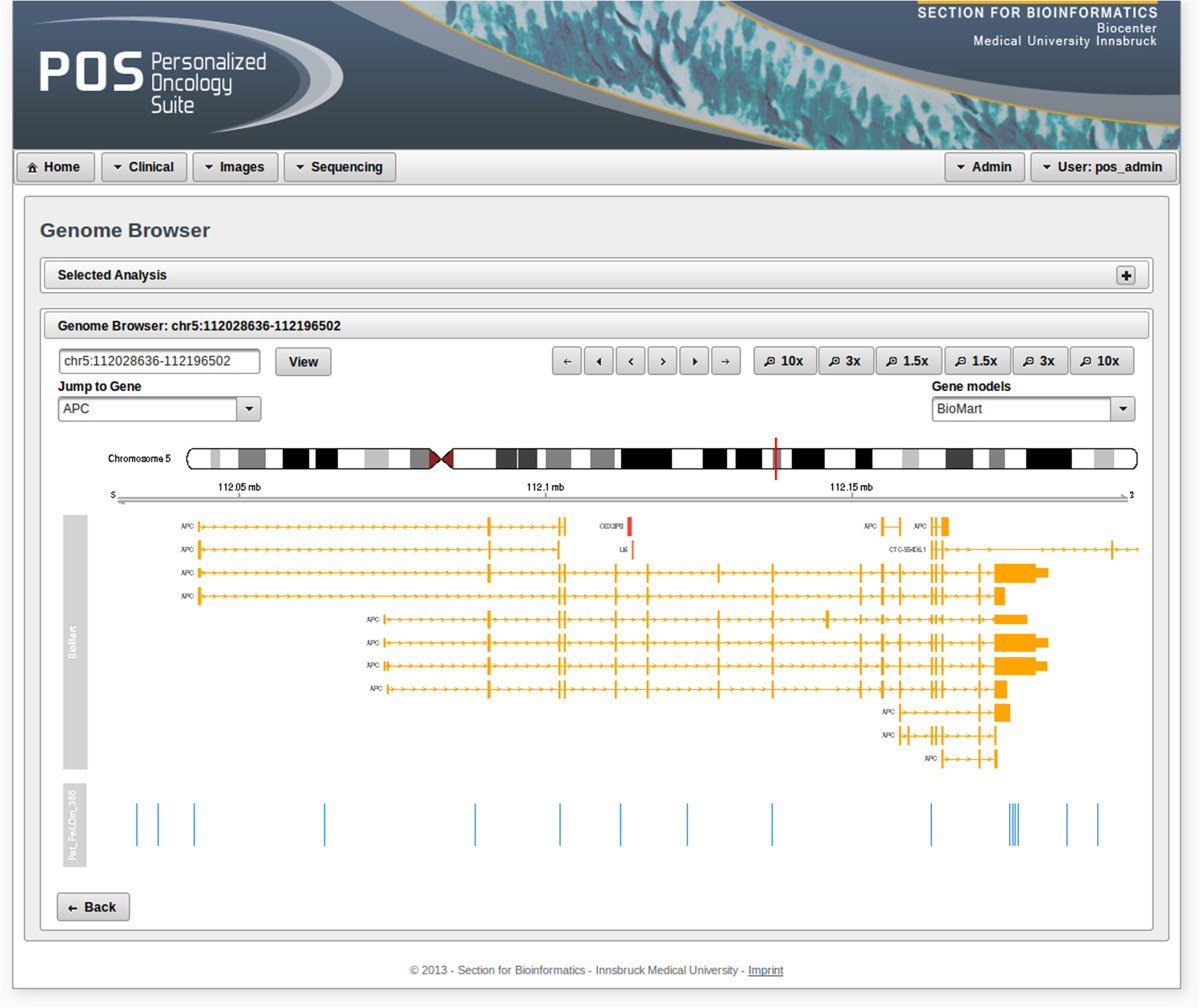
'''"[[Journal:Personalized Oncology Suite: Integrating next-generation sequencing data and whole-slide bioimages|Personalized Oncology Suite: Integrating next-generation sequencing data and whole-slide bioimages]]"''' | |||
Cancer immunotherapy has recently entered a remarkable renaissance phase with the approval of several agents for treatment. [[Cancer informatics|Cancer treatment platforms]] have demonstrated profound tumor regressions including complete cure in patients with metastatic cancer. Moreover, technological advances in next-generation sequencing (NGS) as well as the development of devices for scanning whole-slide bioimages from tissue sections and [[Bioimage informatics|image analysis software]] for quantitation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) allow, for the first time, the development of personalized cancer immunotherapies that target patient specific mutations. However, there is currently no [[bioinformatics]] solution that supports the integration of these heterogeneous datasets. | |||
We have developed a bioinformatics platform – Personalized Oncology Suite (POS) – that integrates clinical data, NGS data and whole-slide bioimages from tissue sections. POS is a web-based platform that is scalable, flexible and expandable. The underlying database is based on a data warehouse schema, which is used to integrate [[information]] from different sources. POS stores clinical data, [[Genomics|genomic]] data (SNPs and INDELs identified from NGS analysis), and scanned whole-slide images. ('''[[Journal:Personalized Oncology Suite: Integrating next-generation sequencing data and whole-slide bioimages|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: December 21—27:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Munkhdalai JCheminformatics2015 7-1.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
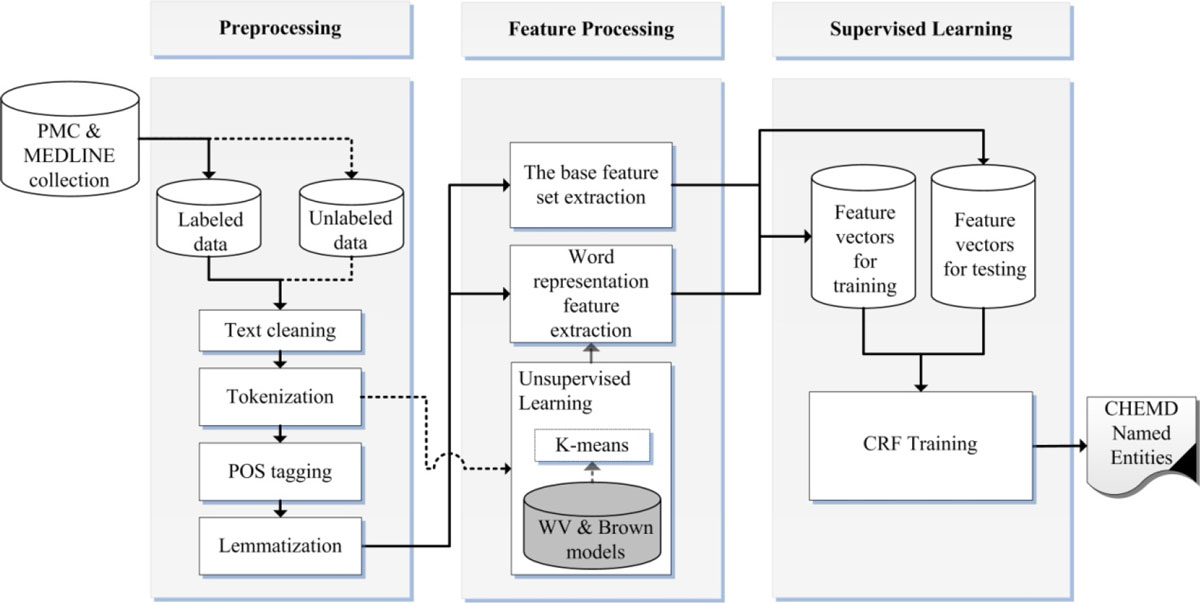
'''"[[Journal:Incorporating domain knowledge in chemical and biomedical named entity recognition with word representations|Incorporating domain knowledge in chemical and biomedical named entity recognition with word representations]]"''' | |||
Chemical and biomedical Named Entity Recognition (NER) is an essential prerequisite task before effective text mining can begin for biochemical-text data. Exploiting unlabeled text data to leverage system performance has been an active and challenging research topic in text mining due to the recent growth in the amount of biomedical literature. | |||
We present a semi-supervised learning method that efficiently exploits unlabeled data in order to incorporate domain knowledge into a named entity recognition model and to leverage system performance. The proposed method includes Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks for text preprocessing, learning word representation features from a large amount of text data for feature extraction, and conditional random fields for token classification. Other than the free text in the domain, the proposed method does not rely on any lexicon nor any dictionary in order to keep the system applicable to other NER tasks in bio-text data. ('''[[Journal:Incorporating domain knowledge in chemical and biomedical named entity recognition with word representations|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: December 14—20:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 GanzingerPeerJCS2015 3.png|220px]]</div> | |||
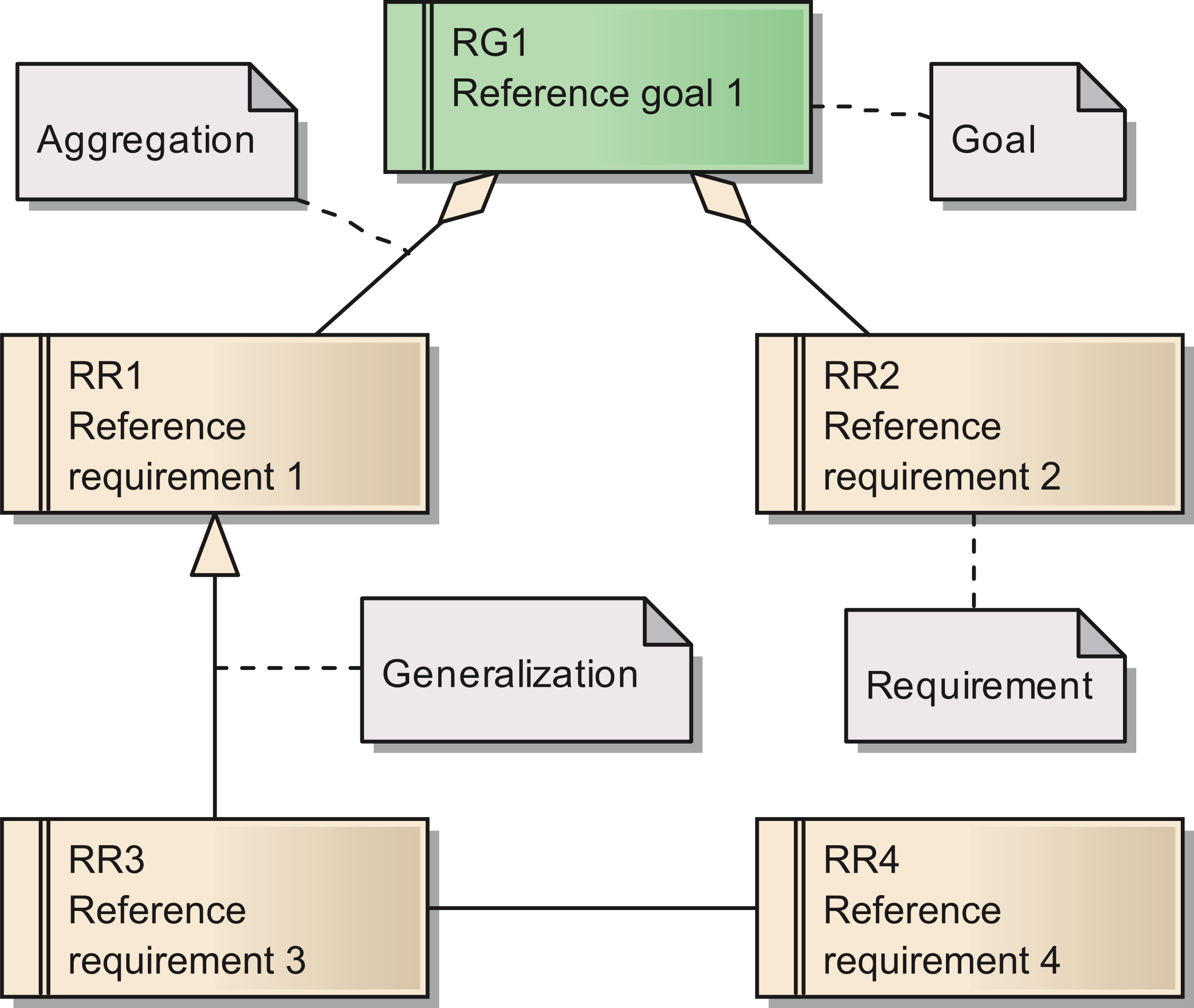
'''"[[Journal:Requirements for data integration platforms in biomedical research networks: A reference model|Requirements for data integration platforms in biomedical research networks: A reference model]]"''' | |||
Biomedical research networks need to integrate research data among their members and with external partners. To support such data sharing activities, an adequate information technology infrastructure is necessary. To facilitate the establishment of such an infrastructure, we developed a reference model for the requirements. The reference model consists of five reference goals and 15 reference requirements. Using the Unified Modeling Language, the goals and requirements are set into relation to each other. In addition, all goals and requirements are described textually in tables. This reference model can be used by research networks as a basis for a resource efficient acquisition of their project specific requirements. Furthermore, a concrete instance of the reference model is described for a research network on liver cancer. The reference model is transferred into a requirements model of the specific network. Based on this concrete requirements model, a service-oriented information technology architecture is derived and also described in this paper. ('''[[Journal:Requirements for data integration platforms in biomedical research networks: A reference model|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: December 7—13:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Barker BMCBio2013 14.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
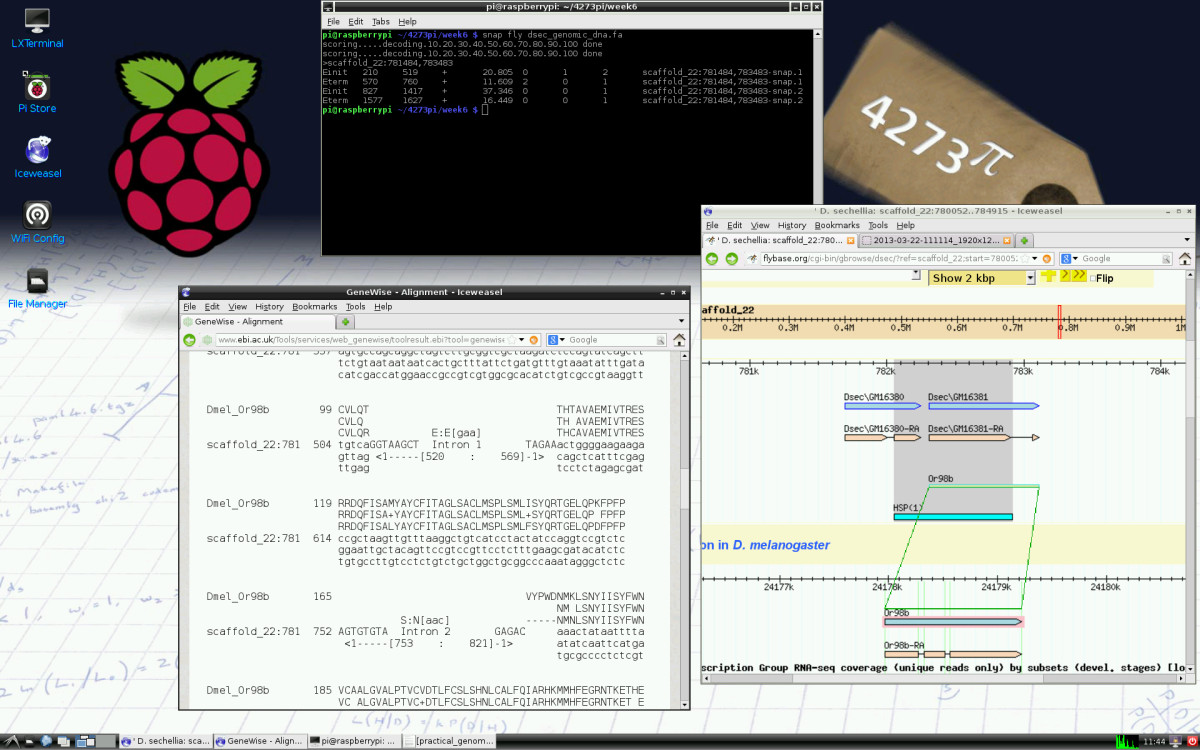
'''"[[Journal:4273π: Bioinformatics education on low cost ARM hardware|4273π: Bioinformatics education on low cost ARM hardware]]"''' | |||
Teaching [[bioinformatics]] at universities is complicated by typical computer classroom settings. As well as running software locally and online, students should gain experience of systems administration. For a future career in biology or bioinformatics, the installation of software is a useful skill. We propose that this may be taught by running the course on GNU/Linux running on inexpensive Raspberry Pi computer hardware, for which students may be granted full administrator access. | |||
We release 4273''π'', an operating system image for Raspberry Pi based on Raspbian Linux. This includes minor customisations for classroom use and includes our Open Access bioinformatics course, ''4273π Bioinformatics for Biologists''. This is based on the final-year undergraduate module BL4273, run on Raspberry Pi computers at the University of St Andrews, Semester 1, academic year 2012–2013. 4273''π'' is a means to teach bioinformatics, including systems administration tasks, to undergraduates at low cost. ('''[[Journal:4273π: Bioinformatics education on low cost ARM hardware|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: November 30–December 6:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Barker IntJourSTEMEd2015 2.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
'''"[[Journal:University-level practical activities in bioinformatics benefit voluntary groups of pupils in the last 2 years of school|University-level practical activities in bioinformatics benefit voluntary groups of pupils in the last 2 years of school]]"''' | |||
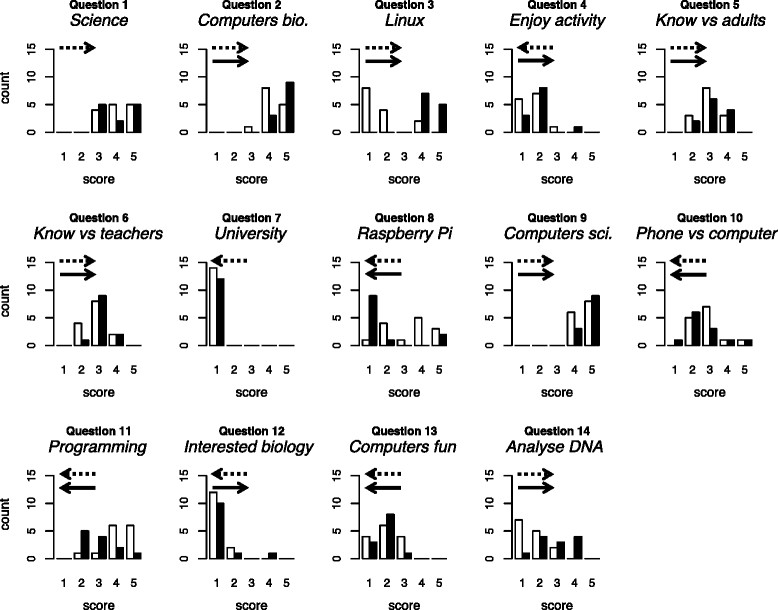
[[Bioinformatics]] — the use of computers in biology — is of major and increasing importance to biological sciences and medicine. We conducted a preliminary investigation of the value of bringing practical, university-level bioinformatics education to the school level. We conducted voluntary activities for pupils at two schools in Scotland (years S5 and S6; pupils aged 15–17). We used material originally developed for an optional final-year undergraduate module and now incorporated into 4273''π'', a resource for teaching and learning bioinformatics on the low-cost Raspberry Pi computer. | |||
Pupils’ feedback forms suggested our activities were beneficial. During the course of the activity, they provide strong evidence of increase in the following: pupils’ perception of the value of computers within biology; their knowledge of the Linux operating system and the Raspberry Pi; their willingness to use computers rather than phones or tablets; their ability to program a computer and their ability to analyse DNA sequences with a computer. We found no strong evidence of negative effects. ('''[[Journal:University-level practical activities in bioinformatics benefit voluntary groups of pupils in the last 2 years of school|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: November 23–29:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig2 Zheng JPathInfo2015 6.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
'''"[[Journal:Support patient search on pathology reports with interactive online learning based data extraction|Support patient search on pathology reports with interactive online learning based data extraction]]"''' | |||
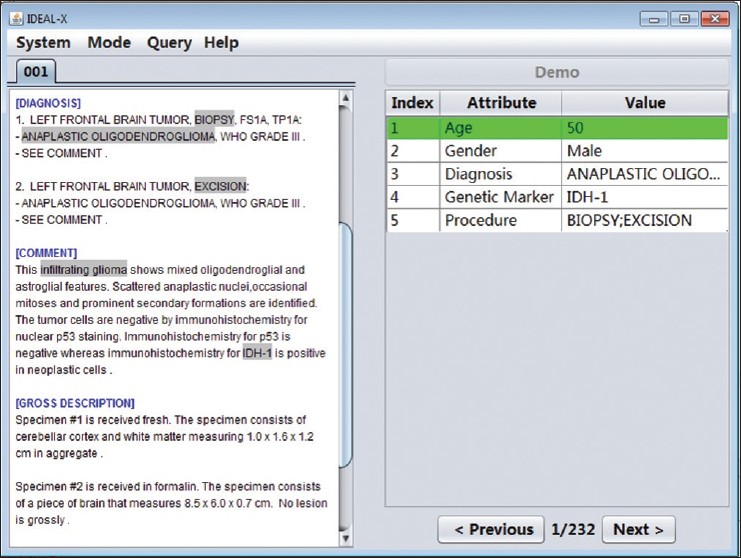
Structural reporting enables semantic understanding and prompt retrieval of clinical findings about patients. While [[LIS feature#Synoptic reporting|synoptic pathology reporting]] provides templates for data entries, information in [[Clinical pathology|pathology]] reports remains primarily in narrative free text form. Extracting data of interest from narrative pathology reports could significantly improve the representation of the information and enable complex structured queries. However, manual extraction is tedious and error-prone, and automated tools are often constructed with a fixed training dataset and not easily adaptable. Our goal is to extract data from pathology reports to support advanced patient search with a highly adaptable semi-automated data extraction system, which can adjust and self-improve by learning from a user's interaction with minimal human effort. | |||
We have developed an online machine learning based information extraction system called IDEAL-X. With its graphical user interface, the system's data extraction engine automatically annotates values for users to review upon loading each report text. The system analyzes users' corrections regarding these annotations with online machine learning, and incrementally enhances and refines the learning model as reports are processed. ('''[[Journal:Support patient search on pathology reports with interactive online learning based data extraction|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: November 16–22:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Kruse JMIRMedInfo2014 2-1.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
'''"[[Journal:Factors associated with adoption of health information technology: A conceptual model based on a systematic review|Factors associated with adoption of health information technology: A conceptual model based on a systematic review]]"''' | |||
The purpose of this systematic review is to identify a full-spectrum of both internal organizational and external environmental factors associated with the adoption of [[health information technology]] (HIT), specifically the EHR. The result is a conceptual model that is commensurate with the complexity of with the health care sector. We performed a systematic literature search in PubMed (restricted to English), EBSCO Host, and Google Scholar for both empirical studies and theory-based writing from 1993-2013 that demonstrated association between influential factors and three modes of HIT: EHR, [[electronic medical record]] (EMR), and computerized provider order entry (CPOE). We also looked at published books on organizational theories. We made notes and noted trends on adoption factors. These factors were grouped as adoption factors associated with various versions of EHR adoption. The resulting conceptual model summarizes the diversity of independent variables (IVs) and dependent variables (DVs) used in articles, editorials, books, as well as quantitative and qualitative studies (n=83). ('''[[Journal:Factors associated with adoption of health information technology: A conceptual model based on a systematic review|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: November 2–15:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1_Joyce_2015.png|220px]]</div> | |||
'''"[[Journal:Generalized procedure for screening free software and open-source software applications|Generalized procedure for screening free software and open-source software applications]]"''' | |||
Free software and [[:Category:Open-source software|open-source software projects]] have become a popular alternative tool in both scientific research and other fields. However, selecting the optimal application for use in a project can be a major task in itself, as the list of potential applications must first be identified and screened to determine promising candidates before an in-depth analysis of systems can be performed. To simplify this process, we have initiated a project to generate a library of in-depth reviews of free software and open-source software applications. Preliminary to beginning this project, a review of evaluation methods available in the literature was performed. As we found no one method that stood out, we synthesized a general procedure using a variety of available sources for screening a designated class of applications to determine which ones to evaluate in more depth. In this paper, we examine a number of currently published processes to identify their strengths and weaknesses. By selecting from these processes we synthesize a proposed screening procedure to triage available systems and identify those most promising of pursuit. ('''[[Journal:Generalized procedure for screening free software and open-source software applications|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: October 26–November 1:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Albers Informatics2015 2-2.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
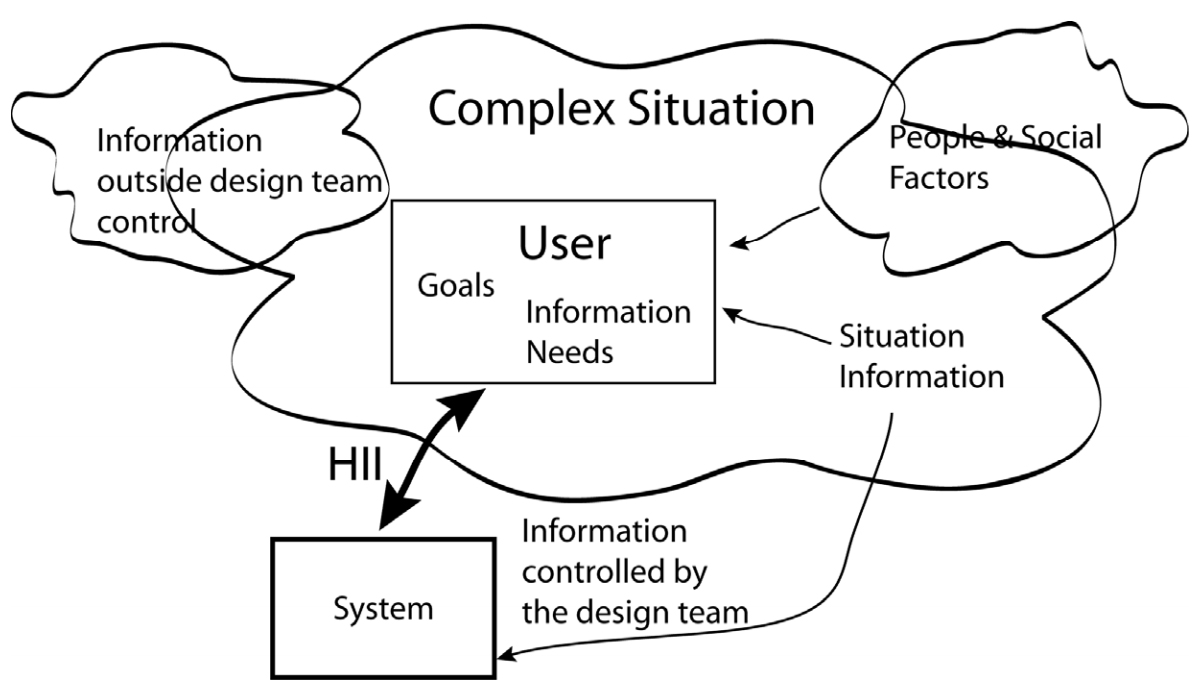
'''"[[Journal:Human–information interaction with complex information for decision-making|Human–information interaction with complex information for decision-making]]"''' | |||
Human–information interaction (HII) for simple [[information]] and for complex information is different because people's goals and information needs differ between the two cases. With complex information, comprehension comes from understanding the relationships and interactions within the information and factors outside of a design team's control. Yet, a design team must consider all these within an HII design in order to maximize the communication potential. This paper considers how simple and complex information requires different design strategies and how those strategies differ. ('''[[Journal:Human–information interaction with complex information for decision-making|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: October 19–25:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig2 Celi JMIRMedInformatics2014 2-2.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
'''"[[Journal:Making big data useful for health care: A summary of the inaugural MIT Critical Data Conference|Making big data useful for health care: A summary of the inaugural MIT Critical Data Conference]]"''' | |||
With growing concerns that big data will only augment the problem of unreliable research, the Laboratory of Computational Physiology at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology organized the Critical Data Conference in January 2014. Thought leaders from academia, government, and industry across disciplines — including clinical medicine, computer science, public health, [[informatics]], biomedical research, health technology, statistics, and epidemiology — gathered and discussed the pitfalls and challenges of big data in health care. The key message from the conference is that the value of large amounts of data hinges on the ability of researchers to share data, methodologies, and findings in an open setting. If empirical value is to be from the analysis of retrospective data, groups must continuously work together on similar problems to create more effective peer review. This will lead to improvement in methodology and quality, with each iteration of analysis resulting in more reliability. ('''[[Journal:Making big data useful for health care: A summary of the inaugural MIT Critical Data Conference|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: October 12–18:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Tab2 Hersh AdvancesMedEdPrac2014 2014-5.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
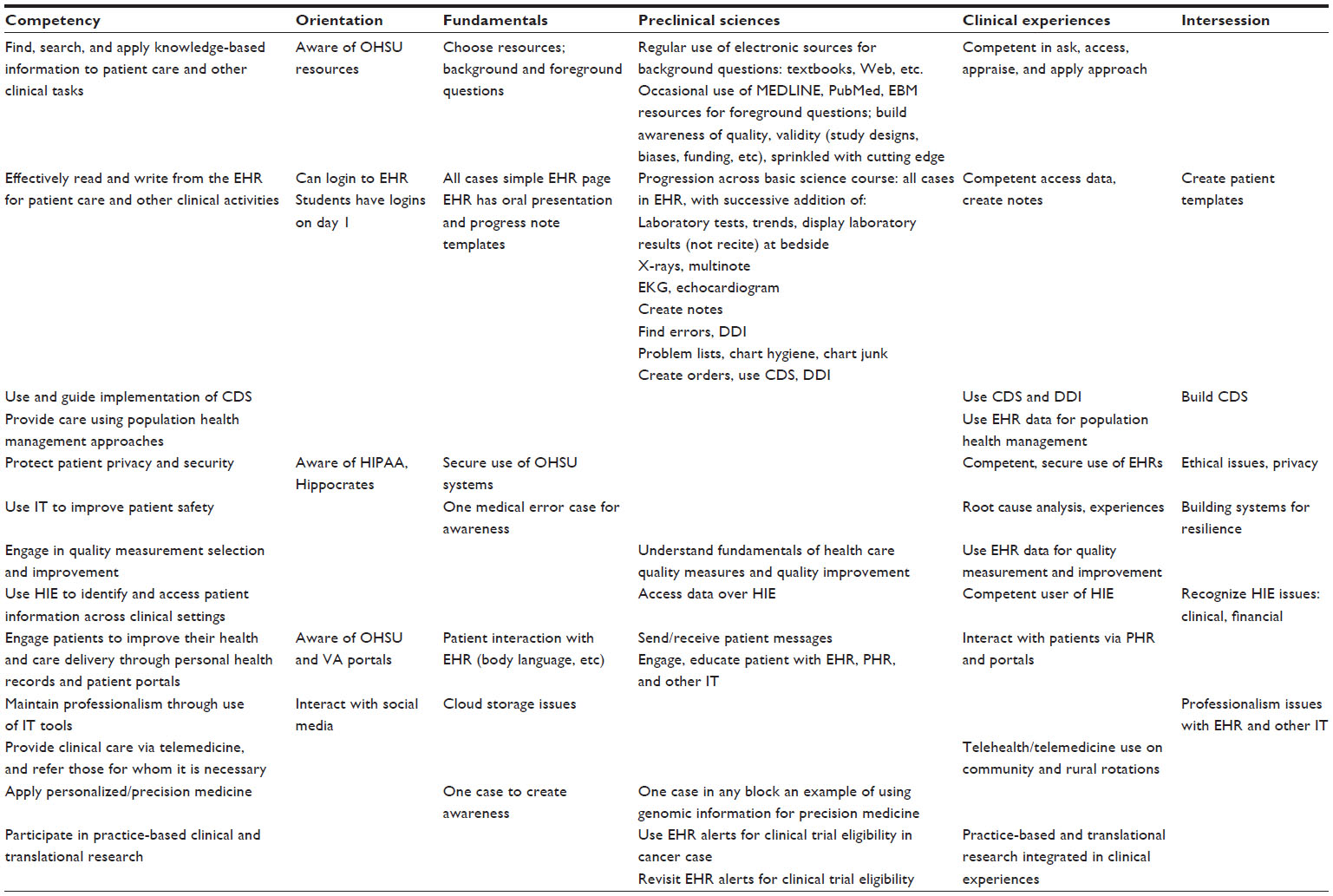
'''"[[Journal:Beyond information retrieval and electronic health record use: Competencies in clinical informatics for medical education|Beyond information retrieval and electronic health record use: Competencies in clinical informatics for medical education]]"''' | |||
Physicians in the 21st century will increasingly interact in diverse ways with information systems, requiring competence in many aspects of [[clinical informatics]]. In recent years, many medical school curricula have added content in [[information]] retrieval (search) and basic use of the [[electronic health record]]. However, this omits the growing number of other ways that physicians are interacting with information that includes activities such as [[Clinical decision support system|clinical decision support]], quality measurement and improvement, personal health records, telemedicine, and personalized medicine. We describe a process whereby six faculty members representing different perspectives came together to define competencies in clinical informatics for a curriculum transformation process occurring at Oregon Health & Science University. From the broad competencies, we also developed specific learning objectives and milestones, an implementation schedule, and mapping to general competency domains. We present our work to encourage debate and refinement as well as facilitate evaluation in this area. ('''[[Journal:Beyond information retrieval and electronic health record use: Competencies in clinical informatics for medical education|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: October 5–11:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig5 Deroulers DiagnosticPath2013 8.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
'''"[[Journal:Analyzing huge pathology images with open source software|Analyzing huge pathology images with open source software]]"''' | |||
Background: Digital pathology images are increasingly used both for diagnosis and research, because slide scanners are nowadays broadly available and because the quantitative study of these images yields new insights in systems biology. However, such virtual slides build up a technical challenge since the images occupy often several gigabytes and cannot be fully opened in a computer’s memory. Moreover, there is no standard format. Therefore, most common open source tools such as ImageJ fail at treating them, and the others require expensive hardware while still being prohibitively slow. | |||
Results: We have developed several cross-platform open source software tools to overcome these limitations. The NDPITools provide a way to transform microscopy images initially in the loosely supported NDPI format into one or several standard TIFF files, and to create mosaics (division of huge images into small ones, with or without overlap) in various TIFF and JPEG formats. They can be driven through ImageJ plugins. The LargeTIFFTools achieve similar functionality for huge TIFF images which do not fit into RAM. We test the performance of these tools on several digital slides and compare them, when applicable, to standard software. A statistical study of the cells in a tissue sample from an oligodendroglioma was performed on an average laptop computer to demonstrate the efficiency of the tools. ('''[[Journal:Analyzing huge pathology images with open source software|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: September 28–October 4:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig2 Stocker BMCBioinformatics2009 10.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
'''"[[Journal:iLAP: A workflow-driven software for experimental protocol development, data acquisition and analysis|iLAP: A workflow-driven software for experimental protocol development, data acquisition and analysis]]"''' | |||
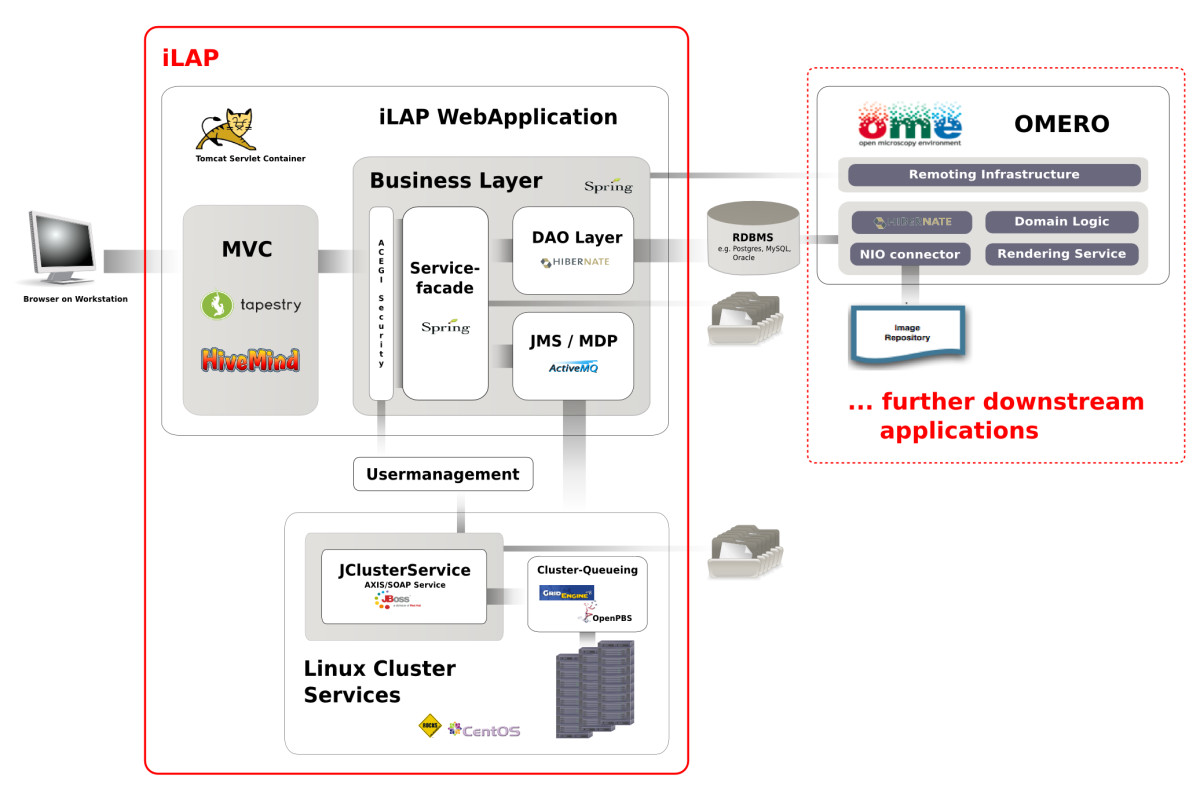
Background: In recent years, the genome biology community has expended considerable effort to confront the challenges of managing heterogeneous data in a structured and organized way and developed [[laboratory information management system]]s (LIMS) for both raw and processed data. On the other hand, [[Electronic laboratory notebook|electronic notebooks]] were developed to record and manage scientific data, and facilitate data-sharing. Software which enables both, management of large datasets and digital recording of [[laboratory]] procedures would serve a real need in laboratories using medium and high-throughput techniques. | |||
Results: We have developed iLAP (Laboratory data management, Analysis, and Protocol development), a workflow-driven information management system specifically designed to create and manage experimental protocols, and to analyze and share laboratory data. The system combines experimental protocol development, wizard-based data acquisition, and high-throughput data analysis into a single, integrated system. We demonstrate the power and the flexibility of the platform using a microscopy case study based on a combinatorial multiple fluorescence in situ hybridization (m-FISH) protocol and 3D-image reconstruction. ('''[[Journal:iLAP: A workflow-driven software for experimental protocol development, data acquisition and analysis|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: September 21–27:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Pic1 Zieth electronic2014 8-2.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
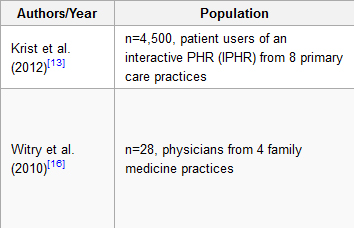
'''"[[Journal:The evolution, use, and effects of integrated personal health records: A narrative review|The evolution, use, and effects of integrated personal health records: A narrative review]]"''' | |||
Objective: To present a summarized literature review of the evolution, use, and effects of Personal Health Records (PHRs). | |||
Methods: Medline and PubMed were searched for ‘personal health records’. Seven hundred thirty-three references were initially screened resulting in 230 studies selected as relevant based on initial title and abstract review. After further review, a total of 52 articles provided relevant information and were included in this paper. These articles were reviewed by one author and grouped into the following categories: PHR evolution and adoption, patient user attitudes toward PHRs, patient reported barriers to use, and the role of PHRs in self-management. | |||
Results: Eleven papers described evolution and adoption, 17 papers described PHR user attitudes, 10 papers described barriers to use, and 11 papers described PHR use in self-management. Three papers were not grouped into a category but were used to inform the Discussion. PHRs have evolved from patient-maintained paper health records to provider-linked [[electronic health record]]s. Patients report enthusiasm for the potential of modern PHRs, yet few patients actually use an electronic PHR. Low patient adoption of PHRs is associated with poor interface design and low health and computer literacy on the part of patient users. ('''[[Journal:The evolution, use, and effects of integrated personal health records: A narrative review|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: August 31–September 6:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Cresswell InformaticsPC2014 21-2.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
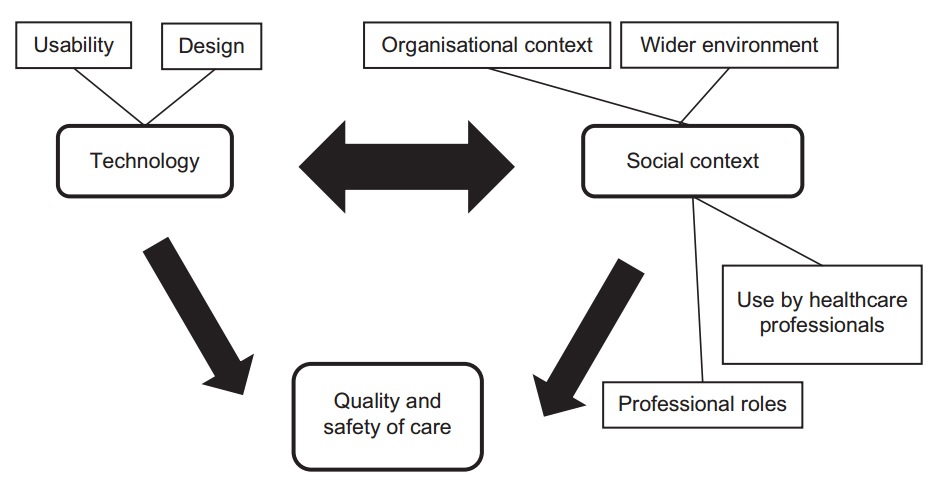
'''"[[Journal:Undertaking sociotechnical evaluations of health information technologies|Undertaking sociotechnical evaluations of health information technologies]]"''' | |||
There is an increasing international recognition that the evaluation of health information technologies should involve assessments of both the technology and the social/organisational contexts into which it is deployed. There is, however, a lack of agreement on definitions, published guidance on how such ‘sociotechnical evaluations’ should be undertaken, and how they distinguish themselves from other approaches. We explain what sociotechnical evaluations are, consider the contexts in which these are most usefully undertaken, explain what they entail, reflect on the potential pitfalls associated with such research, and suggest possible ways to avoid these. ('''[[Journal:Undertaking sociotechnical evaluations of health information technologies|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: August 24–30:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1_Bellary_PerspectivesClinRes2014_5-4.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
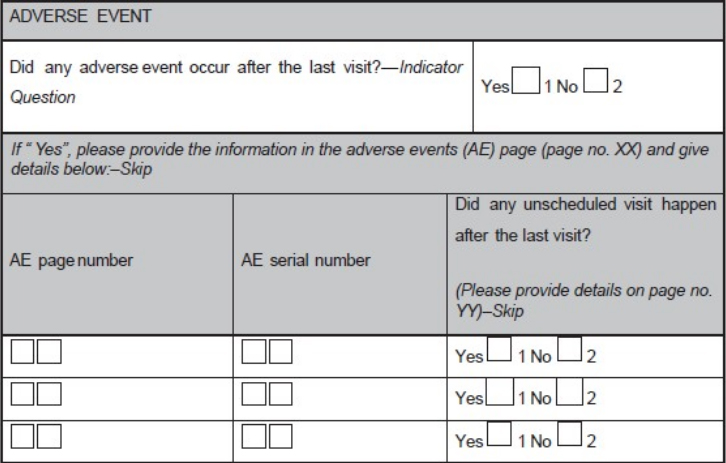
'''"[[Journal:Basics of case report form designing in clinical research|Basics of case report form designing in clinical research]]"''' | |||
Case report form (CRF) is a specialized document in clinical research. It should be study protocol driven, robust in content and have material to collect the study specific data. Though paper CRFs are still used largely, use of electronic CRFs (eCRFs) are gaining popularity due to the advantages they offer such as improved data quality, online discrepancy management and faster database lock etc. Main objectives behind CRF development are preserving and maintaining quality and integrity of data. CRF design should be standardized to address the needs of all users such as investigator, site coordinator, study monitor, data entry personnel, medical coder and statistician. Data should be organized in a format that facilitates and simplifies data analysis. Collection of large amount of data will result in wasted resources in collecting and processing it and in many circumstances, will not be utilized for analysis. Apart from that, standard guidelines should be followed while designing the CRF. CRF completion manual should be provided to the site personnel to promote accurate data entry by them. ('''[[Journal:Basics of case report form designing in clinical research|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: August 17–23:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Onega JournalHMInformatics2014 5-6.gif|220px]]</div> | |||
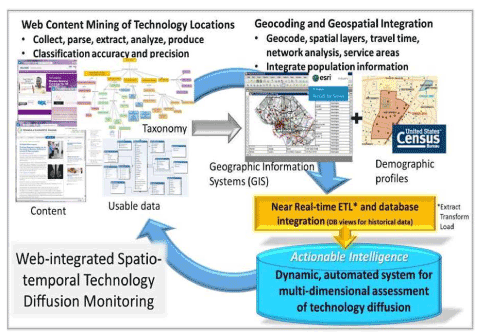
'''"[[Journal:Why health services research needs geoinformatics: Rationale and case example|Why health services research needs geoinformatics: Rationale and case example]]"''' | |||
Delivery of health care in the United States has become increasingly complex over the past 50 years, as health care markets have evolved, technology has diffused, population demographics have shifted, and cultural expectations of health and health care have been transformed. Identifying and understanding important patterns of health care services, accessibility, utilization, and outcomes can best be accomplished by combining data from all of these dimensions in near-real time. The Big Data paradigm provides a new framework to bring together very large volumes of data from a variety of sources and formats, with computing capacity to derive new [[information]], hypotheses, and inferences. The complementary fields of genomics and [[bioinformatics]] have already made great advances only made possible by Big Data approaches. Similar gains can be made by pairing health services research with [[geoinformatics]] –- defined as “the science and technology dealing with the structure and character of spatial information, its capture, its classification and qualification, its storage, processing, portrayal and dissemination, including the infrastructure necessary to secure optimal use of this information”. ('''[[Journal:Why health services research needs geoinformatics: Rationale and case example|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /> | |||
<h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: August 10–16:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig5 Jang JMIRMedInfo2014 2-2.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
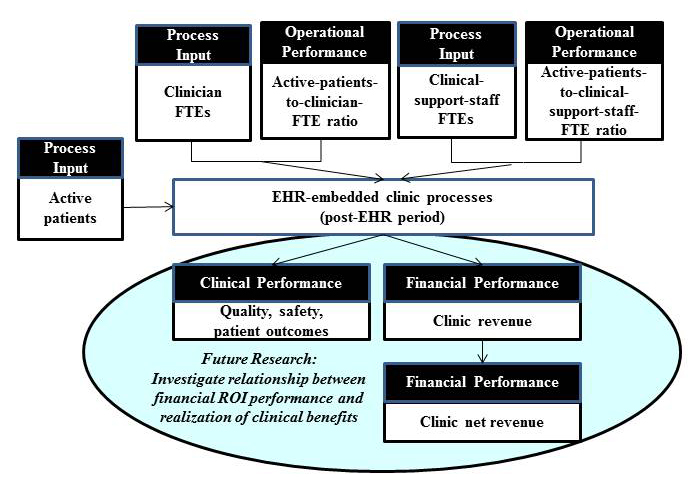
'''"[[Journal:Return on investment in electronic health records in primary care practices: A mixed-methods study|Return on investment in electronic health records in primary care practices: A mixed-methods study]]"''' | |||
The use of [[electronic health record]]s (EHR) in clinical settings is considered pivotal to a patient-centered health care delivery system. However, uncertainty in cost recovery from EHR investments remains a significant concern in primary care practices. | |||
Guided by the question of “When implemented in primary care practices, what will be the return on investment (ROI) from an EHR implementation?”, the objectives of this study are two-fold: (1) to assess ROI from EHR in primary care practices and (2) to identify principal factors affecting the realization of positive ROI from EHR. We used a break-even point, that is, the time required to achieve cost recovery from an EHR investment, as an ROI indicator of an EHR investment. Given the complexity exhibited by most EHR implementation projects, this study adopted a retrospective mixed-method research approach, particularly a multiphase study design approach. For this study, data were collected from community-based primary care clinics using EHR systems. ('''[[Journal:Return on investment in electronic health records in primary care practices: A mixed-methods study|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: August 3–9:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig3 Mickan BMCMedInfoDecMak2014 14.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
'''"[[Journal:Use of handheld computers in clinical practice: A systematic review|Use of handheld computers in clinical practice: A systematic review]]"''' | |||
Many healthcare professionals use smartphones and tablets to inform patient care. Contemporary research suggests that handheld computers may support aspects of clinical diagnosis and management. This systematic review was designed to synthesise high quality evidence to answer the question; Does healthcare professionals’ use of handheld computers improve their access to [[information]] and support clinical decision making at the point of care? | |||
A detailed search was conducted using Cochrane, MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycINFO, Science and Social Science Citation Indices since 2001. Interventions promoting healthcare professionals seeking information or making clinical decisions using handheld computers were included. Classroom learning and the use of laptop computers were excluded. Two authors independently selected studies, assessed quality using the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool and extracted data. High levels of data heterogeneity negated statistical synthesis. Instead, evidence for effectiveness was summarised narratively, according to each study’s aim for assessing the impact of handheld computer use. ('''[[Journal:Use of handheld computers in clinical practice: A systematic review|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: July 27–August 2:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Barrett InformaticsPC2014 21-3.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
'''"[[Journal:Unravelling the tangled taxonomies of health informatics|Unravelling the tangled taxonomies of health informatics]]"''' | |||
Even though [[informatics]] is a term used commonly in healthcare, it can be a confusing and disengaging one. Many definitions exist in the literature, and attempts have been made to develop a clear taxonomy. Despite this, informatics is still a term that lacks clarity in both its scope and the classification of sub-terms that it encompasses. | |||
This paper reviews the importance of an agreed taxonomy and explores the challenges of establishing exactly what is meant by [[health informatics]] (HI). It reviews what a taxonomy should do, summarises previous attempts at categorising and organising HI and suggests the elements to consider when seeking to develop a system of classification. | |||
The paper does not provide all the answers, but it does clarify the questions. By plotting a path towards a taxonomy of HI, it will be possible to enhance understanding and optimise the benefits of embracing technology in clinical practice.('''[[Journal:Unravelling the tangled taxonomies of health informatics|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: July 20–26:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:ANSI logo.gif|220px]]</div> | |||
The '''[[American National Standards Institute]]''' ('''ANSI''') is a private nonprofit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organization also coordinates U.S. standards with international standards so that American products can be used worldwide. For example, standards ensure that people who own cameras can find the film they need for that camera anywhere around the globe. | |||
ANSI accredits standards that are developed by representatives of other standards organizations, government agencies, consumer groups, companies, and others. These standards ensure that the characteristics and performance of products are consistent, that people use the same definitions and terms, and that products are tested the same way. ANSI also accredits organizations that carry out product or personnel certification in accordance with requirements defined in international standards. ANSI's operations office is located in New York City. The ANSI annual operating budget is funded by the sale of publications, membership dues and fees, accreditation services, fee-based programs, and international standards programs. ('''[[American National Standards Institute|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: July 13–19:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
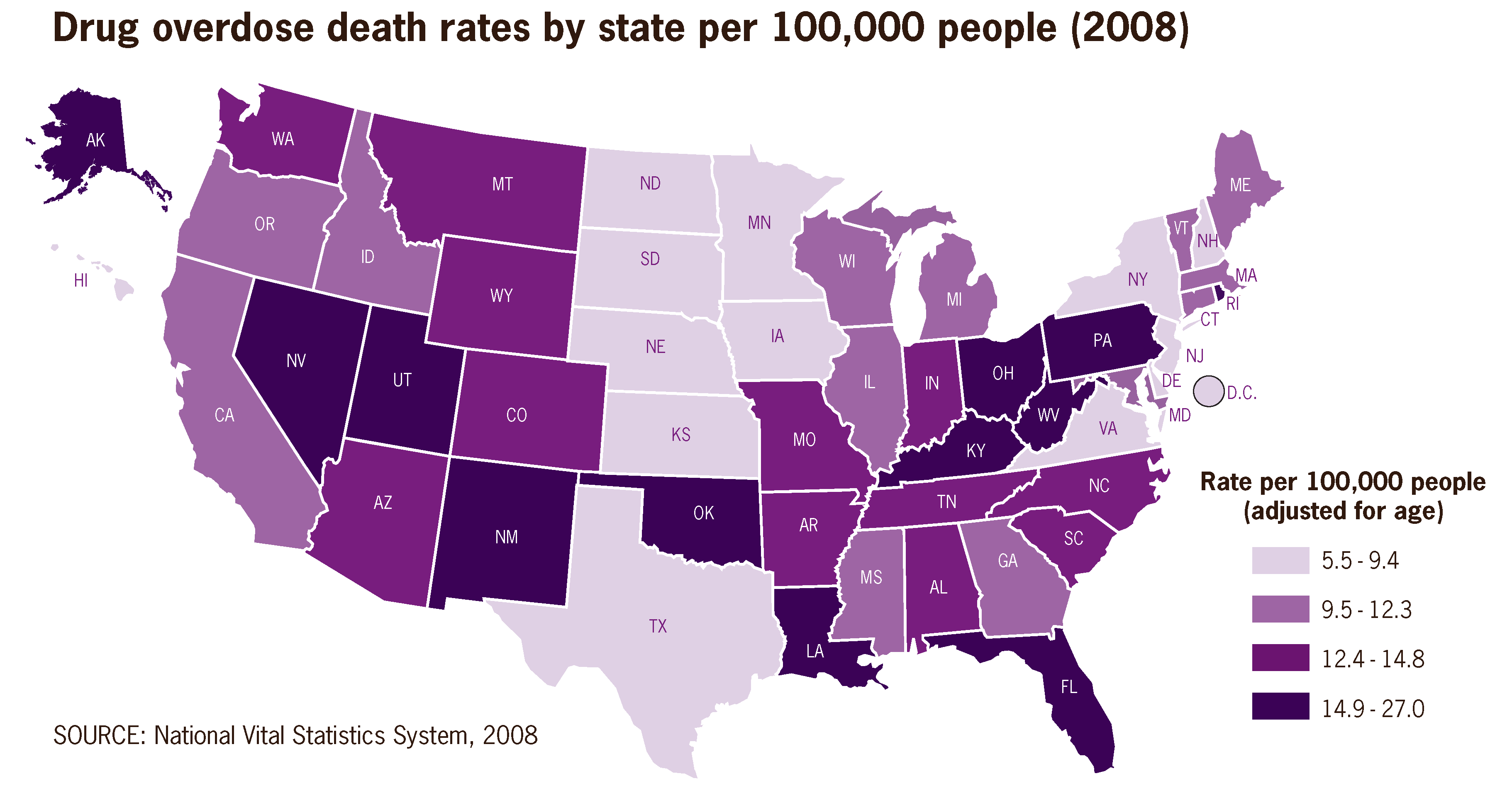
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Drug overdose death rates by state per 100,000 people 2008 US.png|220px]]</div> | |||
'''[[Public health informatics]]''' has been defined as "the systematic application of [[information]] and computer science and technology to public health practice, research, and learning." Like other types of informatics, public health informatics is a multidisciplinary field, involving the studies of [[Informatics (academic field)|informatics]], computer science, psychology, law, statistics, epidemiology, and microbiology. | |||
In 2000, researcher William A. Yasnoff and his colleagues identified four key aspects that differentiate public health informatics from [[Health informatics|medical informatics]] and other informatics specialty areas. Public health informatics focuses on "applications of information science and technology that promote the health of populations as opposed to the health of specific individuals" and that "prevent disease and injury by altering the conditions or the environment that put populations of individuals at risk." It also "explore[s] the potential for prevention at all vulnerable points in the causal chains leading to disease, injury, or disability" and "reflect[s] the governmental context in which public health is practiced." ('''[[Public health informatics|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: July 6–12:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Healthcare Apps for Android Tablets.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
'''[[Health information technology]] (HIT)''' is the application of "hardware and software in an effort to manage and manipulate health data and information." HIT acts as a framework for the comprehensive management of health information originating from consumers, providers, governments, and insurers in order to improve the overall state of health care. Among those improvements, the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) of the United States believes HIT can reduce or eliminate errors from medical transcription, reduce the number of diagnostic tests that get duplicated, and improve patient outcomes and service efficiency among other things. | |||
The "technology" of "health information technology" represents computers, software, and communications infrastructure that can be networked to create systems for manipulating health information. As such, the science of [[Informatics (academic field)|informatics]] and its focus on information processing and systems engineering is also integral to the development, application, and evaluation of HIT. In particular the subdivision of [[health informatics]], which focuses on the resources, devices, and methods required for optimizing the acquisition, storage, retrieval, and use of information in health and biomedicine, is most relevant. However, other subdivisions of informatics such as [[medical informatics]], [[public health informatics]], [[pharmacoinformatics]], and [[translational research informatics]] are able to inform health informatics from different disciplinary perspectives. ('''[[Health information technology|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: June 29–July 5:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:DSS-Figure-1.PNG|220px]]</div> | |||
A '''[[clinical decision support system]]''' ('''CDSS''') is a "computer [system] designed to impact clinician decision making about individual patients at the point in time these decisions are made." As such, it can be viewed as a knowledge management tool used to further clinical advice for patient care based on multiple items of patient data. In the early days, CDSSs were conceived of as being used to literally make decisions for the clinician. The clinician would input the information and wait for the CDSS to output the "right" choice, and the clinician would simply act on that output. However, the modern methodology involves the clinician interacting with the CDSS at the point of care, utilizing both their own knowledge and the CDSS to produce the best diagnosis from the test data. Typically, a CDSS suggests avenues for the physician to explore, and the physician is expected to use their own knowledge and judgement to narrow down possibilities. | |||
CDSSs can be roughly divided into two types: those with knowledge bases and those without. The knowledge-based approach typically covers the diagnosis of many different diseases, while the non-knowledge-based approach often focuses on a narrow list of symptoms, such as symptoms for a single disease. ('''[[Clinical decision support system|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: June 22–28:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Doctor reviewing pdq.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
A '''[[medical practice management system]]''' (also '''practice management system''' or '''PMS''') is a software-based information and enterprise management tool for physician offices that offers a set of key features that support an individual or group medical practice's operations. Those key features include — but are not limited to — appointment scheduling, patient registration, procedure posting, insurance billing, patient billing, payment posting, data and file maintenance, and reporting. | |||
The PMS has traditionally been a stand-alone application, installed on computers in the physician office. But like [[laboratory information management system]]s, [[hospital information system]]s, and other informatics software, trends have shifted to both web-based and cloud-based access to PMS applications. Cloud-based PMSs have been around at least since 2011, and they have become more attractive for several reasons, including the ease of letting the vendor maintain and update the technology from their end, the need for less hardware, and the convenience of accessing the system from anywhere. ('''[[Medical practice management system|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: June 15–21:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
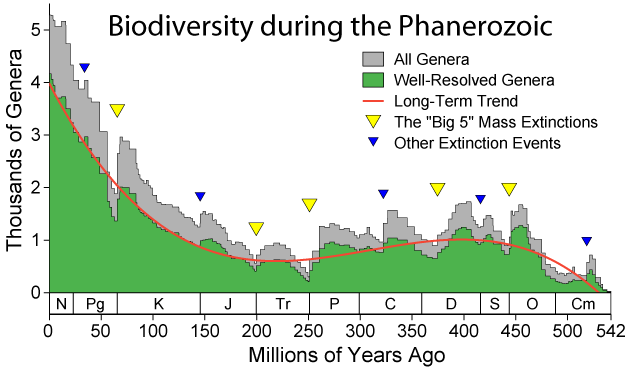
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Phanerozoic Biodiversity.png|220px]]</div> | |||
'''[[Biodiversity informatics]]''' is the application of informatics techniques to biodiversity [[information]] for improved management, presentation, discovery, exploration, and analysis. It typically builds on a foundation of taxonomic, biogeographic, and synecologic information stored in digital form, which, with the application of modern computer techniques, can yield new ways to view and analyze existing information, as well as predictive models for information that does not yet exist. Biodiversity informatics has also been described by others as "the creation, integration, analysis, and understanding of information regarding biological diversity" and a field of science "that brings information science and technologies to bear on the data and information generated by the study of organisms, their genes, and their interactions." | |||
According to correspondence reproduced by Walter Berendsohn, the term "biodiversity informatics" was coined by John Whiting in 1992 to cover the activities of an entity known as the Canadian Biodiversity Informatics Consortium (CBIC), a group involved with fusing basic biodiversity information with environmental economics and geospatial information. Subsequently it appears to have lost at least some connection with the geospatial world, becoming more closely associated with the computerized management of biodiversity information. ('''[[Biodiversity informatics|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: June 8–14:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Day 253 - West Midlands Police - Forensic Science Lab (7969822920).jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
'''The [[American Society of Crime Laboratory Directors/Laboratory Accreditation Board]]''' ('''ASCLD/LAB''') is a Missouri-based not-for-profit that "offers voluntary accreditation to public and private crime laboratories" around the world. | |||
The main objectives of the ASCLD/LAB are: | |||
- to improve the quality of laboratory services provided to the criminal justice system. | |||
- to adopt, develop and maintain criteria which may be used by a laboratory to assess its level of performance and to strengthen its operation. | |||
- to provide an independent, impartial, and objective system by which laboratories can benefit from a total operational review. | |||
- to offer to the general public and to users of laboratory services a means of identifying those laboratories which have demonstrated that they meet established standards. ('''[[The American Society of Crime Laboratory Directors/Laboratory Accreditation Board|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: June 1–7:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:SSTm.png|220px]]</div> | |||
'''[[Environmental informatics]]''' ('''EI''') is a developing field of science that applies [[information]] processing, management, and sharing strategies to the interdisciplinary field of environmental science. Applications include the integration of information and knowledge, the application of computational intelligence to environmental data, and the identification of the environmental impacts of information technology. EI helps scientists define information processing requirements, analyze real-world problems, and solve those problems using informatics methodologies and tools. | |||
As EI has continued to evolve, several other definitions have been offered over the years. Some consider it "an emerging field centering around the development of standards and protocols, both technical and institutional, for sharing and integrating environmental data and information." Others consider it the application of "[r]esearch and system development focusing on the environmental sciences relating to the creation, collection, storage, processing, modelling, interpretation, display and dissemination of data and information." ('''[[Environmental informatics|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: May 25–31:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Linux kernel API.svg|220px]]</div> | |||
An '''[[application programming interface]]''' ('''API''') is a particular set of rules and specifications that software programs can follow to communicate with each other. It serves as an interface between different software programs and facilitates their interaction, similar to the way the user interface facilitates interaction between humans and computers. An API can be created for applications, libraries, operating systems, etc. as a way of defining their "vocabularies" and resource request conventions (e.g. function-calling conventions). It may include specifications for routines, data structures, object classes, and protocols used to communicate between the consumer program and the implementer program of the API. | |||
An API can be generalized for many functions, appearing bundled in the libraries of a programming language, e.g. the Standard Template Library in C++ or the Java API. It can also be function-specific, meant to address a specific problem, e.g. the Google Maps API or the Java API for XML Web Services. Some APIs are language-dependent, meaning they can only use the syntax and elements of a particular language, which makes the API more convenient to use. Of course, an API may also be language-independent, written so that it can be called from several programming languages. This is a desirable feature for a service-oriented API that is not bound to a specific process or system and may be provided as remote procedure calls or web services. ('''[[Application programming interface|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: May 18–24:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:1FYT T-cell receptor and HLA class II complex.png|120px]]</div> | |||
'''[[Immunoinformatics]]''' (sometimes referred to as '''computational immunology''') is a sub-branch of [[bioinformatics]] that focuses on the use of data management and computational tools to improve immunological research. The scope of immunoinformatics covers a wide variety of territory, from genomic and proteomic study of the immune system to molecular- and organism-level modeling, putting it in close ties with [[genome informatics]]. | |||
Immunology researchers like Hans-Georg Rammensee trace the history of immunoinformatics back to the study of theoretical immunology. In June 1987, the Theoretical Immunology Workshop was hosted in Santa Fe, New Mexico to discuss "the topics of immune surveillance, mathematical models of HIV infection, complexities of antigen-antibody systems, immune suppression and tolerance, and idiotypie networks." One of the first immunoinformatics efforts to result in a long-term informatics solution was the construction of the IMGT information system in 1989 by the Laboratoire d'ImmunoGénétique Moléculaire (LIGM). Created to "standardize and manage the complexity of the immunogenetics data" coming out of the lab, the information system went on to become an international public reference for genetic and proteomic data related to immunology. ('''[[Immunoinformatics|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: May 11–17:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Molecular diagnostics qia symphony.jpg|120px]]</div> | |||
The biological and '''[[life sciences industry]]''' is concerned with many aspects of physiological and medical sciences, covering the entire range of plants, bacteria, and animals. As such, there are significant crossover opportunities, such as between fermentation based companies such as beer producers and genetically engineered protein pharmaceutical companies, or between genetic engineering and biofuels. Several types of activities can be grouped under the heading of life sciences, including biorepositories, molecular diagnostics, and pharmaceutical research. | |||
Biorepositories, as their name implies, are essentially libraries of biological specimens. Frequently, biorepositories are focused on cancer research, as the type and variety of cancers require a significant bank of available tumor, tissue, and body fluid samples. Within the U.S. the National Cancer Institute (NCI) has established the Office of Biorepositories and Biospecimen research(OBBR), whose main objective is "developing a common biorepository infrastructure that promotes resource sharing and team science, in order to facilitate multi-institutional, high throughput genomic and proteomic studies." ('''[[Life sciences industry|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: May 4–10:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Silicon single crystal.jpg|120px]]</div> | |||
The [[chemical industry]] is comprised of numerous sectors, with no fewer than 45 different subdivisions, including glass manufacturing, petrochemical manufacturing, electronics chemicals, ceramics, and dye and pigment manufacturing to name a few. | |||
Glass manufacturing is a process that is largely dependent on raw material quality control, as in process controls are limited by the fact that the process for manufacturing glass is high temperature, and does not lend itself to any sort of sampling process. That being said, temperature is actually a key control measure, and multivariate process control methods have been developed to maximize finished product quality. Primary petrochemicals such as ethylene, methanol, and benzene are used to produce a variety of intermediate and derivative products which ultimately are used to produce an amazing array of materials of great importance to the modern industrial world, such as plastics, tires, solvents, and the like. ('''[[Chemical industry|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: April 27–May 3:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | |||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:USMC-100921-M-2155E-002.jpg|220px]]</div> | |||
A '''[[skilled nursing facility]]''' ('''SNF''', pronounced like the English word "sniff"), as defined by the U.S. Social Security Act, is an institution or distinct part of an institution that provides skilled nursing care to residents or physical rehabilitation care to the injured, disabled, or ill. The skilled nursing facility is primarily a designation driven by the [[Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services]] (CMS) and its associated billing. To qualify, a SNF must meet certain requirements, including considerations for quality of life, scope, assessment, and training. | |||
The Federal Nursing Home Reform Act in 1987 set new requirements for nursing facilities, including the SNF. These facilities would have to emphasize quality of life and care to residents, create and assess an individual's care plan, provide the right to remain in care even after a hospital stay and the right to choose a personal physician, provide additional opportunities to residents with mental retardation or illness, and function under minimum federal standards or face even stricter penalties. ('''[[Skilled nursing facility|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |||
|<br /><h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the week: April 20–26:</h2> | |||
<div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | <div style="padding:0.4em 1em 0.3em 1em;"> | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Water Stress Around 2000 A.D. By WaterGAP.jpg|220px]]</div> | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Water Stress Around 2000 A.D. By WaterGAP.jpg|220px]]</div> | ||
Latest revision as of 18:55, 12 April 2024
|
|
If you're looking for other "Article of the Week" archives: 2014 - 2015 - 2016 - 2017 - 2018 - 2019 - 2020 - 2021 - 2022 - 2023 - 2024 |
Featured article of the week archive - 2015
Welcome to the LIMSwiki 2015 archive for the Featured Article of the Week.
Featured article of the week: December 28—January 3:"Personalized Oncology Suite: Integrating next-generation sequencing data and whole-slide bioimages" Cancer immunotherapy has recently entered a remarkable renaissance phase with the approval of several agents for treatment. Cancer treatment platforms have demonstrated profound tumor regressions including complete cure in patients with metastatic cancer. Moreover, technological advances in next-generation sequencing (NGS) as well as the development of devices for scanning whole-slide bioimages from tissue sections and image analysis software for quantitation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) allow, for the first time, the development of personalized cancer immunotherapies that target patient specific mutations. However, there is currently no bioinformatics solution that supports the integration of these heterogeneous datasets. We have developed a bioinformatics platform – Personalized Oncology Suite (POS) – that integrates clinical data, NGS data and whole-slide bioimages from tissue sections. POS is a web-based platform that is scalable, flexible and expandable. The underlying database is based on a data warehouse schema, which is used to integrate information from different sources. POS stores clinical data, genomic data (SNPs and INDELs identified from NGS analysis), and scanned whole-slide images. (Full article...)
|